Effective expense management is crucial for any organization’s financial health. It’s not just about tracking spending; it’s about establishing clear policies, leveraging technology, and fostering a culture of responsible spending. This guide explores best practices, from defining core principles and selecting the right software to implementing robust auditing controls and leveraging data analysis for informed decision-making.
We’ll delve into various strategies for optimizing your expense management processes, including the use of software solutions, the importance of well-defined policies and procedures, and the role of employee training and engagement in ensuring compliance. We will also explore how effective expense management contributes to accurate budgeting, forecasting, and ultimately, the long-term financial success of your organization.
Defining “Expense Management Best Practices”
Effective expense management is crucial for any organization, regardless of size. It ensures financial accuracy, improves budgeting, and ultimately contributes to profitability. Best practices encompass a holistic approach, integrating technology, policy, and employee engagement to streamline the entire expense process.
Effective expense management hinges on several core principles. Firstly, a clear and well-defined expense policy is paramount. This policy should Artikel allowable expenses, reimbursement procedures, and acceptable documentation. Secondly, robust processes are needed for capturing, tracking, and reporting expenses. This includes using appropriate technology to automate data entry and minimize manual processes. Thirdly, a strong emphasis on employee compliance and training is vital to ensure everyone understands and adheres to the expense policy. Finally, regular monitoring and analysis of expense data are essential for identifying trends, anomalies, and areas for improvement.
Characteristics of a Best-in-Class Expense Management System
A best-in-class expense management system should possess several key characteristics. It should be user-friendly and intuitive, enabling employees to easily submit expense reports. Automation is critical, minimizing manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors. The system should integrate seamlessly with other financial systems, such as accounting software, to streamline data flow. Robust reporting and analytics capabilities allow for insightful analysis of spending patterns. Finally, strong security features are crucial to protect sensitive financial data.
Examples of Companies with Excellent Expense Management
While specific internal practices aren’t always publicly available, several companies are known for their commitment to efficient and effective expense management. Companies with strong internal controls, robust auditing procedures, and a culture of financial accountability often exhibit best practices. For example, large multinational corporations often utilize sophisticated expense management software and employ dedicated teams to oversee expense processes. These companies often prioritize data-driven decision-making, using expense data to inform strategic budgeting and resource allocation. Smaller companies, on the other hand, might leverage simpler, cloud-based solutions that still offer automation and real-time visibility into spending. The key is the adaptation of best practices to the specific size and needs of the organization.
Comparison of Expense Management Philosophies
| Philosophy | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized | Improved control, standardized processes, better visibility | Can be rigid, slower approval processes, potential for bottlenecks | Large organizations with complex structures |
| Decentralized | Faster approvals, greater flexibility, increased employee autonomy | Potential for inconsistencies, less control, higher risk of fraud | Smaller organizations with simpler structures |
| Hybrid | Combines benefits of both approaches, allows for customization | Requires careful planning and implementation, may be complex to manage | Organizations seeking a balance between control and flexibility |
| Automated | Reduced manual effort, improved accuracy, faster processing | Requires investment in technology, potential for initial setup complexities | Organizations of all sizes seeking efficiency gains |
Software and Technology Solutions
Effective expense management relies heavily on appropriate software and technology. Choosing the right system can significantly streamline processes, improve accuracy, and reduce administrative overhead. This section explores various solutions, their comparative advantages and disadvantages, and best practices for implementation.
Expense management software automates many manual tasks associated with tracking, categorizing, and reporting expenses. This automation reduces human error, speeds up processing times, and allows for better oversight of spending. The choice between different software options, however, depends on the specific needs and size of the organization.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Expense Management Software
Different expense management software solutions cater to various needs and budgets. Some offer basic features like receipt capture and expense categorization, while others provide advanced functionalities such as automated approvals, integration with accounting systems, and detailed reporting dashboards. A careful evaluation of features and cost is crucial before selecting a solution. For instance, a small business might find a simple, user-friendly solution sufficient, while a large corporation might require a more robust system with advanced analytics capabilities. The choice also depends on factors such as the number of employees, the complexity of expense policies, and the level of integration required with existing accounting systems. Consider factors like ease of use, reporting capabilities, mobile accessibility, and customer support when making a decision.
Cloud-Based versus On-Premise Expense Management Systems
Cloud-based solutions offer several advantages over on-premise systems, including accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, automatic software updates, reduced IT infrastructure costs, and scalability to accommodate changing business needs. On-premise systems, however, offer greater control over data security and customization options. However, they require significant upfront investment in hardware and software, ongoing maintenance, and dedicated IT personnel. The optimal choice depends on the organization’s risk tolerance, IT infrastructure, and budget. A company with robust internal IT capabilities and stringent data security requirements might prefer an on-premise system, while a smaller company might benefit from the cost-effectiveness and ease of use of a cloud-based solution.
Integrating Expense Management Software with Accounting Systems
Seamless integration between expense management software and accounting systems is crucial for efficient financial reporting. This integration automates the transfer of expense data from the expense management system to the accounting system, eliminating manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors. Many modern expense management solutions offer pre-built integrations with popular accounting software such as Xero, QuickBooks, and SAP. However, it’s important to verify compatibility before selecting a solution. A successful integration streamlines the entire financial process, providing a unified view of all financial transactions and enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of financial reporting. Data discrepancies and reconciliation issues are minimized, leading to improved financial control and decision-making.
Expense Reporting Workflow with Software
The following illustrates a typical expense reporting workflow using expense management software:
An employee incurs an expense, captures the receipt using the mobile app, and submits the expense report. The report is routed through an approval workflow, potentially involving multiple approvers based on spending limits and organizational structure. Once approved, the expense data is automatically integrated with the accounting system. The employee receives notification of approval and payment. Managers can monitor expense reports, identify potential issues, and generate reports for analysis.
Policies and Procedures

A well-defined expense reimbursement policy is the cornerstone of effective expense management. It provides clarity for employees, reduces the risk of errors and fraud, and ensures consistent application of rules across the organization. A robust policy simplifies the process, minimizes disputes, and ultimately saves time and money.
A comprehensive expense policy clarifies what constitutes an acceptable business expense and Artikels the necessary steps for reimbursement. This prevents misunderstandings and ensures that only legitimate business expenses are processed. Clear guidelines reduce administrative burden and promote efficient expense processing.
Key Elements of a Comprehensive Expense Policy
A strong expense policy includes several key elements. Firstly, it defines acceptable expenses, specifying which types of expenditures are eligible for reimbursement (e.g., travel, accommodation, meals, client entertainment). Secondly, it Artikels unacceptable expenses, explicitly stating those that will not be reimbursed (e.g., personal expenses, fines, penalties). Thirdly, it details the required documentation for each expense type (e.g., receipts, invoices, itineraries). Finally, it specifies the approval process, including who needs to approve expenses at different levels and the timelines involved. This could involve a hierarchical system where expenses are approved by a manager, then a department head, and finally finance.
Expense Report Guidelines
Clear and concise expense report guidelines are crucial for efficient processing. These guidelines should specify the format of the expense report, the required information (date, description, amount, vendor), and the acceptable methods of submission (e.g., online portal, paper form). For example, the guideline might state: “All expense reports must be submitted within 14 days of the expense incurred. Receipts are required for all expenses over $25. Reports should be itemized and clearly categorized.”
Expense Report Submission Checklist
A checklist ensures employees submit complete and accurate expense reports. This simplifies the process and reduces the likelihood of delays or rejections.
- Have I completed all required fields on the expense report form?
- Have I attached original receipts for all expenses?
- Have I categorized each expense appropriately?
- Have I ensured all expenses are business-related?
- Have I obtained necessary approvals for expenses exceeding the authorized limit?
- Have I reviewed the expense report for accuracy and completeness?
- Have I submitted the report within the stipulated timeframe?
Training and Employee Engagement
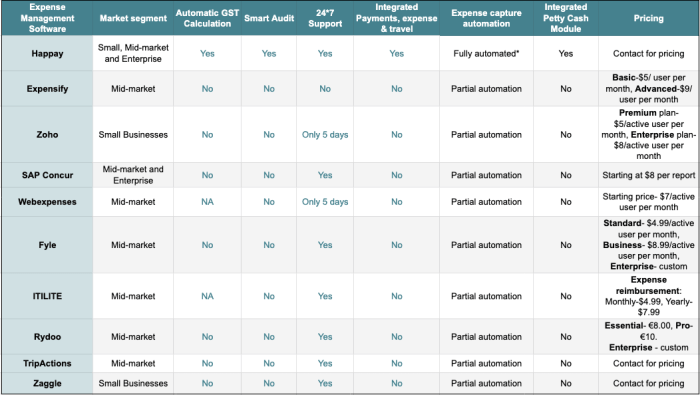
Effective training and ongoing engagement are crucial for successful expense management. A well-trained workforce understands policies, uses systems correctly, and ultimately reduces errors and improves compliance, leading to cost savings and a more efficient financial process. This section Artikels strategies to achieve these goals.
Effective Training Strategies
Comprehensive training programs should encompass all aspects of expense management, from initial policy understanding to the practical application of software and submission procedures. This includes interactive sessions, hands-on exercises, and readily accessible resources. For instance, a combination of online modules, followed by in-person workshops, allows for self-paced learning combined with opportunities for questions and clarification. Regular refresher training, particularly when policies or software updates occur, reinforces best practices and prevents outdated information from leading to errors. Furthermore, providing employees with easily accessible FAQs, cheat sheets, and video tutorials further enhances the learning experience and ensures continued understanding.
Promoting Employee Compliance
Promoting compliance requires a multi-faceted approach. Clear communication is key; ensuring policies are easily understood and accessible through various mediums (e.g., intranet, employee handbook, email) is paramount. Regular reminders and updates about expense reporting guidelines through company newsletters or internal communications platforms reinforce best practices and maintain awareness. Additionally, incorporating expense management into regular performance reviews, with feedback on adherence to guidelines, encourages responsible behavior. A reward system acknowledging consistent compliance can also significantly boost engagement. For example, recognizing employees who consistently submit accurate and timely expense reports could be done through public acknowledgment or small incentives.
Common Expense Reporting Errors and Prevention
Common errors include missing receipts, inaccurate categorization of expenses, and exceeding approved spending limits. Prevention strategies include mandatory receipt submission policies, clear expense categorization guidelines (with examples), and pre-approval processes for larger expenses. Implementing robust expense management software with built-in validation checks can automatically flag potential issues, such as missing information or exceeding spending limits, prompting employees to correct errors before submission. Providing regular feedback on submitted expense reports, highlighting common mistakes and offering corrective guidance, helps employees learn from their errors and improve their accuracy. A dedicated point of contact for expense-related queries ensures prompt resolution of any uncertainties.
Fostering a Culture of Responsible Spending
A culture of responsible spending starts at the top. Leadership should exemplify the desired behavior, setting a clear example through their own expense management practices. Open communication about the company’s financial position and the importance of cost-effective operations can foster a sense of shared responsibility. Regularly communicating the organization’s financial goals and how employee expense management contributes to achieving these goals reinforces the importance of responsible spending. Furthermore, providing employees with the necessary tools and resources to manage their expenses efficiently empowers them to make informed decisions and reduces the likelihood of unnecessary spending. For example, providing access to negotiated corporate rates for travel and accommodations demonstrates a commitment to responsible spending and encourages employees to utilize these resources.
Auditing and Controls
Robust auditing and internal controls are crucial for maintaining the integrity of an organization’s expense management system. These processes not only ensure compliance with regulations but also help prevent fraud, minimize errors, and provide valuable insights into spending patterns. A well-defined audit process, coupled with strong internal controls, fosters transparency and accountability within the organization.
Regular audits of expense reports are essential for identifying and rectifying potential issues before they escalate. Effective internal controls act as a preventative measure, reducing the likelihood of fraudulent activities and minimizing errors.
Expense Report Audit Procedures
A comprehensive expense report audit typically involves several key steps. First, a random sample of expense reports is selected for review, ensuring representation across different departments and employees. Each selected report is then meticulously examined against established company policies and procedures. This includes verifying the legitimacy of expenses, checking for appropriate supporting documentation (receipts, invoices), and ensuring compliance with expense limits and reimbursement rates. Any discrepancies or inconsistencies are flagged for further investigation and resolution. Finally, the audit findings are documented, and corrective actions are implemented to address any identified weaknesses in the expense management system.
Internal Controls to Prevent Fraud and Errors
Implementing strong internal controls is paramount to mitigating the risk of expense report fraud and errors. These controls should encompass various aspects of the expense management process, from expense submission to final approval and reimbursement. Examples include segregation of duties (preventing a single individual from controlling the entire process), mandatory expense report approvals by supervisors or designated personnel, and regular reconciliation of expense reports with accounting records. The use of expense management software with built-in controls, such as automated approval workflows and spending limits, can further enhance the effectiveness of internal controls.
Red Flags in Expense Report Reviews
Several red flags should trigger closer scrutiny during expense report reviews. These include missing or incomplete supporting documentation, expenses exceeding established limits or lacking clear business justification, unusual patterns of spending (e.g., consistently high expenses at the same vendor), and expenses incurred outside of normal business hours or locations. Reports with vague descriptions of expenses or those lacking proper authorization also warrant careful examination. The presence of multiple similar expenses from the same individual within a short time period might indicate potential irregularities.
Expense Report Approval and Auditing Process Flowchart
The flowchart below illustrates a typical expense report approval and auditing process.
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with an employee submitting an expense report. This report would then proceed to a supervisor for approval. Following supervisor approval, the report would move to the accounting department for processing and verification against supporting documentation. Next, a random selection of reports would be chosen for audit. The audit would involve a thorough review for compliance and identification of any discrepancies. Finally, the audited reports would be reconciled, and any necessary corrections or adjustments would be made. The entire process would loop back to the initial expense report submission, ensuring continuous monitoring and improvement.]
Budgeting and Forecasting
Effective expense management is the cornerstone of accurate budgeting. By meticulously tracking and categorizing expenses, businesses gain a clear understanding of their spending habits, identifying areas of potential savings and areas requiring increased allocation. This detailed insight allows for the creation of a realistic and achievable budget, minimizing the risk of financial shortfalls.
Accurate forecasting of future expenses is crucial for effective financial planning and decision-making. Predicting future costs allows businesses to proactively manage their resources, secure necessary funding, and make informed strategic choices. Without reliable expense forecasts, businesses operate with uncertainty, potentially leading to missed opportunities or financial instability.
Expense Forecasting Techniques
Improving the accuracy of expense forecasting involves employing various techniques. These techniques leverage historical data, market trends, and internal factors to generate more precise predictions. The selection of the most appropriate technique depends on the specific business context, industry, and the complexity of its operations.
- Regression Analysis: This statistical method identifies relationships between historical expenses and other relevant variables (e.g., sales revenue, production volume). By analyzing this relationship, businesses can predict future expenses based on projected values of these variables. For example, a company might find a strong correlation between sales and marketing expenses, allowing them to predict marketing costs based on projected sales figures for the next quarter.
- Time Series Analysis: This technique analyzes historical expense data to identify patterns and trends over time. These patterns, such as seasonal variations or long-term growth, can be extrapolated to forecast future expenses. A retail company, for example, might use time series analysis to predict higher expenses during peak holiday seasons.
- Scenario Planning: This approach involves developing multiple forecasts based on different assumptions about future conditions. By considering various scenarios (e.g., optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely), businesses can better prepare for a range of potential outcomes and make more robust decisions. A manufacturing company might create scenarios based on different levels of raw material price increases.
Sample Budget Template
A well-structured budget template is essential for effective expense tracking and forecasting. This template should clearly categorize expenses, allowing for easy monitoring and analysis. The inclusion of forecasting elements allows for proactive financial management.
| Expense Category | January | February | March | Q1 Total | Q2 Forecast | Q3 Forecast | Q4 Forecast | Annual Total Forecast |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salaries | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $120,000 |
| Rent | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $24,000 |
| Utilities | $500 | $500 | $500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $6,000 |
| Marketing | $1,000 | $1,200 | $1,500 | $3,700 | $4,000 | $4,500 | $5,000 | $17,200 |
| Supplies | $300 | $300 | $300 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $3,600 |
| Total Expenses | $13,800 | $14,000 | $14,300 | $42,100 | $42,400 | $42,900 | $42,900 | $169,300 |
Reporting and Analysis

Effective expense management relies heavily on robust reporting and analysis. By systematically tracking, analyzing, and visualizing expense data, organizations can gain valuable insights into spending patterns, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately optimize their financial performance. This section details key performance indicators (KPIs), the importance of regular reporting, visualization methods, and provides a sample expense report.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Expense Management
Several KPIs provide a comprehensive overview of expense management effectiveness. These metrics offer quantifiable insights into spending behavior and help identify areas requiring attention. Monitoring these KPIs allows for proactive adjustments to expense policies and procedures.
| KPI | Description |
|---|---|
| Expense Ratio | Total expenses divided by total revenue. A lower ratio indicates better expense control. |
| Average Expense per Employee | Total expenses divided by the number of employees. Helps identify potential overspending. |
| Compliance Rate | Percentage of expenses submitted with proper documentation and approvals. High compliance suggests effective policy adherence. |
| Average Processing Time | Time taken to process expense reports from submission to reimbursement. Shorter times indicate efficiency. |
Importance of Regular Expense Reporting and Analysis
Regular reporting and analysis are crucial for proactive expense management. Delayed or infrequent analysis can lead to missed opportunities for cost savings and increased financial risk. Consistent monitoring allows for the identification of trends, anomalies, and potential compliance issues before they escalate. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention and course correction. For example, a monthly review of expense reports might reveal a sudden increase in travel expenses in a specific department, prompting an investigation into the cause and potential cost-saving measures.
Methods for Visualizing Expense Data
Effective data visualization is key to identifying trends and anomalies. Various methods can be employed to represent expense data clearly and concisely. These methods facilitate easier identification of patterns and outliers, which might otherwise be missed in raw data.
- Bar charts: Useful for comparing expenses across different departments, categories, or time periods.
- Line graphs: Ideal for showing trends in expenses over time, highlighting seasonal variations or growth patterns.
- Pie charts: Effectively represent the proportion of expenses allocated to different categories.
- Heatmaps: Illustrate expense patterns across different dimensions, such as departments and expense types, highlighting areas of high or low spending.
Sample Expense Report
The following table illustrates a sample expense report incorporating key metrics and data visualization elements. This example uses fictional data for illustrative purposes.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Expenses (Month) | $50,000 |
| Average Expense per Employee | $500 |
| Compliance Rate | 98% |
| Average Processing Time | 2 days |
Emerging Trends in Expense Management
The landscape of expense management is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and a growing need for greater efficiency and transparency. Automation, artificial intelligence, and mobile accessibility are transforming how businesses handle expenses, leading to significant improvements in accuracy, speed, and cost savings. This section explores some of the key emerging trends shaping the future of expense management.
Automation’s Impact on Expense Management Processes
Automation is revolutionizing expense management by streamlining previously manual and time-consuming tasks. Automated solutions can handle tasks such as receipt capture, data entry, and expense report generation, significantly reducing the workload on finance teams and minimizing human error. For instance, optical character recognition (OCR) technology can automatically extract data from receipts, eliminating the need for manual data entry. Workflow automation tools can route expense reports for approval, ensuring timely processing and reducing bottlenecks. The result is a more efficient and accurate expense management process, freeing up valuable time and resources for other strategic initiatives.
Artificial Intelligence in Expense Reporting and Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in expense reporting and analysis. AI-powered systems can analyze large volumes of expense data to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential areas for cost savings. For example, AI can detect potentially fraudulent expenses or identify areas where spending is exceeding budget. AI algorithms can also learn from past expense data to predict future spending patterns, enabling more accurate budgeting and forecasting. This proactive approach to expense management helps businesses make informed decisions and optimize their spending. One example is AI’s ability to flag unusually high expenses in a specific category, prompting investigation and potentially preventing significant losses.
Benefits of Mobile Expense Management Apps
Mobile expense management apps are transforming how employees submit and manage their expenses. These apps offer several key benefits, including real-time expense tracking, simplified receipt capture (often through photo uploads), and immediate access to expense reports. Employees can submit expense reports from anywhere, at any time, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing delays. The immediate feedback and transparency provided by these apps improve employee satisfaction and compliance. For example, an employee on a business trip can instantly capture and upload receipts, ensuring accurate record-keeping and reducing the risk of lost or misplaced documents. Many apps also offer features like mileage tracking and currency conversion, simplifying the process further.
Innovative Solutions Shaping the Future of Expense Management
Several innovative solutions are emerging to further enhance expense management. These include integrated platforms that combine expense management with other financial processes, such as accounting and budgeting. Blockchain technology offers the potential to improve the security and transparency of expense transactions. Predictive analytics, powered by AI and machine learning, can provide insights into future spending trends, enabling proactive budget management. Furthermore, the integration of expense management systems with corporate travel booking platforms streamlines the entire travel and expense process, providing a holistic view of corporate spending. For example, a company might implement a system that automatically reconciles travel bookings with expense reports, eliminating manual reconciliation and reducing errors.
Final Review
By implementing the expense management best practices Artikeld here, organizations can streamline their processes, reduce costs, improve financial accuracy, and foster a culture of responsible spending. From choosing the right software and establishing clear policies to conducting regular audits and leveraging data analytics, a comprehensive approach to expense management is essential for achieving long-term financial stability and success. Remember that continuous improvement and adaptation to emerging technologies are key to maintaining a best-in-class expense management system.
Question Bank
What are some common red flags in expense reports?
Missing receipts, excessive spending in certain categories, unusual patterns, expenses lacking sufficient justification, and inconsistencies between expenses and project records are all potential red flags.
How often should expense reports be audited?
The frequency of audits depends on the organization’s size and risk tolerance. However, regular audits, at least quarterly, are recommended to ensure compliance and identify potential issues early.
What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) for expense management?
Key KPIs include expense-to-revenue ratio, average processing time for expense reports, error rate in expense reports, and compliance rate with expense policies.
How can I improve employee engagement with expense management policies?
Provide clear and concise training, use user-friendly software, offer regular feedback, and recognize employees for their compliance with expense reporting guidelines. Make the process simple and straightforward.