Know-Your-Customer (KYC) regulations are a cornerstone of modern financial integrity, acting as a crucial safeguard against illicit activities like money laundering and terrorist financing. These regulations, which mandate businesses to verify the identity of their clients, have evolved significantly over time, adapting to increasingly sophisticated financial crime techniques. Understanding KYC’s intricacies is paramount for businesses operating in regulated sectors, impacting not only compliance but also operational efficiency and reputation.
This guide delves into the core principles of KYC, exploring its historical development, key components, and the technological advancements shaping its future. We will examine the interplay between KYC and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, the penalties for non-compliance, and emerging trends impacting businesses globally. Whether you are a seasoned compliance professional or simply seeking a better understanding of this crucial regulatory landscape, this comprehensive overview will provide valuable insights.
Introduction to Know-Your-Customer (KYC) Regulations
Know-Your-Customer (KYC) regulations are a set of procedures and policies designed to identify and verify the identity of clients and customers engaging in financial transactions. These regulations are crucial for preventing financial crimes such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud. Their global implementation aims to maintain the integrity of the financial system and protect businesses and consumers alike.
KYC regulations help financial institutions understand their customers’ risk profiles, enabling them to take appropriate measures to mitigate potential threats. The effectiveness of KYC procedures directly impacts a financial institution’s ability to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) laws. A robust KYC program is not just a legal requirement; it is a critical component of responsible business practice.
The Evolution of KYC Regulations
The evolution of KYC regulations has been a gradual process, driven by increasing concerns about financial crime and the need for greater transparency in financial markets. Early forms of KYC focused primarily on identifying high-risk customers. However, post 9/11, the focus shifted to a more comprehensive approach, encompassing enhanced due diligence and ongoing monitoring of customer activities. The global financial crisis of 2008 further accelerated the development and implementation of stricter KYC standards, highlighting the interconnectedness of the global financial system and the potential for widespread damage from financial crimes. Today, KYC regulations are constantly evolving to adapt to new technologies and evolving criminal methods. International organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) play a crucial role in setting global standards and promoting best practices.
Industries Heavily Regulated by KYC
Several industries are subject to stringent KYC regulations due to their high susceptibility to financial crimes. The financial services sector, including banks, investment firms, and insurance companies, is at the forefront. Other industries facing significant KYC scrutiny include casinos and gambling establishments, real estate agencies, and businesses involved in the trade of precious metals and gemstones. The level of KYC scrutiny varies depending on the specific industry and the nature of the transactions involved, with higher-risk activities necessitating more rigorous procedures. Furthermore, the increasing use of digital currencies and fintech platforms has expanded the scope of KYC regulations to include these emerging areas.
Comparison of KYC Regulations Across Countries
The specific requirements of KYC regulations differ across jurisdictions, reflecting varying legal frameworks and enforcement priorities. The following table provides a comparison of KYC regulations in the US, UK, and EU, focusing on key aspects:
| Aspect | United States | United Kingdom | European Union |
|---|---|---|---|
| Governing Legislation | Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), USA PATRIOT Act | Money Laundering Regulations 2017 | Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD5) |
| Customer Identification Requirements | Requires identification verification, including government-issued ID | Similar to US, emphasizing robust identification procedures | Similar to US and UK, with a focus on digital identification methods |
| Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) | Applied to high-risk customers, including politically exposed persons (PEPs) | EDD procedures are mandated for high-risk customers and transactions | EDD is a core component, with specific requirements for PEPs and high-risk jurisdictions |
| Record Keeping Requirements | Detailed record-keeping requirements, including transaction records | Strict record-keeping obligations, subject to audits and inspections | Comprehensive record-keeping mandates, aligned with AMLD5 requirements |
Key Elements of KYC Regulations
Effective Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations are crucial for maintaining financial integrity and preventing illicit activities. A robust KYC program involves several interconnected elements, working together to ensure compliance and mitigate risk. These elements are not isolated but form a holistic system designed to identify and verify customer identities and assess their risk profiles.
Core Components of a KYC Compliance Program
A typical KYC compliance program comprises several key components. These include customer identification procedures, ongoing monitoring, risk assessment methodologies, record-keeping practices, and a comprehensive training program for staff. The effectiveness of each component is vital for the overall success of the program. A weakness in any one area can compromise the entire system.
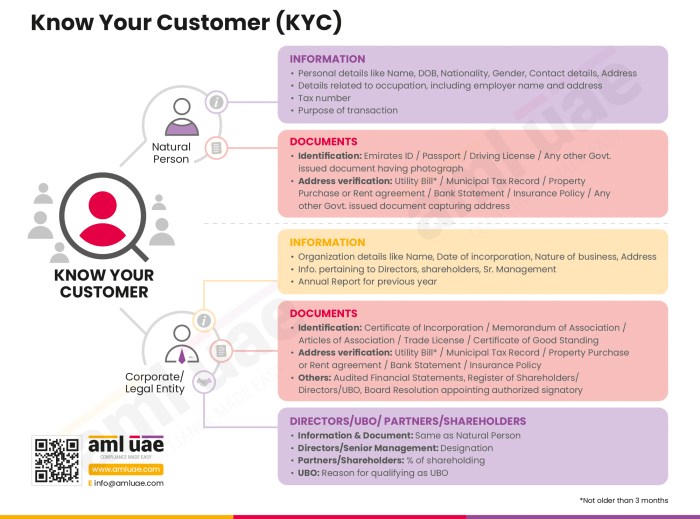
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Process
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is the cornerstone of any effective KYC program. It involves a systematic process of verifying a customer’s identity and assessing their risk profile. This process typically involves collecting identifying information, such as government-issued identification, proof of address, and potentially additional documentation depending on the customer’s risk profile. The level of due diligence required varies depending on the customer’s risk assessment. For example, a high-risk customer might require more stringent verification procedures compared to a low-risk customer. CDD processes must be documented and auditable to ensure compliance.
Risk Assessment in KYC Compliance
Risk assessment is an integral part of KYC compliance. It involves evaluating the potential risks associated with a customer or transaction. Factors considered in a risk assessment include the customer’s geographic location, the nature of their business, and the source of their funds. The outcome of the risk assessment dictates the level of due diligence required. A higher risk assessment necessitates more rigorous scrutiny of the customer and their activities. For instance, a customer involved in high-risk industries, such as money laundering or terrorist financing, will be subjected to more intense scrutiny than a customer with a low-risk profile. Regular review and updating of risk assessments are critical to adapt to changing circumstances.
Maintaining Accurate Customer Records
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date customer records is crucial for KYC compliance. These records must be securely stored and easily accessible for audits and regulatory reviews. The information contained in these records should be accurate, complete, and current. Regular updates are essential to reflect any changes in a customer’s circumstances. This might include changes in address, contact information, or business activities. Data security is paramount, and robust measures should be in place to protect customer information from unauthorized access or disclosure. These measures might include encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Furthermore, a clear retention policy should be established and followed to ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
KYC and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance

KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations are closely intertwined, both designed to prevent financial crime. While distinct, they work synergistically to protect the financial system’s integrity. Understanding their relationship is crucial for businesses operating within regulated financial environments.
KYC regulations focus on verifying the identity of customers and understanding their business activities, while AML regulations target the prevention and detection of money laundering and terrorist financing. KYC procedures form a fundamental building block of a comprehensive AML compliance program.
Relationship Between KYC and AML Regulations
KYC regulations are a crucial component of AML compliance. By diligently identifying and verifying customer identities, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of becoming involved in money laundering schemes. AML regulations often mandate specific KYC procedures as a prerequisite for conducting business. The information gathered during KYC due diligence—such as identifying information, source of funds, and beneficial ownership—is essential for assessing the risk of money laundering and reporting suspicious activities. A robust KYC program allows for proactive identification of potentially risky customers, preventing them from using the financial system for illicit activities.
KYC Procedures in AML Efforts
KYC procedures directly contribute to AML efforts in several ways. Firstly, the thorough identification and verification process makes it difficult for criminals to conceal their identities and engage in illicit transactions. Secondly, the ongoing monitoring of customer activities allows for the early detection of suspicious patterns or transactions that might indicate money laundering. Thirdly, the information gathered during KYC due diligence provides valuable data for risk assessment and the development of targeted AML strategies. For example, if a customer’s declared income is significantly lower than their transaction volume, this discrepancy might trigger further investigation and potentially a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR).
AML/KYC Investigation Flowchart
The following describes a typical AML/KYC investigation flowchart. Note that the specifics may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the suspicion.
Imagine a flowchart with the following steps:
1. Trigger Event: A suspicious transaction or activity is detected (e.g., unusually large cash deposit, complex wire transfers, or a mismatch between customer profile and transaction activity).
2. Initial Assessment: The compliance team reviews the available information to determine the level of risk.
3. Data Collection: Further information is gathered from internal and external sources (e.g., customer database, public records, financial databases).
4. Analysis: The collected data is analyzed to identify patterns and potential links to money laundering or terrorist financing.
5. Decision Making: Based on the analysis, a decision is made whether to file a SAR, conduct further investigation, or take other appropriate action.
6. Reporting: If necessary, a SAR is filed with the relevant authorities.
7. Monitoring: The customer’s activity is monitored for any further suspicious behavior.
Common Red Flags Indicating Potential Money Laundering Activity
A robust AML program requires the ability to recognize red flags. The following are examples of common red flags that may indicate potential money laundering activity:
The identification of these red flags warrants a thorough investigation and potentially the filing of a SAR. Examples include:
- Structuring transactions to avoid reporting thresholds.
- Use of shell companies or other opaque corporate structures.
- Unusual cash deposits or withdrawals.
- High-volume transactions with little or no apparent economic purpose.
- Transactions involving known or suspected criminals.
- Significant discrepancies between declared income and transaction volume.
- Sudden and unexplained increases in wealth.
- Use of multiple accounts or jurisdictions to conceal the source of funds.
- Attempts to conceal the identity of the beneficial owner.
- Transactions involving jurisdictions known for weak AML/KYC regulations.
Technological Advancements in KYC
The financial industry’s increasing reliance on digital transactions has spurred significant innovation in Know Your Customer (KYC) processes. Technology is playing a crucial role in streamlining KYC procedures, enhancing accuracy, and reducing compliance costs. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and other advanced technologies is transforming how businesses verify customer identities and mitigate risks associated with financial crime.
Technological advancements are improving KYC processes by automating previously manual tasks, enhancing data analysis capabilities, and improving the overall efficiency and accuracy of identity verification. This allows businesses to onboard clients faster while maintaining a robust compliance posture. This shift towards automation also reduces the potential for human error, a common source of KYC failures.
AI-Powered KYC Verification
AI algorithms are increasingly used to analyze vast amounts of data, including government-issued IDs, utility bills, and bank statements, to verify customer identities. Machine learning models can identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate fraudulent activity, flagging suspicious transactions or applications for further review. For instance, AI can detect inconsistencies in address information or discrepancies between provided documents and existing databases. This technology significantly reduces the time and resources required for manual verification, enabling faster onboarding of legitimate customers.
Blockchain Technology in KYC
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to store and share KYC data. By creating a shared, immutable record of customer identities, blockchain can reduce the duplication of efforts across different financial institutions. This eliminates the need for repeated identity verification processes, improving efficiency and reducing costs. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain enhances data security and privacy, mitigating the risk of data breaches. Imagine a scenario where a customer’s KYC information is securely stored on a blockchain, accessible only to authorized parties with proper encryption and verification methods. This would simplify the process for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions, as KYC information can be easily shared and verified without compromising security or privacy.
Challenges and Opportunities of Technological Advancements in KYC
While technological advancements offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges. The increasing reliance on technology raises concerns about data security and privacy. Robust security measures are crucial to prevent data breaches and protect sensitive customer information. Additionally, the complexity of some technologies can pose a barrier to adoption for smaller businesses. Furthermore, the rapid pace of technological change necessitates ongoing investment in training and infrastructure to maintain compliance with evolving regulations. However, these challenges are balanced by the opportunity to significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of KYC processes, leading to reduced costs and improved customer experience. The opportunities also extend to the development of innovative solutions that address the specific needs of various industries and regulatory environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Automated KYC Systems
The decision to implement automated KYC systems requires careful consideration of the benefits and drawbacks.
The advantages of using automated KYC systems are significant:
- Increased efficiency and speed of customer onboarding.
- Reduced operational costs associated with manual verification.
- Improved accuracy in identity verification, reducing the risk of errors.
- Enhanced detection of fraudulent activities through advanced analytics.
- Better compliance with KYC/AML regulations.
However, it is important to acknowledge the potential disadvantages:
- High initial investment costs for technology implementation and maintenance.
- Potential for bias in AI algorithms if not properly trained and monitored.
- Risk of data breaches and security vulnerabilities if systems are not adequately protected.
- Need for ongoing training and updates to keep pace with technological advancements.
- Potential for exclusion of customers who lack access to technology or digital literacy.
Penalties for Non-Compliance with KYC Regulations

Non-compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations carries significant consequences, impacting a company’s financial stability, reputation, and legal standing. These penalties vary depending on the jurisdiction, the severity of the violation, and the company’s history of compliance. Ignoring KYC requirements can lead to substantial fines, legal battles, and damage to public trust.
The potential repercussions of failing to meet KYC standards are multifaceted and far-reaching. Companies face a range of penalties, from administrative fines to criminal prosecution, depending on the nature and extent of the non-compliance. Furthermore, reputational damage can be substantial, leading to loss of business and difficulty attracting investors.
Examples of Significant Fines and Legal Actions
Several high-profile cases illustrate the severe consequences of KYC violations. For instance, in 2012, a major international bank was fined billions of dollars for failing to adequately implement KYC procedures, resulting in transactions linked to money laundering and terrorist financing going undetected. Another example involves a smaller financial institution that received a substantial fine and faced reputational damage after failing to properly verify the identity of its customers, leading to regulatory scrutiny and a loss of customer confidence. These examples highlight the significant financial and reputational risks associated with inadequate KYC compliance.
Impact of Non-Compliance on a Company’s Reputation
The reputational damage stemming from KYC violations can be devastating. A company found to be non-compliant may face a loss of public trust, difficulty attracting and retaining customers, and challenges securing funding from investors. Negative media coverage and regulatory scrutiny can further amplify the negative impact, making it difficult for the company to recover its reputation. This reputational damage can extend beyond the immediate consequences, potentially impacting future business opportunities and overall long-term viability.
Scenario: Repercussions for Insufficient KYC Measures
Imagine a newly established online cryptocurrency exchange, “CryptoQuick,” that prioritizes rapid user onboarding to gain market share. To achieve this, CryptoQuick implements minimal KYC checks, primarily relying on self-reported information without sufficient verification. A significant portion of their user base consists of anonymous accounts, making it extremely difficult to trace transactions. This lax approach attracts individuals involved in illicit activities, and substantial sums of money are laundered through the platform. Regulatory authorities launch an investigation, discovering CryptoQuick’s insufficient KYC measures. The exchange faces substantial fines, a temporary suspension of operations, and extensive legal battles. The negative publicity severely damages CryptoQuick’s reputation, leading to a loss of investors and customers, ultimately forcing the company to close down. This scenario underscores the critical importance of robust KYC measures in maintaining the integrity of financial institutions and protecting against illicit activities.
Future Trends in KYC Regulations
The landscape of Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, increasing cross-border transactions, and the emergence of new financial instruments. Understanding these emerging trends and anticipating future challenges is crucial for businesses operating in a globally interconnected financial system. This section will explore key future trends, focusing on the impact of globalization and the adaptation of KYC to novel technologies like cryptocurrency.
Emerging Trends in KYC Compliance
Several key trends are shaping the future of KYC compliance. Increased automation through artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is streamlining the verification process, making it faster and more efficient. This includes automated identity verification, risk scoring, and ongoing monitoring. Furthermore, there’s a growing emphasis on data privacy and security, with regulations like GDPR influencing how KYC data is collected, stored, and processed. A move towards a more holistic risk-based approach is also apparent, where KYC processes are tailored to the specific risk profile of each customer. Finally, greater collaboration and information sharing between financial institutions and regulatory bodies is improving the effectiveness of KYC efforts globally.
Potential Future Challenges Related to KYC
Maintaining KYC compliance in the face of evolving technologies and regulatory landscapes presents several significant challenges. The increasing complexity of financial products and services, coupled with the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), necessitates more sophisticated KYC procedures. The need to balance effective KYC with data privacy concerns presents another significant challenge. Finding the right balance between robust security and streamlined user experience is also crucial. Moreover, ensuring consistent KYC standards across different jurisdictions and adapting to the rapidly changing regulatory environment remains a constant challenge for businesses operating internationally. Maintaining the accuracy and integrity of KYC data over time is another important hurdle, especially with the potential for data breaches or errors.
The Impact of Globalization on KYC Compliance
Globalization has significantly increased the complexity of KYC compliance. Businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions must navigate a patchwork of varying KYC regulations, each with its own specific requirements and enforcement mechanisms. This necessitates a global perspective on KYC, requiring organizations to adapt their procedures to comply with local laws in each country they operate in. The increased cross-border flow of funds also makes it more difficult to track illicit activities, demanding stronger international cooperation and information sharing between regulatory bodies. The harmonization of KYC standards across jurisdictions remains a significant goal, though challenges persist due to differing legal frameworks and priorities.
Adaptation of KYC Regulations to Cryptocurrency
The rise of cryptocurrency presents unique challenges for KYC compliance. The decentralized and pseudonymous nature of many cryptocurrencies makes it difficult to verify the identity of users and track transactions. Regulatory bodies are actively working to adapt KYC regulations to this new financial landscape, often focusing on “Travel Rule” compliance, which requires exchanges to collect and share information about senders and recipients of cryptocurrency transfers exceeding certain thresholds. This often involves implementing robust transaction monitoring systems and collaborating with other cryptocurrency exchanges to trace the flow of funds. The challenge lies in balancing the need for effective KYC with the inherent principles of decentralization and privacy that underpin many cryptocurrencies. A common approach involves requiring cryptocurrency exchanges to implement KYC/AML procedures similar to those used in traditional finance, albeit with adaptations tailored to the specific characteristics of digital assets. For example, exchanges may verify the identity of users through various methods, such as document verification and biometric authentication, before allowing them to trade cryptocurrencies.
Outcome Summary
Navigating the complex world of Know-Your-Customer regulations requires a multifaceted approach encompassing robust compliance programs, technological innovation, and a proactive understanding of evolving regulatory landscapes. By implementing effective KYC procedures, businesses not only mitigate risks associated with financial crime but also enhance their operational efficiency, build trust with stakeholders, and safeguard their reputation in the long term. Staying informed about emerging trends and technological advancements is vital for maintaining compliance and adapting to the ever-changing regulatory environment.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between KYC and AML?
While closely related, KYC focuses on verifying customer identity, while AML aims to prevent money laundering through various measures, including KYC procedures. KYC is a component of a broader AML program.
How often should KYC checks be performed?
The frequency of KYC checks depends on the risk assessment of the customer and the nature of the business. High-risk customers may require more frequent reviews.
What are some common red flags for potential money laundering?
Examples include unusually large cash transactions, complex or unusual transaction patterns, and attempts to conceal the source of funds.
Can small businesses avoid KYC compliance?
No, KYC regulations apply to businesses of all sizes operating in regulated sectors. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties.



