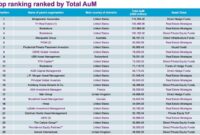
Effectively managing your investments requires diligent tracking and analysis. This review delves into the world of investment tracking tools, exploring their various types, key features, and crucial considerations for individual investors. From simple spreadsheets to sophisticated software, we’ll examine the options available and guide you toward making an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and comfort level with technology.
We’ll navigate the complexities of choosing the right tool, considering factors like cost, ease of use, security features, and integration with other financial platforms. Through illustrative examples and a comparative analysis, we aim to empower you with the knowledge needed to confidently select and utilize an investment tracking tool that optimizes your investment journey.
Introduction to Investment Tracking Tools
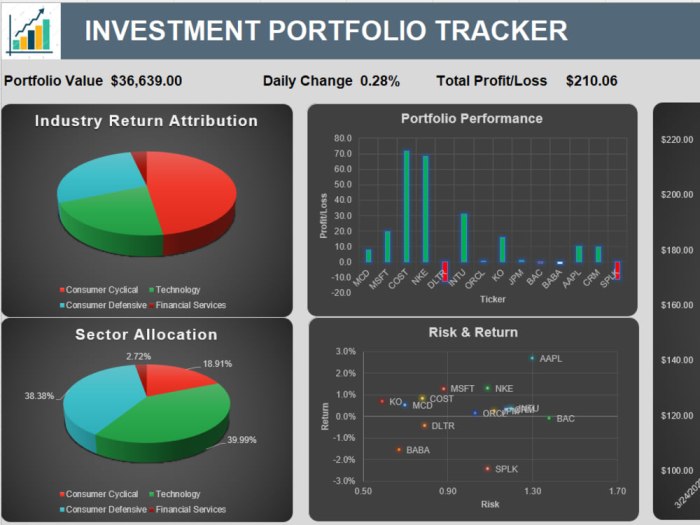
Investing wisely requires careful monitoring of your portfolio’s performance. Investment tracking tools are indispensable for this purpose, providing a structured way to manage and analyze your investments. They range from simple spreadsheets to sophisticated software applications, each offering varying levels of functionality to suit diverse investor needs and technological comfort levels.
Investment tracking tools are essentially software or applications designed to monitor and analyze investment portfolios. They provide a centralized location to record transactions, calculate returns, and visualize portfolio performance over time. This allows investors to make informed decisions based on real-time data and historical trends.
Types of Investment Tracking Tools
Various tools cater to different investment tracking needs. Choosing the right tool depends on factors such as investment complexity, technical proficiency, and budget. Some common options include spreadsheets, dedicated investment tracking software, and mobile applications.
- Spreadsheets (e.g., Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets): These offer a basic, customizable approach, allowing investors to manually input transactions and calculate metrics like returns and portfolio allocation. While simple, they can become cumbersome for larger portfolios or complex investment strategies.
- Dedicated Investment Tracking Software (e.g., Personal Capital, Quicken Premier): These programs provide more advanced features than spreadsheets, often including automatic data imports from brokerage accounts, sophisticated reporting capabilities, and tax optimization tools. They usually come with a subscription fee.
- Mobile Apps (e.g., Mint, Acorns): These offer convenient access to portfolio information on the go. Features may vary, from simple balance tracking to more advanced analytics. Many are free, while others offer premium subscriptions for expanded functionality.
Benefits of Using Investment Tracking Tools for Individual Investors
Utilizing investment tracking tools offers numerous advantages for individual investors seeking to optimize their investment strategies and gain better control over their financial future. These tools empower investors with crucial information and streamline the investment management process.
- Improved Portfolio Oversight: A centralized view of all investments allows for easy monitoring of performance, identifying underperforming assets and opportunities for rebalancing.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Access to real-time data and historical performance analysis enables informed investment decisions, reducing emotional reactions to market fluctuations.
- Simplified Tax Reporting: Many tools automatically generate reports needed for tax preparation, simplifying a time-consuming task.
- Goal Tracking: Several tools allow setting financial goals (e.g., retirement, down payment) and tracking progress toward achieving them.
- Increased Accountability: Regularly reviewing portfolio performance through these tools fosters greater accountability and discipline in investment strategies.
Key Features of Investment Tracking Tools
Choosing the right investment tracking tool can significantly simplify portfolio management and enhance your investment decision-making process. A robust tool goes beyond simple record-keeping; it offers a range of features designed to provide comprehensive insights into your financial health. Understanding these key features and how different tools implement them is crucial for selecting the best fit for your individual needs.
A well-designed investment tracking tool should offer a suite of features to streamline portfolio management and analysis. These features typically include account aggregation, real-time data updates, performance analysis tools, tax reporting capabilities, and customizable dashboards. The specific implementation and sophistication of these features vary across different tools, impacting their overall usability and effectiveness. Some tools excel in specific areas, while others provide a more balanced approach. This comparison will help you identify the essential features and weigh their importance based on your investment strategy and technical proficiency.
Essential Features and Their Importance
The following table summarizes key features commonly found in investment tracking tools, their descriptions, importance ratings, and examples of tools that offer them. Importance is rated as High, Medium, or Low based on their overall impact on portfolio management and analysis.
| Feature Name | Description | Importance Rating | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Account Aggregation | Connects to various brokerage accounts, banks, and retirement accounts to consolidate all investment holdings in one place. | High | Personal Capital, Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget) |
| Real-time Data Updates | Provides up-to-the-minute pricing and valuation information for all assets in your portfolio. | High | Bloomberg Terminal (professional), Yahoo Finance (limited) |
| Performance Tracking & Analysis | Calculates portfolio returns, benchmarks performance against indices, and generates reports on investment gains/losses. | High | Personal Capital, Quicken Premier |
| Tax Reporting | Generates reports summarizing capital gains, dividends, and other tax-relevant information for tax preparation. | High | TaxAct, TurboTax (integration with some investment tools) |
| Customizable Dashboards | Allows users to personalize their view of portfolio data, selecting key metrics and visualizations relevant to their investment goals. | Medium | Many tools offer varying levels of customization. |
| Goal Setting & Planning | Provides tools to set financial goals (retirement, education, etc.) and track progress towards those goals. | Medium | Personal Capital, Betterment |
| Security & Data Encryption | Ensures the security of sensitive financial data through robust encryption and security protocols. | High | Reputable tools typically employ industry-standard security measures. |
| Mobile Accessibility | Offers mobile apps for convenient access to portfolio data and management features on smartphones and tablets. | Medium | Most modern tools offer mobile apps. |
| Customer Support | Provides readily available assistance through various channels (email, phone, chat) to address user questions and technical issues. | Medium | Quality varies significantly between providers. |
Different Types of Investment Tracking Tools
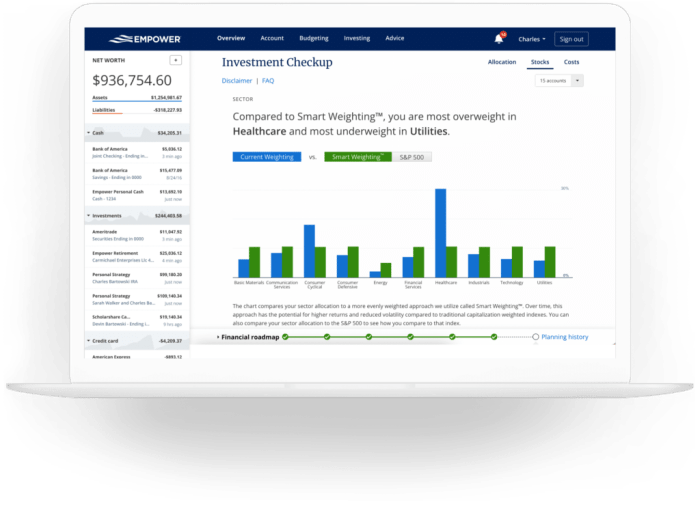
Investment tracking tools come in various forms, each designed to cater to specific needs and investment strategies. Understanding the distinctions between these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate tool to manage your financial portfolio effectively. The choice depends largely on the complexity of your investments, your comfort level with technology, and your specific tracking goals.
Portfolio Trackers
Portfolio trackers provide a centralized view of all your investments, regardless of where they are held. This includes stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, and other assets. They aggregate data from various sources, providing a comprehensive overview of your portfolio’s performance, allocation, and overall value. These tools often offer features like performance charts, asset allocation breakdowns, and personalized reporting.
Advantages of portfolio trackers include consolidated views of your holdings, simplified performance monitoring, and easy identification of areas for improvement in your portfolio diversification. Disadvantages may include the need to manually input data for some accounts if direct integration isn’t available, and potential subscription fees for advanced features.
Use cases for portfolio trackers:
- Monitoring overall portfolio performance and growth.
- Assessing asset allocation and identifying potential imbalances.
- Generating personalized reports for tax purposes or financial planning.
- Tracking the progress towards specific financial goals.
Expense Trackers
Expense trackers focus specifically on monitoring investment-related expenses, such as brokerage fees, transaction costs, and advisory fees. While not directly tracking the value of your investments, they play a vital role in understanding the overall cost of investing and optimizing your returns. Some sophisticated expense trackers can even categorize expenses automatically, making analysis simpler.
The advantage of using an expense tracker is the ability to identify areas where you can reduce investment costs. A disadvantage is that it requires diligent record-keeping to ensure accuracy. Many expense trackers are integrated with bank accounts and credit cards for automated data entry, but manual entry is still often necessary.
Use cases for expense trackers:
- Analyzing the impact of fees on investment returns.
- Identifying opportunities to reduce investment costs.
- Tracking expenses across multiple brokerage accounts.
- Preparing for tax reporting by accurately documenting investment-related expenses.
Investment Tracking Tools with Tax Software Integration
These tools offer a significant advantage by directly integrating with popular tax software applications. This seamless integration streamlines the process of preparing tax returns, particularly for investors with complex portfolios. The tools often automatically generate reports compliant with tax regulations, reducing the risk of errors and simplifying a potentially tedious process.
The primary advantage is the time saved during tax preparation. A disadvantage is that the level of integration can vary, and some tools may not support all tax software programs. The cost of such tools can also be higher than standalone portfolio or expense trackers.
Use cases for investment tracking tools with tax software integration:
- Generating tax reports compliant with relevant regulations.
- Simplifying the tax preparation process for investors with complex portfolios.
- Reducing the risk of errors during tax reporting.
- Streamlining the flow of investment data between tracking tools and tax software.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Investment Tracking Tool
Selecting the right investment tracking tool can significantly improve your investment management experience. The ideal tool will depend on your individual needs and investment strategy. Careful consideration of several key factors will ensure you choose a tool that effectively supports your financial goals. This section Artikels those critical factors and offers guidance on how to evaluate potential tools.
Security and Data Privacy
Security is paramount when choosing an investment tracking tool. Your financial data is highly sensitive, and a breach could have severe consequences. Prioritize tools that employ robust security measures, including encryption both in transit and at rest, two-factor authentication, and regular security audits. Look for tools with transparent privacy policies that clearly Artikel how your data is collected, used, and protected. Consider tools that are compliant with relevant data privacy regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. A reputable company with a proven track record of data security should be your top choice. For example, a tool boasting bank-level encryption and regular penetration testing demonstrates a higher commitment to security than one with only basic password protection.
Ease of Use and User Interface
The tool should be intuitive and easy to navigate, regardless of your technical expertise. A cluttered or confusing interface can quickly become frustrating, especially when dealing with complex financial information. Consider the tool’s overall design, the clarity of its instructions, and the availability of helpful support resources such as tutorials or FAQs. Test the tool’s features yourself – importing data, generating reports, and navigating different sections – to assess its usability. A well-designed tool will streamline your workflow, allowing you to focus on making informed investment decisions rather than wrestling with the software. For instance, a tool with a drag-and-drop interface for portfolio construction and clear, concise reporting dashboards will be significantly easier to use than one with complex menus and confusing terminology.
Features and Functionality
While ease of use is crucial, the tool must also offer the features you need to effectively manage your investments. This includes features like portfolio tracking, transaction recording, performance analysis, tax reporting capabilities, and integration with brokerage accounts. Consider your specific needs and prioritize tools that offer the most relevant features. For example, if you are a long-term investor primarily focused on growth, you might prioritize tools with robust performance analysis and charting capabilities. If you are an active trader, you might need real-time data feeds and advanced charting options. A tool that lacks the essential features for your investment style will ultimately prove less useful, regardless of how user-friendly it is.
Cost and Value
Investment tracking tools vary widely in price, from free options to subscription services with varying levels of functionality. Consider the cost relative to the features offered and the value it provides. A free tool might suffice for simple portfolio tracking, but a more comprehensive tool may be worth the cost if you need advanced features or detailed reporting. Carefully compare the pricing plans of different tools, considering what features are included in each tier. Evaluate whether the premium features justify the higher cost based on your investment needs and the frequency of your usage. For instance, a tool charging a yearly subscription of $50 with comprehensive features might be more cost-effective than a free tool that requires significant manual data entry and lacks advanced analysis capabilities.
Data Import and Integration
Efficient data management is critical. Evaluate how easily the tool can import data from your brokerage accounts and other financial institutions. Seamless integration saves time and reduces the risk of errors. Consider whether the tool supports automatic data imports or requires manual entry. Automatic imports are generally preferable as they eliminate the potential for human error and ensure your data is always up-to-date. Tools offering direct connections to major brokerage platforms or support for various file formats (CSV, OFX, etc.) will significantly improve your data management efficiency. For example, a tool that automatically downloads your transactions from your brokerage account daily is far more efficient than one requiring you to manually upload transaction data from your bank statements.
Illustrative Examples of Investment Tracking Tools
This section details three distinct investment tracking tools, highlighting their functionalities, user interfaces, and target audiences. Each example includes a hypothetical user scenario to illustrate practical application. A comparative analysis then follows, focusing on key features discussed previously.
Tool A: The Comprehensive Portfolio Manager
This tool offers a robust feature set designed for experienced investors with diverse portfolios. Its interface is sophisticated, incorporating customizable dashboards, advanced charting capabilities, and in-depth performance analysis tools. The user experience prioritizes data visualization and detailed reporting, making it ideal for users who require granular control and a high level of customization. It caters to users who actively manage a significant number of investments across various asset classes.
A hypothetical user, Sarah, a seasoned investor with holdings in stocks, bonds, real estate, and cryptocurrencies, utilizes Tool A to track her entire portfolio. She leverages its advanced charting tools to analyze historical performance and identify trends, utilizes the custom dashboard to monitor key metrics like portfolio diversification and risk exposure, and generates detailed reports for tax purposes. The tool’s robust reporting features allow her to easily monitor the performance of individual investments and the overall portfolio.
Tool B: The Beginner-Friendly Investment Tracker
Tool B is designed for novice investors and those seeking a straightforward, user-friendly experience. Its interface is clean and intuitive, prioritizing simplicity and ease of use. The core functionalities focus on basic portfolio tracking, transaction recording, and performance summaries. While lacking the advanced features of more sophisticated tools, it offers a gentle introduction to investment tracking for those new to the process. This tool’s target user is someone just starting to invest and wants a simple way to monitor their progress.
Imagine John, a recent college graduate who has started investing in a few ETFs. He uses Tool B to record his initial investments and track their growth over time. The simple interface allows him to easily input transactions and view his portfolio’s overall performance with clear, concise summaries. The lack of overwhelming features makes it easy for him to understand his investment progress without being intimidated by complex data.
Tool C: The Specialized Real Estate Investment Tracker
Tool C caters specifically to real estate investors. Its interface is tailored to the nuances of real estate investment, incorporating features like property valuation tools, rental income tracking, and expense management capabilities. It provides specialized reporting focused on metrics relevant to real estate, such as capitalization rates and cash-on-cash returns. The target user base consists of individuals and companies focused on real estate investments.
Consider David, a real estate investor with multiple rental properties. He uses Tool C to track the income and expenses associated with each property, calculate rental yields, and project future cash flows. The tool’s specialized features, such as built-in depreciation calculators and property valuation tools, enable him to efficiently manage his portfolio and make informed investment decisions. The streamlined interface for real estate-specific data makes his investment management significantly easier.
Comparative Analysis of the Three Tools
The following table summarizes a comparison of the three tools based on key features previously discussed:
| Feature | Tool A | Tool B | Tool C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Functionality | Extensive | Basic | Specialized (Real Estate) |
| Reporting Capabilities | Advanced | Basic | Specialized (Real Estate Metrics) |
| Target User | Experienced Investors | Beginner Investors | Real Estate Investors |
| Cost | High | Low | Moderate |
Security and Privacy Considerations
Using investment tracking tools necessitates entrusting sensitive financial data to third-party platforms. This introduces several security and privacy risks that users must understand and mitigate to protect their assets and personal information. Failing to adequately address these concerns can lead to significant financial losses or identity theft.
Understanding and implementing best practices for securing your financial data within these platforms is crucial. This involves careful selection of tools, proactive monitoring, and adherence to strong security protocols. Reputable investment tracking tools prioritize user security and incorporate robust measures to protect against various threats.
Data Encryption and Transmission
Protecting data both at rest and in transit is paramount. Reputable investment tracking tools employ robust encryption methods, such as AES-256, to safeguard sensitive information stored on their servers. Furthermore, data transmitted between the user’s device and the tool’s servers should be encrypted using protocols like HTTPS to prevent interception by malicious actors. The absence of these security measures significantly increases the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Access Controls and Authentication
Strong authentication mechanisms are essential to prevent unauthorized access to user accounts. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide multiple forms of verification (e.g., password, one-time code from a mobile app), should be a standard feature. Additionally, robust password policies, including minimum length requirements and complexity rules, should be enforced. Regular password changes and the avoidance of reusing passwords across multiple platforms are also crucial. Account lockout mechanisms after multiple failed login attempts further enhance security.
Security Audits and Compliance
Regular security audits and penetration testing by independent security firms are vital for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities. Compliance with relevant security standards and regulations, such as SOC 2 (System and Organization Controls 2), demonstrates a commitment to data security. These certifications provide assurance that the tool provider has implemented appropriate security controls and regularly assesses its security posture. Transparency regarding these audits and compliance certifications builds trust and reassures users about the platform’s commitment to data protection.
Data Backup and Recovery
The tool should offer robust data backup and recovery mechanisms to protect against data loss due to technical failures or cyberattacks. Regular backups should be performed and stored securely, ideally in geographically separate locations. A clear and well-documented recovery process should be in place to ensure users can quickly restore their data in case of an incident. The provider’s commitment to data recovery demonstrates a proactive approach to minimizing the impact of potential disruptions.
Integration with Other Financial Tools
The ability of an investment tracking tool to seamlessly integrate with other financial platforms is a crucial factor determining its overall utility and user-friendliness. Effective integration streamlines the investment management process, minimizing manual data entry and enhancing the accuracy and comprehensiveness of your financial overview. This interconnectedness fosters a more efficient and informed investment strategy.
Integration with other financial tools, such as brokerage accounts, banking apps, and tax software, significantly reduces the effort required to manage investments. The benefits include automated data updates, eliminating the need for manual data entry which is prone to errors. Challenges can arise from differing data formats and security protocols between different platforms, requiring careful consideration of compatibility and data security. However, the advantages of streamlined data management typically outweigh these hurdles.
Benefits of Integration
Seamless integration offers several key advantages. Automated data synchronization between your investment tracker and brokerage accounts ensures your portfolio valuations are always up-to-date. This real-time data allows for informed decision-making based on current market conditions. Furthermore, integration with banking apps can provide a holistic view of your financial situation, allowing you to track your investments alongside your cash flow and expenses. This comprehensive perspective facilitates better financial planning and budgeting. Finally, linking to tax software can simplify tax preparation by automatically importing relevant investment data.
Examples of Seamless Integration Features
Several investment tracking tools offer sophisticated integration capabilities. For instance, some tools directly connect to popular brokerage platforms like Fidelity, Schwab, and Vanguard, automatically downloading transaction history, account balances, and asset holdings. This eliminates the tedious process of manually inputting data. Other tools offer open APIs, allowing for custom connections to a wider range of financial institutions. This flexibility allows users to integrate with niche platforms or services not directly supported by the tool itself. A well-designed interface might display a consolidated view of all linked accounts, providing a single dashboard for managing all aspects of one’s finances. This consolidated view reduces the need to switch between multiple applications.
Challenges of Integration
While the benefits of integration are significant, challenges exist. Data security and privacy are paramount concerns. Integrating with multiple platforms necessitates robust security measures to protect sensitive financial information. Differences in data formats and API standards between various financial institutions can pose technical hurdles for developers. Ensuring consistent and accurate data transfer across platforms requires sophisticated data mapping and validation processes. Furthermore, some financial institutions may have limitations or restrictions on the type of data that can be accessed via APIs, potentially limiting the functionality of the integration. For example, a brokerage account might not allow the automated download of certain types of transaction details.
Final Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the selection of an investment tracking tool is a personal one, dependent on individual needs and preferences. However, by carefully considering the factors Artikeld in this review – including functionality, security, ease of use, and integration capabilities – investors can significantly enhance their ability to monitor, analyze, and ultimately, improve their investment performance. Remember, the right tool can empower you to make more informed decisions, leading to greater financial success.
FAQ Compilation
What is the best investment tracking tool for beginners?
The “best” tool depends on individual needs, but user-friendly options with intuitive interfaces and good customer support are ideal for beginners. Look for tools with clear tutorials and readily available help.
Are investment tracking tools secure?
Reputable tools employ robust security measures like encryption and two-factor authentication. However, it’s crucial to choose established providers with strong security reputations and to follow best practices for online security.
How much do investment tracking tools cost?
Costs vary widely, from free basic tools to subscription-based services with advanced features. Consider your needs and budget when making a selection.
Can I import data from my brokerage account?
Many tools offer direct import functionality from various brokerage accounts, simplifying the data entry process. Check for compatibility with your specific brokerage before choosing a tool.