Business model innovation represents a fundamental shift in how companies create, deliver, and capture value. It transcends mere product or process improvements, instead focusing on reimagining the core logic of how a business operates within its market. This involves a deep understanding of customer needs, competitive dynamics, and emerging technological landscapes, ultimately leading to sustainable competitive advantage.
Successful business model innovation often requires a willingness to challenge established practices and embrace experimentation. Companies must be agile enough to adapt to changing market conditions and innovative enough to create entirely new value propositions. This exploration delves into the key aspects of identifying opportunities, designing innovative models, implementing changes, and measuring success.
Defining Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation represents a fundamental shift in how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It’s not simply about tweaking existing products or processes; it’s about reimagining the entire architecture of how a business operates to better meet customer needs and achieve sustainable competitive advantage. This contrasts sharply with product innovation (improving existing products or creating new ones) and process innovation (improving the efficiency of internal operations), which focus on individual components rather than the overarching system.
Business model innovation focuses on the entire value chain, from identifying customer needs to delivering a solution and generating revenue. It encompasses everything from revenue streams and customer segments to key activities and partnerships. Successful implementation often requires a holistic approach, challenging deeply ingrained assumptions and exploring new ways of interacting with the market.
Examples of Successful Business Model Innovations
Several companies have successfully redefined their industries through impactful business model innovations. Netflix, for instance, transitioned from a DVD-rental-by-mail service to a streaming giant, fundamentally altering how people consume entertainment. This involved shifting from a transactional model to a subscription model, expanding its content library, and leveraging technology to deliver a seamless user experience. Similarly, Spotify disrupted the music industry by moving from a model of individual song purchases to a subscription-based streaming service, offering a vast catalog of music for a fixed monthly fee. This provided consumers with greater access to music while generating a predictable revenue stream for Spotify. Another prime example is Airbnb, which revolutionized the hospitality industry by creating a platform connecting homeowners with travelers seeking accommodations, bypassing traditional hotels and creating a vast network of unique lodging options.
Comparative Analysis of Business Model Innovation Types
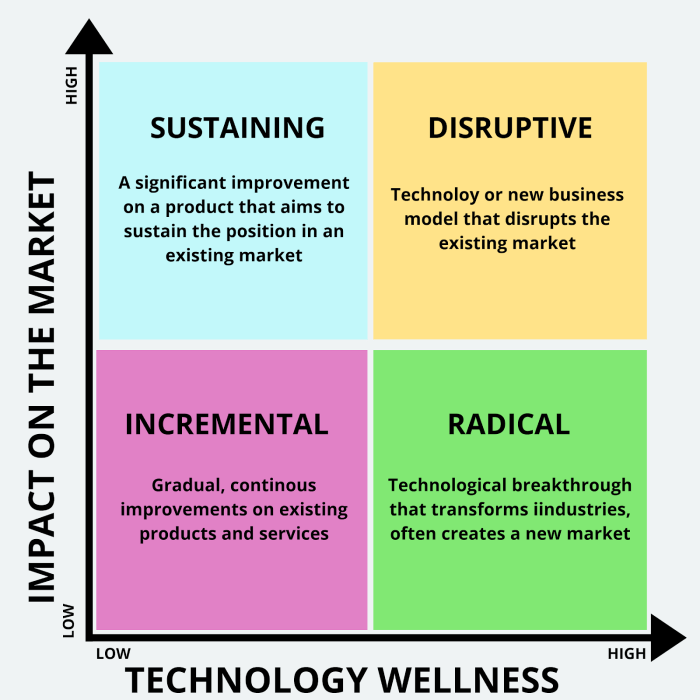
Different types of business model innovation exist, each characterized by its approach to change. Disruptive innovation, as exemplified by Netflix and Spotify, introduces a simpler, more affordable, and often more accessible alternative to existing offerings, initially targeting niche markets before expanding to broader audiences. Architectural innovation involves reconfiguring existing components of a business model in novel ways, creating new value propositions. For example, a company might integrate its existing product with a new technology to offer a more comprehensive solution. Incremental innovation, on the other hand, involves making smaller, iterative changes to an existing business model, such as optimizing pricing strategies or improving customer service processes. While seemingly less dramatic, these incremental adjustments can significantly enhance efficiency and profitability. The choice of which type of innovation to pursue depends heavily on the specific context, competitive landscape, and organizational capabilities.
Identifying Opportunities for Business Model Innovation
Spotting opportunities for business model innovation requires a proactive and insightful approach. It involves systematically analyzing customer needs, competitive dynamics, and industry trends to uncover areas ripe for disruption and value creation. This process isn’t about incremental improvements; it’s about fundamentally rethinking how value is delivered to customers.
Identifying unmet customer needs and market gaps is the cornerstone of successful business model innovation. Understanding these gaps allows businesses to create offerings that resonate deeply with their target audience and solve problems that existing solutions fail to address adequately. This necessitates a shift from a product-centric to a customer-centric mindset.
Methods for Identifying Unmet Customer Needs and Market Gaps
Effective identification of unmet needs relies on a multi-faceted approach. This involves going beyond simple market research and actively engaging with customers to understand their frustrations, desires, and pain points. This understanding informs the development of innovative solutions that address those specific needs.
- Customer Surveys and Interviews: Directly soliciting feedback through structured surveys and in-depth interviews provides invaluable insights into customer experiences and unmet needs. For example, a survey could reveal dissatisfaction with existing customer service channels, prompting the development of a more responsive, AI-powered support system.
- Focus Groups and Ethnographic Studies: Observing customers in their natural environment and conducting focus group discussions can reveal hidden needs and unspoken frustrations. For example, observing how consumers use a product can highlight usability issues that aren’t readily apparent through surveys.
- Social Media Monitoring and Online Reviews: Analyzing social media conversations and online reviews can provide a wealth of information about customer sentiment and unmet needs. For instance, a high volume of negative reviews regarding a product’s delivery speed might suggest an opportunity to innovate in the logistics aspect of the business model.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyzing competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, as well as their customer reviews, can reveal gaps in the market that your business can fill. For example, identifying a competitor’s lack of personalized customer service could create an opportunity to offer a superior experience.
Analyzing the Competitive Landscape and Identifying Potential Areas for Business Model Disruption
A thorough competitive analysis is crucial for identifying areas where a disruptive business model can gain traction. This involves understanding the competitive dynamics, identifying industry weaknesses, and exploring alternative approaches to value creation.
A robust framework for this analysis could include:
- Identify Key Competitors: List all major players and emerging competitors in the market.
- Analyze their Business Models: Examine their value propositions, revenue streams, cost structures, and key activities.
- Identify Market Gaps and Weaknesses: Look for areas where competitors are failing to meet customer needs or are inefficient in their operations.
- Explore Disruptive Opportunities: Consider how new technologies or business models can address these gaps and disrupt the existing competitive landscape.
- Assess Competitive Advantages: Determine what makes your proposed business model superior and more sustainable.
Understanding Industry Trends and Technological Advancements in Identifying Innovation Opportunities
Staying abreast of industry trends and technological advancements is paramount. These factors can significantly influence customer needs and create new opportunities for business model innovation. Failing to do so risks becoming obsolete.
“The pace of technological change is accelerating, creating both challenges and opportunities for businesses. Those who fail to adapt risk being left behind.”
Examples of how these factors drive innovation:
- The rise of e-commerce has drastically altered retail business models, creating opportunities for online marketplaces, subscription services, and personalized shopping experiences.
- The growth of mobile technology has enabled the development of location-based services, mobile payment systems, and on-demand delivery platforms, fundamentally changing how businesses interact with their customers.
- Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming customer service, product development, and marketing, creating opportunities for more efficient and personalized experiences.
Designing Innovative Business Models
Designing a truly innovative business model requires a structured approach that blends creativity with rigorous analysis. It’s not just about a new product; it’s about a fundamentally different way of creating, delivering, and capturing value. This section Artikels a step-by-step process for developing such models, emphasizing market understanding, value proposition refinement, and sustainable revenue generation.
A Step-by-Step Process for Business Model Development
Developing a new business model is an iterative process. It requires careful consideration of the market, the customer, and the overall value proposition. The following steps provide a framework for this process.
- Market Research and Analysis: Thorough market research is crucial. This involves identifying target customer segments, understanding their needs and pain points, analyzing the competitive landscape, and assessing market size and potential. Tools like surveys, focus groups, and competitive analysis reports are invaluable. For example, before launching a new sustainable clothing line, extensive research into consumer preferences for eco-friendly materials and ethical sourcing is essential.
- Value Proposition Design: Once the market is understood, define a compelling value proposition. This Artikels the specific benefits your business model offers to customers, differentiating it from competitors. This should address the identified customer needs and pain points revealed in the market research. For example, a value proposition for a sustainable clothing line might highlight the use of organic cotton, fair trade practices, and durable, long-lasting garments.
- Revenue Model Creation: Determine how the business will generate revenue. This could involve various models such as subscriptions, freemium, advertising, licensing, or a combination thereof. The chosen revenue model must align with the value proposition and be sustainable in the long term. For example, the sustainable clothing line might use a premium pricing strategy, reflecting the higher quality and ethical production.
- Business Model Canvas Development: Use the Business Model Canvas to visualize and refine the entire model. This ensures all elements are interconnected and coherent. This is discussed further below.
- Testing and Iteration: Test the business model through prototypes, pilot programs, or minimum viable products (MVPs). Gather feedback and iterate based on the results. This ensures the model is adaptable and responsive to market dynamics.
Key Components of a Successful Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing a business model. It helps to ensure all key components are aligned and working together effectively.
| Key Partners | Key Activities | Key Resources | Value Propositions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suppliers, distributors, strategic alliances | Production, marketing, sales, customer service | Physical assets, intellectual property, human capital | Problem solved, needs fulfilled, benefits offered |
| Customer Relationships | Channels | Customer Segments | Cost Structure |
| Personal assistance, self-service, automated services | Online, retail stores, direct sales | Mass market, niche market, segmented market | Fixed costs, variable costs |
| Revenue Streams | |||
| Sales, subscriptions, advertising, licensing |
Incorporating Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
Integrating sustainability and ethical considerations is no longer a “nice-to-have” but a necessity for long-term success. Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency and accountability from businesses.
To incorporate these aspects, consider:
- Environmental Impact: Minimize the environmental footprint throughout the entire value chain, from sourcing materials to product disposal. This could involve using recycled materials, reducing waste, and investing in renewable energy.
- Social Responsibility: Ensure fair labor practices, ethical sourcing, and community engagement. This might involve working with certified suppliers, paying fair wages, and supporting local communities.
- Transparency and Accountability: Be transparent about the business’s environmental and social impact. This could involve publishing sustainability reports, obtaining relevant certifications (e.g., B Corp), and engaging with stakeholders.
- Long-term Value Creation: Focus on creating long-term value for all stakeholders, not just shareholders. This involves considering the environmental and social consequences of business decisions.
Implementing and Scaling Business Model Innovation
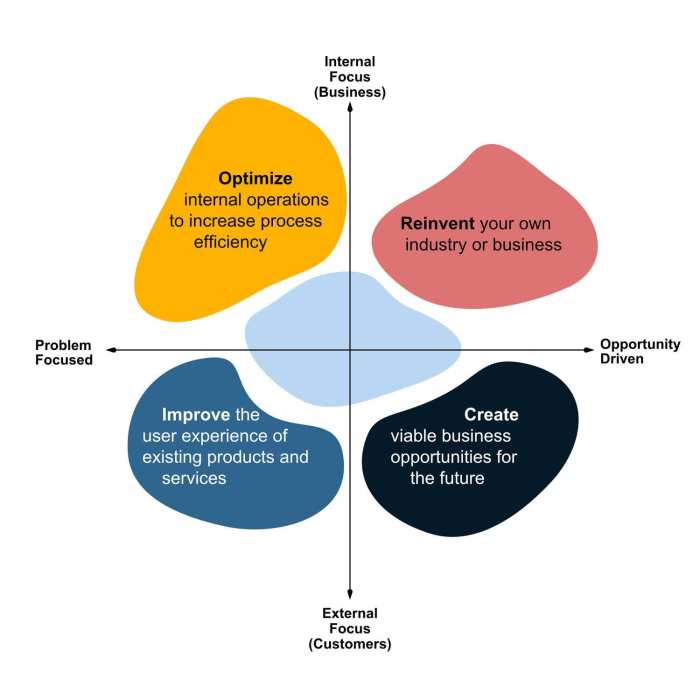
Implementing a new business model, even a brilliantly conceived one, presents significant hurdles for established organizations. The inherent inertia of existing systems, processes, and ingrained cultures often clash with the disruptive nature of innovation, creating a complex challenge that requires careful planning and execution. Successfully navigating this transition necessitates a deep understanding of organizational dynamics and a strategic approach to change management.
Successfully implementing and scaling a new business model requires a multifaceted strategy. This involves overcoming internal resistance, managing organizational change, and adapting the model for diverse markets and customer segments. The following sections delve into the key challenges and strategies involved in this crucial phase of business model innovation.
Challenges in Implementing a New Business Model
Implementing a new business model within an existing organization often encounters significant resistance. Established processes, entrenched cultures, and employee resistance to change can significantly hinder progress. For example, a company shifting from a product-focused model to a subscription-based one might face resistance from sales teams accustomed to one-time transactions, requiring extensive retraining and a change in sales incentives. Furthermore, legacy systems may not be compatible with the new model, requiring substantial investment in new technology and infrastructure. Finally, internal conflicts between departments with differing interests can create friction and slow down implementation. A lack of clear communication and a poorly defined implementation plan further exacerbate these challenges.
Strategies for Managing Organizational Change and Resistance to Innovation
Effectively managing organizational change during business model innovation requires a comprehensive approach. Open and transparent communication is paramount; keeping employees informed throughout the process, addressing their concerns, and actively soliciting their feedback can significantly reduce resistance. Furthermore, providing comprehensive training and development programs equips employees with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in the new model. Leadership buy-in and visible support from senior management are also critical; their active participation and advocacy for the change can significantly influence employee attitudes and behaviors. Incentivizing adoption through performance-based rewards can further motivate employees to embrace the new business model. Finally, establishing a strong change management team with clear responsibilities and accountability helps to guide the implementation process and address challenges effectively.
Methods for Scaling a Successful Business Model
Once a new business model proves successful in its initial market, scaling it to new markets and customer segments requires careful consideration. Market research is crucial; understanding the specific needs and preferences of target customers in different regions or segments is essential for adapting the model effectively. A phased rollout approach, starting with a pilot program in a carefully selected market, allows for testing and refinement before wider deployment. Localization of the model, adapting it to local cultural nuances and regulatory environments, is vital for success in international markets. Strategic partnerships with local players can provide valuable access to markets and resources. Finally, continuous monitoring and evaluation of the model’s performance in different markets allows for timely adjustments and improvements, ensuring long-term sustainability and growth.
Measuring the Success of Business Model Innovation
Successfully launching a new business model requires more than just a good idea; it necessitates a robust framework for measuring its effectiveness. Understanding whether your innovation is achieving its intended goals is crucial for making informed decisions, optimizing performance, and securing future investments. This section Artikels key performance indicators (KPIs) and methods for tracking the impact of business model innovation on key business metrics.
Key Performance Indicators for Evaluating Business Model Innovation Success
A comprehensive evaluation of business model innovation requires a multifaceted approach, tracking several key performance indicators (KPIs) simultaneously. These KPIs should align with the specific objectives of the innovation. For instance, a business model focused on increased customer lifetime value will have different KPIs than one aiming for rapid market penetration.
KPIs for Business Model Innovation
The selection of appropriate KPIs is vital. Focusing on a few critical metrics provides a clearer picture than attempting to track everything. Here are some examples:
- Revenue Growth: This is a fundamental metric, directly reflecting the financial success of the new model. A significant increase in revenue compared to the previous model indicates positive impact.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): A decrease in CAC suggests the new model is more efficient at attracting customers. This is particularly important for models aiming for scalability.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): An increase in CLTV shows the model is successfully fostering long-term customer relationships and generating repeat business. This is crucial for sustainable growth.
- Customer Churn Rate: A decrease in churn indicates higher customer retention, suggesting the model is meeting customer needs effectively.
- Market Share: An increase in market share demonstrates the model’s competitive advantage and its ability to capture a larger portion of the target market.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): This metric gauges customer loyalty and satisfaction, providing insights into the model’s overall effectiveness in creating positive customer experiences.
Tracking and Measuring the Impact on Key Business Metrics
Tracking the impact of a new business model on key metrics requires a well-defined system for data collection and analysis. This typically involves integrating data from various sources, including CRM systems, sales data, marketing analytics, and customer feedback surveys. Regular monitoring and analysis of these metrics allow for timely adjustments to the model based on performance.
Tracking and Measuring Business Model Impact
Effective tracking involves establishing baselines before implementing the new model. This provides a benchmark against which to measure the changes brought about by the innovation. For example, if the goal is to reduce CAC, track the CAC before and after implementing the new model to quantify the improvement. Similarly, for revenue growth, compare the revenue generated before and after the implementation. Continuous monitoring is key, allowing for early identification of issues and opportunities for improvement.
Visual Representation of Business Model Innovation and Improved Financial Performance
Imagine a line graph. The X-axis represents time (months or quarters), and the Y-axis represents revenue. Before the implementation of the new business model (let’s say at month 0), the revenue line shows a relatively flat or slow-growing trend. At month 3, the new business model is launched. The revenue line then shows a clear upward trend, indicating a significant increase in revenue following the implementation. The slope of the line after month 3 is steeper than before, visually demonstrating the positive impact of the business model innovation on financial performance. This visual representation clearly showcases the relationship between the implementation of the new model and the subsequent improvement in revenue. A similar graph could be constructed to visualize changes in other key metrics like CLTV or CAC. For instance, a line graph showing CAC would demonstrate a downward trend post-implementation, highlighting the cost-effectiveness of the new business model.
Case Studies of Business Model Innovation

Examining real-world examples of business model innovation provides valuable insights into successful strategies and the challenges encountered during implementation. These case studies illustrate the diverse approaches companies take to adapt, innovate, and thrive in dynamic markets. By analyzing these examples, we can better understand the key factors contributing to success or failure.
Netflix’s Business Model Innovation
Netflix’s transformation from a DVD-by-mail service to a global streaming giant exemplifies a radical business model innovation. Initially, Netflix disrupted the traditional video rental industry by offering a subscription-based model with unlimited rentals, eliminating late fees and offering convenience. This convenience, coupled with a vast library, proved highly appealing to consumers. The subsequent shift to streaming represented another significant leap, requiring substantial investment in content acquisition and technological infrastructure. This move further disrupted the entertainment industry, challenging traditional television networks and cable providers. While incredibly successful, Netflix faces ongoing challenges including intense competition from other streaming platforms, rising content costs, and the need to constantly adapt to evolving consumer preferences.
The success of Netflix’s business model hinges on its ability to consistently offer a vast, diverse, and high-quality library of content, delivered through a user-friendly and accessible platform.
Comparison of Spotify and Pandora’s Business Models
Spotify and Pandora, both prominent music streaming services, employ distinct business models. Spotify utilizes a freemium model, offering a free, ad-supported tier alongside a premium subscription for ad-free listening and additional features. This model attracts a large user base while generating revenue from both subscriptions and advertising. Pandora, on the other hand, historically relied primarily on a free, ad-supported model with a limited premium offering. This model, while initially successful in establishing a large audience, proved less lucrative compared to Spotify’s dual-tiered approach. Spotify’s success can be attributed to its broader appeal, offering a wider variety of music and features, while Pandora’s relative decline reflects its limitations in revenue generation and its less comprehensive service. The difference highlights the importance of a robust and diversified revenue model in a competitive market.
The Pivot of IBM
IBM’s transformation from a hardware-focused company to a leader in cloud computing and artificial intelligence illustrates a successful business model pivot. Facing declining demand for traditional hardware in the face of increasing competition, IBM strategically invested in developing and expanding its cloud computing and AI capabilities. This shift involved substantial changes in its research and development, sales, and marketing strategies. By focusing on high-value services and solutions, IBM successfully transitioned its business model, securing a prominent position in the rapidly growing cloud and AI markets. This strategic pivot demonstrates the importance of adaptability and foresight in responding to market shifts and emerging technological trends.
Final Wrap-Up

Ultimately, mastering business model innovation is crucial for long-term success in today’s dynamic business environment. By systematically identifying opportunities, designing effective models, and meticulously measuring results, organizations can navigate disruption, create new markets, and achieve sustainable growth. The ability to adapt and evolve business models is no longer a luxury but a necessity for survival and prosperity.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between business model innovation and product innovation?
Product innovation focuses on improving or creating new products or services. Business model innovation focuses on changing how a company creates, delivers, and captures value, often involving changes to the entire business model, not just the product itself.
How can I identify potential areas for business model disruption in my industry?
Analyze unmet customer needs, identify inefficiencies in existing models, examine emerging technologies, and study the competitive landscape to pinpoint opportunities for disruption. Look for areas where you can offer superior value or significantly reduce costs.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when implementing a new business model?
Common pitfalls include insufficient market research, inadequate change management, underestimating resource requirements, and failing to adapt the model based on feedback and results. A phased approach and iterative development can mitigate these risks.



