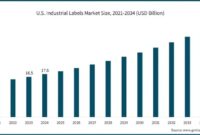
Market research reports are the bedrock of informed business decisions. They provide a structured analysis of market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes, offering invaluable insights for strategic planning and resource allocation. This report delves into the creation and utilization of these crucial documents, covering everything from defining research objectives to interpreting complex data sets and presenting compelling findings.
From understanding the different types of market research reports – industry analyses, consumer behavior studies, and competitor assessments – to mastering data visualization techniques, this guide equips readers with the knowledge and skills to navigate the world of market research effectively. We’ll explore the research process itself, from initial concept to final report dissemination, emphasizing the importance of both primary and secondary data collection methods. Finally, we’ll showcase how businesses of all sizes leverage these reports to achieve their strategic goals, illustrating their impact with real-world examples.
Defining Market Research Reports

Market research reports are crucial documents that synthesize data and analysis to provide insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes. They serve as valuable tools for businesses to make informed decisions regarding product development, marketing strategies, and overall business planning. A well-structured report presents findings clearly and concisely, enabling stakeholders to quickly grasp key takeaways and implications.
Market research reports typically consist of several core components. These include an executive summary providing a concise overview of the report’s key findings and recommendations; a detailed methodology section outlining the research approach and data collection methods employed; a comprehensive analysis of the findings, presented using various data visualization techniques; and finally, conclusions and recommendations based on the analyzed data. The structure might vary slightly depending on the specific objectives of the research and the target audience.
Types of Market Research Reports
Market research reports come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose. Industry reports offer an in-depth analysis of a particular industry, encompassing market size, growth trends, key players, and future prospects. For example, an industry report on the renewable energy sector might detail the growth of solar and wind power, government regulations impacting the industry, and the competitive landscape among major renewable energy companies. Consumer reports focus on understanding consumer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns related to specific products or services. A consumer report on the preferences of coffee drinkers might detail the popularity of various coffee types, preferred brewing methods, and price sensitivity. Competitor analysis reports focus on evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, identifying market opportunities and threats, and informing strategic decision-making. A competitor analysis report on the athletic shoe market might compare the market share, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns of major brands like Nike, Adidas, and Under Armour.
Data Visualization Techniques in Market Research Reports
Effective data visualization is essential for presenting complex data in a clear and understandable manner. Various techniques are used to enhance comprehension and facilitate decision-making.
| Technique | Description | Example | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bar Charts | Used to compare different categories or groups of data. | A bar chart comparing the market share of different brands of smartphones. Taller bars represent a larger market share. | Easy to understand and compare different categories. |
| Line Graphs | Illustrate trends and changes over time. | A line graph showing the growth of e-commerce sales over the past five years. The upward slope of the line indicates increasing sales. | Effectively displays trends and patterns over time. |
| Pie Charts | Show the proportion of different parts of a whole. | A pie chart illustrating the distribution of consumer preferences for different types of soft drinks. Each slice represents a different drink type and its size corresponds to its popularity. | Clearly shows the relative proportions of different categories. |
| Scatter Plots | Show the relationship between two variables. | A scatter plot showing the correlation between advertising spending and sales revenue. A positive correlation would suggest that increased spending leads to higher sales. | Reveals the correlation and potential relationship between variables. |
The Research Process

Conducting effective market research involves a systematic process, ensuring that insights are relevant, reliable, and actionable. This process, while adaptable to specific needs, generally follows a structured approach, moving from initial conception to the final dissemination of findings. Each stage plays a crucial role in the overall success of the research endeavor.
The research process typically unfolds in several key stages. These stages build upon each other, ensuring that the research remains focused and efficient. A deviation from this structured approach can lead to inconsistencies and unreliable results. Therefore, a well-defined process is essential for delivering high-quality market research.
Defining Research Objectives
Clearly defined objectives are the foundation of any successful market research project. These objectives should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). Vague objectives lead to unclear methodologies and ultimately, unhelpful conclusions. For example, instead of aiming to “understand the market,” a SMART objective might be “to determine the market share of organic food products in the UK within the next six months.” This precision ensures that the research remains focused and the results are easily interpreted and used for decision-making.
Developing the Research Design
Once the objectives are established, a research design is formulated. This Artikels the specific methods and techniques that will be employed to gather and analyze data. This stage involves crucial decisions regarding the target population, sample size, data collection methods (primary and secondary research), and the analysis techniques to be used. A well-defined research design ensures that the data collected is relevant, reliable, and sufficient to address the research objectives. For instance, if the objective is to understand consumer preferences, a survey might be deemed appropriate; if the objective is to track market trends, secondary data analysis might suffice.
Data Collection
This stage involves the actual gathering of data using the methods Artikeld in the research design. Data collection can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring careful planning and execution. The accuracy and reliability of the data collected are paramount to the validity of the research findings.
Primary Research Methods
Primary research involves collecting original data directly from the source. This offers unique insights but is often more expensive and time-consuming than secondary research.
- Surveys (online, telephone, in-person): Gathering quantitative and qualitative data about consumer opinions, behaviors, and preferences.
- Focus groups: Moderated discussions with small groups of individuals to explore specific topics in detail.
- Interviews (structured, semi-structured, unstructured): In-depth conversations with individuals to gain detailed insights.
- Observations: Systematic watching and recording of behaviors in natural settings.
- Experiments: Controlled tests to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
Secondary Research Methods
Secondary research involves using existing data that has been collected by others. This is generally a more cost-effective and quicker method than primary research, but the data might not always perfectly align with the research objectives.
- Market reports and industry publications: Accessing pre-existing analyses and insights from market research firms.
- Government statistics and census data: Utilizing publicly available data on demographics, economic indicators, and other relevant factors.
- Company records and internal data: Using sales figures, customer databases, and other internal information.
- Academic journals and research papers: Consulting peer-reviewed studies and publications for relevant information.
- Online databases: Accessing various databases containing market information, industry trends, and consumer data.
Data Analysis
Once the data is collected, it is analyzed using appropriate statistical and qualitative methods. This stage involves cleaning, organizing, and interpreting the data to extract meaningful insights. The choice of analytical techniques depends on the type of data collected and the research objectives. For quantitative data, statistical software might be used; for qualitative data, thematic analysis or content analysis might be employed.
Report Writing and Dissemination
The final stage involves compiling the research findings into a comprehensive report and disseminating the information to stakeholders. The report should clearly present the research objectives, methodology, findings, and conclusions. Effective communication is key to ensuring that the insights are understood and utilized by decision-makers. Dissemination might involve presentations, written reports, or online dashboards.
Market Research Project Workflow
The following flowchart illustrates a typical workflow:
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with “Define Research Objectives,” leading to “Develop Research Design,” then branching into “Primary Research” and “Secondary Research,” both converging at “Data Analysis,” followed by “Report Writing” and finally “Report Dissemination.”] The flowchart visually represents the sequential nature of the process, highlighting the interdependencies between the different stages. Each stage builds upon the previous one, ensuring a logical and efficient flow of the research process. This visual representation is useful for project management and monitoring progress.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
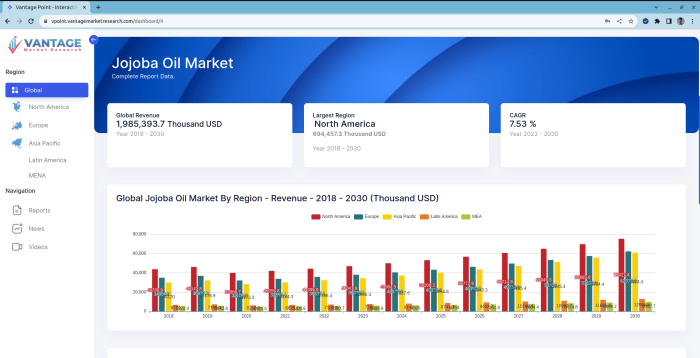
Data analysis is the crucial bridge between raw market research data and actionable insights. This stage involves transforming collected data into meaningful information that can inform strategic decision-making. Effective data analysis requires a systematic approach, encompassing data cleaning, statistical techniques, and careful interpretation of findings, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the final report.
Data Cleaning and Preparation
Before any analysis can begin, the collected data must be thoroughly cleaned and prepared. This process involves several key steps to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Errors, inconsistencies, and missing values can significantly skew results. Therefore, meticulous cleaning is paramount.
- Handling Missing Values: Missing data points can be addressed through various methods, such as imputation (replacing missing values with estimated values based on existing data) or exclusion (removing data points with missing values). The choice of method depends on the nature of the data and the extent of missing values. For example, if a small percentage of survey responses are missing, imputation might be suitable. However, if a significant portion of data is missing, exclusion might be necessary to maintain data integrity.
- Identifying and Correcting Errors: Data entry errors, inconsistencies in responses, and outliers (extreme values that deviate significantly from the rest of the data) need to be identified and corrected or removed. Data validation checks, such as range checks and consistency checks, can help identify these errors. For instance, an age value of 200 would clearly be an error and needs to be corrected or removed.
- Data Transformation: This may involve converting data into a suitable format for analysis. For example, categorical variables (like gender or brand preference) might need to be recoded into numerical values for statistical analysis. This process often involves creating dummy variables (0 or 1 values representing the presence or absence of a category).
Statistical Techniques in Market Research
A range of statistical techniques are employed in market research to analyze data and draw meaningful conclusions. The choice of technique depends on the type of data (quantitative or qualitative) and the research objectives.
- Descriptive Statistics: These summarize the main features of the data, providing a basic understanding of the dataset. Measures like mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and frequency distributions are commonly used to describe the central tendency, variability, and distribution of the data.
- Inferential Statistics: These techniques allow researchers to make inferences about a population based on a sample of data. Common methods include t-tests (comparing means of two groups), ANOVA (comparing means of three or more groups), chi-square tests (analyzing relationships between categorical variables), and regression analysis (modeling the relationship between variables).
- Correlation Analysis: This examines the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two or more variables. A correlation coefficient, ranging from -1 to +1, indicates the strength and direction of the relationship.
Interpreting Key Findings
Interpreting findings requires careful consideration of both quantitative and qualitative data. Quantitative data provides numerical insights, while qualitative data offers richer contextual understanding. Integrating both is essential for a comprehensive interpretation.
| Variable | Data Type | Sample Data | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Age | Quantitative | Mean: 35, Median: 32, Standard Deviation: 8 | The average customer age is 35, with a median of 32 indicating a slightly skewed distribution. The standard deviation of 8 suggests a relatively wide range of customer ages. |
| Brand Preference | Qualitative | Brand A: 45%, Brand B: 30%, Brand C: 25% | Brand A holds the largest market share (45%), followed by Brand B (30%) and Brand C (25%). This suggests a strong preference for Brand A. |
| Customer Satisfaction | Quantitative (Scale 1-5) | Mean: 4.2 | Customers exhibit a high level of satisfaction (mean score of 4.2 out of 5), indicating positive overall sentiment towards the product or service. |
| Open-Ended Feedback | Qualitative | Recurring themes: ease of use, attractive design | Qualitative feedback highlights ease of use and attractive design as key positive attributes. This complements the quantitative data, providing a richer understanding of customer satisfaction. |
Report Structure and Presentation
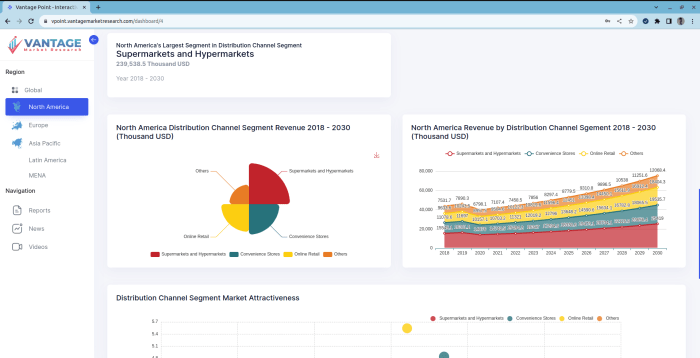
A well-structured market research report is crucial for effective communication of findings and recommendations. Clear organization enhances readability and allows stakeholders to quickly grasp key insights. This section details the typical structure and provides examples of effective presentation techniques.
A standard market research report follows a logical flow, guiding the reader from the overall summary to detailed findings and concluding recommendations. This structure ensures that information is presented in a clear and concise manner, maximizing understanding and impact. Effective data visualization plays a key role in this process, transforming complex datasets into easily digestible visuals.
Typical Report Sections
The typical sections of a market research report include an executive summary, methodology, findings, and recommendations. The executive summary provides a concise overview of the entire report, highlighting key findings and recommendations. The methodology section details the research approach, including data collection methods and sample size. The findings section presents the results of the data analysis, while the recommendations section offers actionable insights based on the findings. Additional sections may include an introduction, background information, limitations, and appendices, depending on the complexity and scope of the research.
Sample Market Research Report: “SmartMug”
Let’s consider a hypothetical product, “SmartMug,” a self-heating mug that maintains the ideal temperature of a beverage. A market research report on this product might be structured as follows:
* Executive Summary: This section would briefly summarize the market opportunity for SmartMug, key findings regarding consumer interest and price sensitivity, and the recommended marketing strategy. For example, it might state that the market for SmartMugs shows strong potential among young professionals and students, with a willingness to pay a premium for convenience and temperature control.
* Methodology: This section would describe the research methods used, such as online surveys, focus groups, and competitor analysis. It would specify the sample size, demographics, and data collection techniques employed. For instance, it might mention that 500 online surveys were conducted among young professionals aged 25-40, with a balanced representation of genders.
* Findings: This section would present the key findings of the research. It would include data on consumer preferences, price sensitivity, brand awareness, and competitor analysis. Data tables and charts would be used to visualize the findings. For example, a chart showing the percentage of respondents willing to pay different price points for the SmartMug.
* Recommendations: This section would provide actionable recommendations based on the findings. It might suggest target marketing strategies, pricing strategies, product development recommendations, and distribution channels. For instance, a recommendation might be to focus marketing efforts on social media platforms frequented by the target demographic and to offer a tiered pricing structure.
Effective Data Visualization Techniques
Data visualization is critical for effectively communicating complex information. Different chart types are suited for different types of data and insights.
Choosing the appropriate visualization method is crucial for clear and impactful communication.
- Bar Charts: Ideal for comparing categorical data, such as market share of different brands or sales figures across different regions.
- Line Charts: Excellent for showing trends over time, such as sales growth over several quarters or website traffic over a year.
- Pie Charts: Useful for displaying proportions or percentages of a whole, such as the market share distribution among competitors.
- Scatter Plots: Show the relationship between two variables, helping identify correlations, such as the relationship between price and demand.
- Heatmaps: Visually represent data in a matrix format, showing intensity of values through color gradients, useful for visualizing large datasets.
For example, a bar chart could effectively compare the market share of different self-heating mug brands, while a line chart could illustrate the growth in sales of SmartMug over a period of time. A scatter plot might show the correlation between price and consumer demand for SmartMug.
Applications and Uses of Market Research Reports
Market research reports are invaluable tools for businesses of all sizes and across diverse industries. They provide actionable insights that inform strategic decisions, leading to improved efficiency, increased profitability, and a stronger competitive advantage. The information gleaned from these reports allows companies to understand their target markets, identify opportunities, and mitigate potential risks, ultimately driving business growth and success.
Market research reports are used extensively throughout the business lifecycle, from initial concept development to ongoing operational adjustments. Their applications are diverse and impact numerous aspects of a company’s operations.
Strategic Decision-Making
Market research reports are fundamental to effective strategic decision-making. By analyzing market trends, competitive landscapes, and consumer behavior, businesses can make informed choices about resource allocation, product development, marketing strategies, and overall business direction. For instance, a report revealing a declining demand for a particular product line might prompt a company to reallocate resources to a more promising area, preventing further losses and maximizing return on investment. Similarly, identifying a niche market with high growth potential allows businesses to strategically target their efforts and resources for maximum impact. A comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, provided through market research, enables businesses to anticipate competitor actions and develop proactive strategies to maintain a competitive edge.
Product Development and Marketing Campaigns
Market research plays a pivotal role in the development of new products and the execution of effective marketing campaigns. Reports detailing consumer preferences, needs, and pain points guide the design and features of new products, ensuring they meet market demands and resonate with the target audience. For example, a report indicating a preference for sustainable packaging could influence a company’s decision to adopt eco-friendly materials. Furthermore, market research informs the development of targeted marketing campaigns by identifying the most effective channels to reach the desired customer segments and crafting messaging that resonates with their values and preferences. Data on customer demographics, psychographics, and buying behavior allows for precise targeting, increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of marketing spend. A company launching a new mobile app, for example, might use market research to determine the optimal advertising platforms and tailor their messaging to specific user groups.
Value Across Businesses and Industries
The value of market research reports varies depending on the size and industry of the business. Small businesses might leverage reports to understand their local market, identify competitive threats, and refine their marketing efforts. For example, a small bakery might commission a report to understand local consumer preferences for different types of bread and pastries, helping them tailor their offerings and optimize their menu. Larger corporations, on the other hand, may use market research to inform complex strategic decisions involving mergers and acquisitions, international expansion, and the development of entirely new product lines. Similarly, industries with rapid technological advancements or highly volatile market conditions (like technology or fashion) rely heavily on frequent market research to stay ahead of the curve. Conversely, industries with slower-moving markets (like utilities) might require less frequent, but still valuable, market research to track long-term trends and anticipate future changes. In essence, the value proposition of market research scales with the size and complexity of the business and the dynamism of its market environment.
Illustrative Examples

Market research reports, when effectively utilized, can profoundly influence a company’s trajectory. Their value lies not just in the data collected, but in the strategic insights derived and the subsequent actions implemented. The following examples demonstrate the transformative power of well-executed market research.
Impact of Market Research on Company Strategy: The Case of “Coffee Crave”
Coffee Crave, a small regional coffee roaster, faced stagnant growth. Their market share was plateauing, and they lacked a clear understanding of consumer preferences beyond their immediate locality. They commissioned a comprehensive market research report focusing on consumer demographics, purchasing habits, preferred coffee types, and competitor analysis across a wider geographic area. The report revealed a significant untapped market for ethically sourced, single-origin coffees amongst younger, environmentally conscious consumers. This demographic was largely underserved in the region. Based on this insight, Coffee Crave adjusted its product line, introducing several new single-origin coffees with detailed information about their origin and ethical sourcing practices. They also redesigned their packaging to reflect their commitment to sustainability. This strategic shift, directly informed by the market research, led to a 30% increase in sales within the first year, expanding their market reach significantly. The report also identified a price sensitivity in the market, suggesting a need to offer different price points. This led to the introduction of a value range of blends, further boosting sales.
Identifying New Market Opportunities: The Emergence of “Smart Pet Collars”
A hypothetical market research report investigating the pet care industry identified a growing trend: increasing consumer adoption of smart technology for pet monitoring and management. The report highlighted a gap in the market for “smart pet collars” that offered advanced features beyond basic GPS tracking. Specifically, the report suggested a demand for collars incorporating health monitoring sensors (heart rate, activity levels), integrated communication features (allowing for remote voice commands and two-way audio), and personalized activity tracking. This new market opportunity, highlighted by the research, describes a hypothetical product that combines the convenience of smart technology with pet care. This hypothetical product would integrate health monitoring sensors, remote communication features, and personalized activity tracking. The market research report provided detailed insights into the potential market size, target demographics, and competitive landscape, enabling a company to develop a viable business plan for launching such a product. The report predicted strong growth potential driven by increasing pet ownership and the willingness of pet owners to invest in their pets’ well-being and technology. The success of similar products in other sectors (e.g., wearable fitness trackers) supported this prediction.
Ultimate Conclusion
Ultimately, the value of a market research report lies in its ability to translate raw data into actionable intelligence. By understanding the methodologies, analytical techniques, and presentation strategies Artikeld in this report, businesses can gain a significant competitive edge. The ability to accurately predict market trends, identify emerging opportunities, and understand consumer needs is paramount for success, and market research reports provide the critical framework for achieving these objectives. Whether you’re launching a new product, refining a marketing campaign, or simply seeking to understand your competitive landscape, a well-constructed market research report is an invaluable tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Qualitative research explores in-depth insights and opinions (e.g., focus groups, interviews), while quantitative research uses numerical data and statistical analysis (e.g., surveys, experiments) to measure and quantify phenomena.
How much does a market research report cost?
The cost varies significantly depending on scope, complexity, and the research firm. Small-scale reports might cost a few thousand dollars, while extensive, multi-country studies can cost hundreds of thousands.
How long does it take to create a market research report?
The timeframe depends on the project’s scope and complexity. Simple reports might take weeks, while larger, more complex studies could take several months.
Who uses market research reports?
Businesses of all sizes, across various industries, utilize market research reports. This includes startups, established corporations, and government agencies needing market intelligence.