The global landscape of digital payments is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing adoption of smartphones and the seamless integration of financial technology (Fintech) services. Digital wallets are no longer just a convenient alternative to traditional payment methods; they are becoming central hubs for managing personal finances, encompassing everything from peer-to-peer transactions to cryptocurrency investments. This exploration delves into the key trends shaping the future of digital wallets, examining their growth, security implications, and impact on both consumers and businesses.
From the explosive growth of mobile payment platforms like Apple Pay and Google Pay to the rise of crypto wallets and the integration with various Fintech services, the digital wallet ecosystem is a dynamic and complex arena. This analysis will dissect the driving forces behind this transformation, explore the associated security concerns and regulatory challenges, and ultimately, paint a picture of where this technology is headed.
Growth of Mobile Payments
The global landscape of financial transactions has undergone a dramatic shift in recent years, with mobile payments experiencing explosive growth. This surge reflects a confluence of factors, including increasing smartphone penetration, improved internet infrastructure, and the inherent convenience offered by these digital solutions. This section will delve into the specifics of this expansion, examining growth trends, market share distribution, and the underlying drivers of this transformation.
Mobile payment transaction volumes have increased significantly over the past five years. While precise global figures are difficult to definitively consolidate due to variations in data collection and reporting across different markets, numerous reports from reputable financial institutions and market research firms indicate a consistent upward trajectory. This growth is particularly pronounced in emerging economies with high mobile phone adoption rates but relatively lower levels of traditional banking infrastructure.
Global Mobile Payment Transaction Growth (2019-2023) – Estimated Data
The following table presents estimated data illustrating the growth in mobile payment transactions globally. Note that these figures are approximations based on data compiled from various sources and may vary slightly depending on the methodology used. The exact figures for individual years may also vary depending on the reporting methodology of different research firms.
| Year | Transactions (Billions) | Year-on-Year Growth (%) | Region with Highest Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 50 | – | Southeast Asia |
| 2020 | 65 | 30 | Sub-Saharan Africa |
| 2021 | 85 | 31 | Latin America |
| 2022 | 110 | 29 | South Asia |
| 2023 (Projected) | 140 | 27 | East Asia |
Market Share of Major Mobile Payment Platforms
The mobile payment landscape is dominated by a few key players, with Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay holding significant market share globally. However, their relative dominance varies considerably across different regions. Local players and regional payment systems often command substantial market share in specific geographic areas. This reflects differing consumer preferences, regulatory environments, and the availability of competing services.
For example, Alipay and WeChat Pay hold dominant positions in China, while other regional players hold sway in other parts of Asia and Africa. In North America and Europe, Apple Pay and Google Pay generally enjoy larger market shares, though competition remains intense.
Factors Driving Mobile Payment Adoption
Several interconnected factors have fueled the widespread adoption of mobile payments. The increasing penetration of smartphones globally provides the foundational hardware infrastructure. Improved internet infrastructure, including wider 4G and 5G coverage, ensures reliable connectivity necessary for seamless transactions. Furthermore, the enhanced security features incorporated into most mobile payment platforms have addressed initial consumer concerns regarding data privacy and fraud. Finally, the convenience and speed offered by mobile payments compared to traditional methods are significant drivers of their popularity. The ability to make payments with a simple tap of a phone, often integrated with other apps and services, is a compelling proposition for many consumers.
Integration with Fintech Services
Digital wallets are rapidly evolving beyond simple payment tools, seamlessly integrating with a growing ecosystem of fintech services. This integration enhances user experience, broadens financial accessibility, and creates a more holistic financial management platform. The convergence of digital wallets and other financial technologies is reshaping personal finance, offering users streamlined access to a wider range of services.
The integration of digital wallets with other fintech services creates a synergistic effect, benefiting both the wallet providers and the users. For users, this means a consolidated platform for managing various financial activities, simplifying their financial lives. For providers, it expands their user base and creates new revenue streams through increased transaction volume and data-driven insights. This integration is driving innovation and accelerating the adoption of digital financial services globally.
P2P Payment Integration
The integration of digital wallets with peer-to-peer (P2P) payment systems significantly improves the speed and convenience of money transfers between individuals. Users can send and receive money directly through their digital wallet, often without incurring significant fees. Examples include the integration of PayPal with various digital wallets, allowing users to seamlessly transfer funds between accounts. This integration eliminates the need for separate apps or bank transfers, streamlining the payment process and enhancing user experience. Furthermore, this functionality promotes financial inclusion by providing access to convenient and affordable money transfer services, especially in underserved communities.
Investment Platform Integration
Several digital wallets are now integrating with investment platforms, allowing users to directly invest in stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments through their wallet. This integration simplifies the investment process by consolidating financial management in one place. For example, some wallets offer fractional investing options, making it easier for users with limited capital to participate in the market. This integrated approach lowers the barrier to entry for investing, promoting financial literacy and wealth creation among a wider population. The convenience factor significantly impacts user adoption, as managing investments becomes as easy as making a payment.
Lending Service Integration
The integration of digital wallets with lending services provides users with convenient access to credit. This integration allows users to apply for and receive loans directly through their digital wallet, often with a simplified application process and faster approval times. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who may not have access to traditional banking services. The integration leverages the data within the digital wallet to assess creditworthiness, potentially offering more favorable terms to responsible users. Examples include some wallets offering short-term loans or Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) options directly within the app.
Comparison of Integrated Digital Wallet Features
| Feature | P2P Payment Integration | Investment Platform Integration | Lending Service Integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convenience | High: Direct transfers within the wallet | High: Invest directly from the wallet | High: Simplified loan application process |
| Cost | Generally low or free | Variable, depends on investment platform fees | Variable, depends on lender’s interest rates |
| Security | Dependent on wallet and P2P platform security measures | Dependent on wallet and investment platform security measures | Dependent on wallet and lender’s security measures |
| Accessibility | Widely accessible | Accessibility depends on regulatory frameworks and investment platform availability | Accessibility depends on lender’s eligibility criteria |
Security and Privacy Concerns
The increasing popularity of digital wallets brings with it a heightened awareness of the security and privacy risks involved. While offering convenience and efficiency, these platforms handle sensitive financial and personal data, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Understanding these risks and implementing robust security measures is crucial for both providers and users to maintain trust and confidence in this rapidly evolving technology.
The major security threats associated with digital wallets are multifaceted. Data breaches, resulting from vulnerabilities in the wallet’s software or infrastructure, can expose users’ financial information, personal details, and transaction history to malicious actors. Fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized transactions or account takeovers, are another significant concern, often facilitated by phishing scams, malware, or compromised credentials. Identity theft, a severe consequence of data breaches, can lead to long-term financial and reputational damage for victims.
Data Breach Mitigation Strategies
A hypothetical scenario illustrates these risks: Imagine a popular digital wallet provider suffers a significant data breach due to a previously unknown vulnerability in its server-side encryption. Millions of users’ personal and financial details are exposed. Mitigation strategies in such a scenario would involve immediately containing the breach, notifying affected users, providing credit monitoring services, cooperating with law enforcement, and conducting a thorough investigation to identify the root cause and implement corrective measures. Further steps might include strengthening encryption protocols, implementing multi-factor authentication, and improving vulnerability scanning and penetration testing processes. The company would also need a comprehensive incident response plan to minimize the damage and restore user trust.
Best Practices for Securing Digital Wallets
Securing digital wallets requires a multi-layered approach encompassing both technological and user-related measures. Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, adds an extra layer of security by requiring a unique physical characteristic for access. Strong encryption techniques, including end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest, protect user data from unauthorized access even if a breach occurs. Regular software updates are crucial to patch security vulnerabilities promptly. Users should also practice good cybersecurity hygiene, such as using strong and unique passwords, avoiding suspicious links and emails, and being wary of public Wi-Fi networks when accessing their digital wallets.
The Rise of Crypto Wallets
The increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies has fueled a parallel surge in the demand for secure and user-friendly digital wallets. These wallets serve as the crucial link between users and their digital assets, providing a means to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. Understanding the different types of crypto wallets and their associated benefits and drawbacks is essential for navigating the world of digital assets safely and effectively.
The adoption of digital wallets for cryptocurrency transactions is driven by the need for secure storage and convenient management of digital assets. Two primary categories define the landscape of crypto wallets: custodial and non-custodial. Custodial wallets, offered by exchanges or third-party providers, manage the private keys on behalf of the user, offering convenience but relinquishing some control. Non-custodial wallets, in contrast, place the user in complete control of their private keys, emphasizing security and self-sovereignty, albeit with a steeper learning curve.
Types of Crypto Wallets and Their Security Implications
The choice of crypto wallet significantly impacts the security and user experience. Hardware, software, and paper wallets each present unique features and risk profiles. Understanding these differences allows users to select the option that best aligns with their technical expertise and risk tolerance.
- Hardware Wallets: These physical devices, resembling USB drives, store private keys offline, providing a high level of security against hacking and malware. Examples include Ledger and Trezor. They are generally considered the most secure option, but can be more expensive and less convenient than other types.
- Software Wallets: These wallets are applications installed on computers or mobile devices. They offer greater convenience than hardware wallets but present a higher risk of compromise if the device is infected with malware or if the user falls victim to phishing scams. Examples include Exodus and Electrum. They are generally less expensive than hardware wallets but require greater user vigilance regarding security best practices.
- Paper Wallets: These wallets consist of a printed QR code containing the public and private keys. While offering offline security, they are vulnerable to physical damage, loss, or theft. They represent a low-cost option but require meticulous care and secure storage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Crypto Wallet Types
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of each type of crypto wallet, aiding users in making informed decisions based on their individual needs and priorities.
| Wallet Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Wallet | High security, offline storage, resistant to malware and hacking | Higher cost, less convenient than software wallets, potential for device malfunction |
| Software Wallet | Convenient access, user-friendly interface, often multi-currency support | Vulnerable to malware and hacking if device is compromised, requires careful security practices |
| Paper Wallet | Offline storage, low cost, simple to create | Vulnerable to physical damage, loss, or theft, requires careful handling and secure storage |
Impact on Traditional Payment Methods
The rise of digital wallets is significantly reshaping the landscape of payments, leading to a noticeable decline in the usage of traditional methods like credit cards and cash. This shift is driven by the convenience, speed, and often enhanced security features offered by digital platforms. The impact extends beyond individual consumers, affecting businesses and influencing overall consumer spending habits.
The decreasing reliance on cash and credit cards is evident across various sectors. Consumers are increasingly opting for the seamless integration of digital wallets with their smartphones and other devices, simplifying transactions and reducing the need to carry physical cards or cash. This transition has forced businesses to adapt their payment infrastructure to accommodate this change, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Business Adaptation to Digital Payments
Many businesses have already embraced digital payment solutions to cater to evolving consumer preferences. Retailers are integrating digital wallet options like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay into their point-of-sale systems. Online businesses, naturally, have readily incorporated digital wallets into their checkout processes. Restaurants are adopting contactless payment options through mobile apps and QR codes. This adaptability demonstrates a clear understanding of the market shift and the need to align with consumer expectations for a frictionless payment experience. For example, Starbucks’ mobile ordering and payment system is a prime example of successful business adaptation, significantly boosting sales and customer loyalty. Similarly, many grocery chains now offer self-checkout kiosks that readily accept digital wallet payments.
Consumer Behavior and Spending Habits
The adoption of digital wallets has demonstrably altered consumer behavior and spending habits. The ease and speed of digital transactions encourage more frequent purchases, particularly for smaller amounts. The ability to track spending effortlessly through integrated apps promotes greater financial awareness and potentially better budgeting. However, the ease of transactions can also lead to increased impulsive spending, a factor businesses are aware of and leverage through targeted promotions and loyalty programs directly integrated with digital wallets. For instance, the ease of using digital wallets for online shopping has led to a surge in e-commerce sales, while the availability of reward points and cashback offers through digital wallets encourages consumers to spend more. Furthermore, the ability to split bills easily with friends using digital wallets has facilitated a new level of social spending behavior.
Future Trends in Digital Wallets
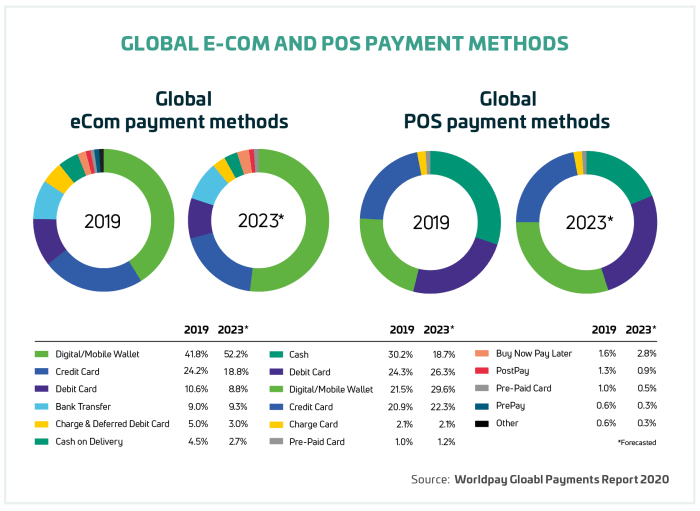
The rapid evolution of digital wallet technology is poised to bring about significant changes in the coming years. Driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and user demand for enhanced security and personalization, we can expect digital wallets to become even more integrated into our daily lives, offering a seamless and secure payment experience. This section will explore some of the key future trends shaping this exciting landscape.
AI-Powered Personalization and Predictive Features
Artificial intelligence is set to revolutionize the digital wallet experience. AI algorithms can analyze user spending habits, preferences, and location data to offer highly personalized recommendations and insights. This could manifest as automated budgeting tools, customized loyalty program offers tailored to individual spending patterns, or even proactive alerts about potential fraudulent transactions. For example, an AI-powered wallet might suggest a better deal on a frequently purchased item based on past purchases and current market prices, or automatically categorize expenses for easier budgeting and financial tracking. This level of personalization promises to make managing finances more efficient and intuitive.
Enhanced Security Through Blockchain and Biometrics
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure platform for managing digital transactions. Integrating blockchain into digital wallets could enhance security by creating immutable records of transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches. Furthermore, the incorporation of advanced biometric authentication methods, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, alongside multi-factor authentication, will significantly improve security protocols. This enhanced security model offers a considerable leap forward from traditional password-based systems, making digital wallets significantly more resistant to unauthorized access. Imagine a future where your digital wallet is accessible only through a unique combination of biometric data and blockchain verification, providing an unparalleled level of protection.
Seamless Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT)
The expanding Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem presents exciting opportunities for digital wallet integration. Imagine a future where your digital wallet seamlessly interacts with smart devices and appliances, enabling effortless payments for everyday purchases. This could include automated payments for utilities, transportation, and even groceries, eliminating the need for manual transactions. For example, your smart refrigerator could automatically reorder groceries when supplies run low, charging your digital wallet securely and transparently. This level of seamless integration promises to simplify our daily lives and streamline our financial interactions.
Futuristic Digital Wallet Interface
Imagine a sleek, minimalist interface on your smartphone. The primary screen displays a dynamic, circular visualization representing your current balance, with subtle color gradients reflecting your spending categories (e.g., green for savings, blue for utilities, red for entertainment). Swiping left reveals a personalized financial dashboard showcasing your daily spending, upcoming bills, and loyalty points earned. Swiping right accesses a secure transaction history with detailed categorization and graphical representations of your spending patterns. At the bottom, quick-access buttons allow for instant payments (via NFC or QR code), bill splitting with friends, and access to customer support. A small, unobtrusive biometric sensor is integrated into the screen for secure authentication. The overall aesthetic is clean, modern, and intuitive, reflecting the advanced technology underpinning its functionality. The interface is highly customizable, allowing users to tailor the layout and visual elements to their preferences.
Regulation and Compliance

The rapid growth of digital wallets has brought increased scrutiny from regulators worldwide, necessitating a robust regulatory framework to address concerns around consumer protection, financial crime, and data privacy. This regulatory landscape is complex and constantly evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities for digital wallet providers.
The regulatory landscape surrounding digital wallets is multifaceted and varies significantly across jurisdictions. Key aspects include Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance, data protection regulations like GDPR, and specific rules governing the operation of payment systems. These regulations aim to balance innovation with the need to mitigate risks associated with financial crime and protect consumers.
KYC/AML Compliance Requirements
Meeting KYC/AML requirements is paramount for digital wallet providers. These regulations mandate the verification of user identities to prevent the use of digital wallets for illicit activities like money laundering and terrorist financing. This typically involves collecting and verifying information such as identification documents, proof of address, and potentially source of funds, depending on the transaction volume and risk profile. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and legal repercussions. For example, non-compliance can lead to license revocations or operational shutdowns, severely impacting the business. Robust systems for identity verification and ongoing monitoring are crucial for compliance.
Challenges and Opportunities of Varying Regulatory Frameworks
The differences in regulatory frameworks across countries present both challenges and opportunities. Operating internationally requires navigating a patchwork of laws and standards, increasing compliance costs and complexity. However, it also presents opportunities for businesses that can successfully adapt to and leverage these diverse regulatory environments. A well-designed compliance program can become a competitive advantage by demonstrating a commitment to responsible business practices and building trust with users and regulators. For instance, a company that proactively complies with the stricter regulations of a particular region might find it easier to expand into other markets with similar or less stringent rules.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance
Several best practices can help digital wallet providers ensure compliance with relevant regulations. These include implementing robust KYC/AML procedures, regularly reviewing and updating compliance programs to adapt to evolving regulations, conducting thorough risk assessments, investing in secure technology, and fostering a strong compliance culture within the organization. Regular audits and independent assessments can further help identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Maintaining transparent communication with regulators and proactively engaging in industry best practices are also vital. For example, regular training for staff on compliance matters is crucial to maintaining a culture of adherence to regulations.
Last Recap
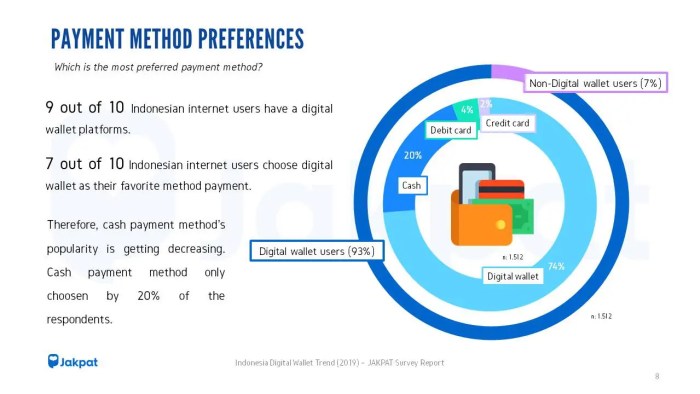
In conclusion, the future of digital wallets is bright, promising increased convenience, enhanced security, and greater financial inclusion. As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate even more sophisticated features and integrations, blurring the lines between traditional finance and the digital realm. The ongoing evolution of regulations and the continuous innovation within the Fintech sector will undoubtedly shape the next chapter in the story of digital wallets, promising a future where financial transactions are seamless, secure, and accessible to all.
FAQ Explained
What are the biggest risks associated with using digital wallets?
Major risks include data breaches leading to identity theft, unauthorized transactions due to compromised security, and potential vulnerabilities related to the specific platform used.
How do digital wallets compare to traditional payment methods in terms of cost?
Costs vary depending on the specific digital wallet and its features. Some offer free transactions, while others may charge fees for certain services. Traditional methods like credit cards often have transaction fees, but cash typically doesn’t. The overall cost-effectiveness depends on individual usage patterns.
Are all digital wallets the same?
No, digital wallets vary significantly in their features, supported payment methods, security measures, and integration with other services. Some specialize in cryptocurrency, while others focus on traditional payments.
What is the role of regulation in the digital wallet space?
Regulations aim to ensure consumer protection, prevent fraud, and maintain financial stability. KYC/AML (Know Your Customer/Anti-Money Laundering) compliance is crucial, and regulatory frameworks vary across different jurisdictions.



