Sample Market Research Report: Unlocking the secrets of successful market analysis! This guide delves into the fascinating world of market research, revealing the intricate process of crafting compelling reports that drive informed business decisions. From defining the scope and selecting appropriate methodologies to presenting findings with impactful visuals and interpreting the results, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of market research with confidence and a touch of humor. Prepare to be amazed by the power of data!
We’ll explore various report types, from the quantitative precision of surveys to the qualitative richness of focus groups, showcasing how each contributes to a holistic understanding of your target market. We’ll uncover the secrets of effective data collection, analysis, and presentation, demonstrating how to transform raw data into compelling narratives that resonate with stakeholders. Get ready to become a market research maestro!
Defining the Scope of a Sample Market Research Report
So, you’re diving into the wonderfully weird world of market research reports? Buckle up, because it’s a journey filled with data, insights, and the occasional existential crisis about the true meaning of consumer behavior. Let’s navigate this fascinating landscape together.
A sample market research report, much like a well-trained puppy, needs structure and purpose. It’s not just a random collection of charts and graphs; it’s a carefully crafted narrative that aims to answer specific questions about a market. Think of it as a detective story, where the market is the crime scene and your report is the meticulously detailed case file.
Typical Components of a Market Research Report
A typical market research report, regardless of size or scope, usually includes an executive summary (the tl;dr version), methodology (how the data was gathered – think of it as the detective’s detailed account of their investigation), findings (the juicy evidence), analysis (interpreting the evidence), and conclusions and recommendations (the verdict!). Oh, and let’s not forget the inevitable appendix, where all the supporting data hides – like a secret stash of clues.
Differences Between Quantitative and Qualitative Market Research Reports
Quantitative research is all about numbers – hard data, surveys, and statistical analysis. It’s like counting the number of paw prints left at the crime scene. Qualitative research, on the other hand, delves into the “why” behind the numbers. It’s the detective interviewing witnesses and trying to understand the motivations of the culprit. Quantitative reports often present data in charts and graphs, while qualitative reports might focus on in-depth interviews or focus groups, providing rich, nuanced insights into consumer opinions and experiences.
Importance of a Clearly Defined Target Audience
Defining your target audience is paramount. Without a clear understanding of who you’re talking to, your report is like a poorly aimed dart – it might hit the board, but it certainly won’t hit the bullseye. A well-defined target audience allows you to tailor your research questions, data collection methods, and report findings to be relevant and insightful for the intended recipients. It’s like knowing exactly who the suspect is before you start your investigation.
Examples of Industries Using Sample Market Research Reports
Sample market research reports are used across a vast range of industries. From the whimsical world of pet food to the serious business of pharmaceuticals, understanding market trends and consumer preferences is crucial for success. Below is a table showcasing a few examples, although the real world is far more complex and exciting (and maybe a little less predictable).
| Industry | Report Type | Target Audience | Key Findings (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pet Food | Quantitative | Pet Food Manufacturers | Increased demand for organic and grain-free options. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Qualitative | Drug Development Teams | Patient satisfaction with a new drug delivery system. |
| Technology | Quantitative & Qualitative | Marketing and Product Development Teams | Consumer preference for specific features in a new smartphone. |
| Cosmetics | Qualitative | Product Managers | Consumer feedback on the texture and scent of a new moisturizer. |
Data Collection and Methodology in Sample Reports: Sample Market Research Report
Gathering data for market research is like a thrilling treasure hunt, except the treasure is insightful consumer behavior, not buried gold. This section details the methods employed to unearth those valuable nuggets of information, ensuring our sample reports are as robust and reliable as a well-built pirate ship (though hopefully less prone to scurvy).
The process of data collection hinges on two primary pillars: primary data collection and secondary data collection. Think of primary data as freshly baked bread – warm, delicious, and specifically made to your order. Secondary data, on the other hand, is more like a well-stocked bakery – offering a wide variety of pre-made options, some of which might be exactly what you need.
Primary Data Collection Methods
Primary data collection involves gathering information directly from the source – your target audience. This ensures the data is relevant and tailored to your specific research questions. Several tried-and-true methods exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right method depends heavily on the research objectives and available resources (and, let’s be honest, the budget).
- Surveys: These are like sending out a carefully crafted questionnaire to a wide audience, allowing for efficient data collection from a large sample size. The downside? Response rates can be unpredictable, and poorly designed surveys can yield biased or inaccurate results. Think of it like fishing with a net – you catch a lot, but some might slip through, and some might not be what you were hoping for.
- Interviews: One-on-one conversations allow for deeper insights and the ability to probe respondents for more detailed answers. However, this method is time-consuming and expensive, limiting the sample size. It’s like fly-fishing – precise and rewarding, but requires patience and skill.
- Focus Groups: These group discussions provide a platform for observing group dynamics and gaining qualitative insights. The challenge lies in managing group dynamics and ensuring all participants feel comfortable contributing. Think of it as a lively town hall meeting – potentially chaotic, but potentially very revealing.
Secondary Data Collection and Reputable Sources
Secondary data collection involves utilizing existing data that has already been collected by others. This is a cost-effective way to supplement primary data and provide a broader context for your findings. However, it’s crucial to evaluate the credibility and reliability of your sources.
Reputable sources for secondary data include government agencies (like the U.S. Census Bureau or Eurostat), academic databases (like JSTOR or Scopus), industry reports (from firms like Nielsen or Statista), and reputable market research companies. Always check the methodology and data collection techniques employed by the original researchers to assess the quality of the information.
Sampling Techniques and Their Impact on Report Reliability
Sampling techniques are crucial for ensuring the representativeness of your research findings. A poorly chosen sample can lead to biased and unreliable conclusions. Imagine trying to understand the entire ocean by only examining a single drop of water – it’s simply not going to work.
Different sampling methods exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Probability sampling (like simple random sampling or stratified sampling) ensures every member of the population has a known chance of being selected, leading to more generalizable results. Non-probability sampling (like convenience sampling or snowball sampling) is easier and cheaper but may not be representative of the entire population. The choice of sampling technique significantly impacts the reliability and generalizability of your findings.
Data Analysis Methods in Sample Reports
Once the data is collected, the real fun begins – analyzing it to extract meaningful insights. A variety of methods can be used, depending on the type of data and the research questions.
- Descriptive Statistics: These methods summarize and describe the main features of the data, such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. Think of it as creating a detailed map of your data landscape.
- Inferential Statistics: These methods use sample data to make inferences about the population. This involves hypothesis testing and confidence intervals, allowing researchers to draw conclusions beyond the immediate sample. It’s like using a small piece of the puzzle to deduce the entire picture.
- Regression Analysis: This statistical method explores the relationship between variables, allowing researchers to identify predictors of outcomes. For example, understanding the relationship between advertising spending and sales.
- Qualitative Data Analysis: This involves analyzing non-numerical data, such as interview transcripts or focus group discussions, to identify themes and patterns. This often involves coding and thematic analysis, allowing researchers to uncover nuanced insights.
Presentation of Findings in Sample Reports
Presenting your market research findings is akin to unveiling a delicious cake – you’ve put in the hard work, now it’s time to showcase the masterpiece! A well-presented report not only conveys your data but also leaves a lasting impression on your audience, making them clamor for more (more insights, that is!). Remember, clarity and visual appeal are your secret ingredients.
Visualizing data effectively is crucial for conveying complex information in a digestible format. Charts and graphs aren’t just pretty pictures; they’re powerful tools that transform raw data into compelling narratives. Think of them as the sprinkles and frosting on your research cake!
Chart and Graph Examples, Sample market research report
The following examples illustrate how different chart types can effectively present various aspects of market research data. We’ll avoid overly technical jargon and instead focus on the storytelling potential of each visualization.
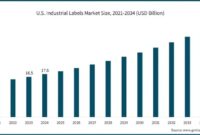
A bar chart, for instance, is perfect for comparing the market share of different competing brands. Imagine a bar chart showing the market dominance of Brand A (a towering 45%), followed by Brand B (a respectable 30%), and Brand C (a slightly less impressive 15%). The remaining 10% could be represented as “Other,” clearly indicating the competitive landscape. This visual immediately communicates the relative success of each brand without overwhelming the reader with numerical data.
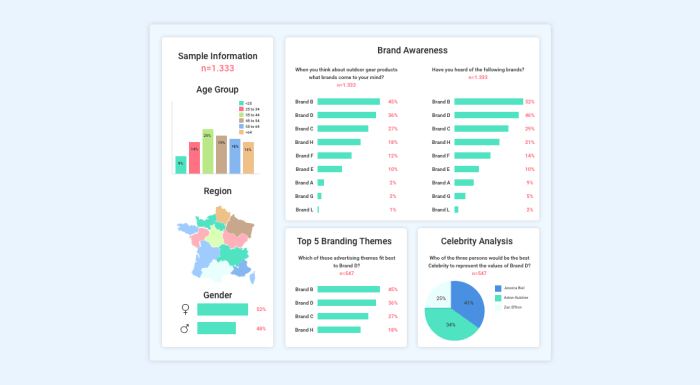
Next, a pie chart excels at showcasing proportions. Let’s say we’re analyzing consumer demographics. A pie chart could beautifully illustrate the age distribution of our target market, clearly dividing the segments into 18-25, 26-35, 36-45, and 45+. The size of each slice instantly reveals the dominant age group within the consumer base. It’s visually appealing and readily understandable.
For showcasing trends over time, a line graph is indispensable. Consider tracking website traffic over a six-month period. A line graph would eloquently depict the fluctuations in traffic, highlighting peak seasons and potential dips. This visual representation would make it easy to identify trends and inform strategic marketing decisions.
Finally, a scatter plot can reveal correlations between two variables. For example, a scatter plot could show the relationship between advertising spend and sales revenue. Clustering of points would suggest a positive correlation, while a dispersed pattern might indicate a weaker relationship. This allows for deeper insights into the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Narrative Flow of Key Findings
Organizing your findings into a coherent narrative is paramount. Think of it as crafting a compelling story around your data. Begin with a summary of your key findings, then delve into the details, supporting each claim with evidence from your charts and graphs. Maintain a logical flow, ensuring a smooth transition between sections. Don’t overwhelm the reader with excessive detail; focus on the most impactful results. For example, you might start by stating the overall market size, then move on to discussing key segments, and finally, conclude with predictions for future growth.
Limitations and Potential Biases
No research is perfect! Acknowledging limitations and potential biases is not only ethical but also enhances the credibility of your report. It demonstrates intellectual honesty and encourages critical thinking. For example, you might mention a small sample size that could limit the generalizability of your findings, or acknowledge potential response bias due to the survey method used. Transparency is key.
Implications for Business Decisions
This section translates your findings into actionable recommendations. This is where your research truly shines, demonstrating its practical value. Consider focusing on the most impactful insights and their implications for business strategy. For example, if your research reveals a growing demand for a particular product, you might recommend expanding production or launching a targeted marketing campaign.
We strongly recommend investing in a targeted marketing campaign focusing on the 18-25 age demographic, given their significant market share and high engagement with our product. This campaign should leverage social media platforms popular with this group.
Report Structure and Formatting
Crafting a market research report is akin to building a delicious cake: you need the right ingredients (data), the perfect recipe (methodology), and a stunning presentation (formatting) to ensure it’s both informative and utterly irresistible to your audience. A well-structured report guides the reader effortlessly through your findings, preventing them from getting lost in a sea of data – a fate worse than a stale cupcake.
The structure of a professional market research report follows a logical progression, ensuring that your key insights are highlighted effectively. A haphazard approach, on the other hand, is about as appealing as a chocolate cake made with sawdust.
Typical Report Sections
A typical market research report includes several key sections, each serving a specific purpose. Think of these sections as the different layers of a magnificent mille-feuille – each layer contributes to the overall deliciousness. The omission of any layer would be a culinary crime! These sections are essential for clear communication and a professional presentation.
- Executive Summary: This is the amuse-bouche of your report – a concise overview of the key findings, conclusions, and recommendations. It’s the first (and sometimes only) part many readers will see, so make it count! Think of it as the tantalizing preview of a blockbuster movie.
- Introduction: This section sets the stage, providing background information on the research topic and outlining the report’s objectives. It’s like the appetizer – it whets the reader’s appetite for the main course.
- Methodology: This section details the research design, data collection methods, and sample characteristics. Transparency is key here – you’re inviting your readers into your kitchen to see how the magic happens. Think of it as a detailed recipe.
- Findings: This is the main course – the heart of your report, presenting the data collected and analyzed. Clear, concise presentation is vital here, ensuring that your readers can easily digest the information.
- Conclusions: This section interprets the findings and draws meaningful conclusions. It’s the palate cleanser – it helps the reader to process and reflect on the main course.
- Recommendations: This section offers actionable suggestions based on the research findings. This is the dessert – a sweet ending that leaves a lasting impression.
- Appendices (Optional): This section contains supplementary materials, such as detailed tables, questionnaires, or raw data. Think of it as the extra ingredients – useful for those who want to delve deeper.
Importance of Clear and Concise Writing
Clarity and conciseness are paramount in a market research report. Rambling prose is the culinary equivalent of a soggy bottom – nobody wants it. Use precise language, avoid jargon, and structure your sentences for easy comprehension. Every word should serve a purpose; extraneous words are like unwanted guests at a dinner party.
Effective Visual Aids
Visual aids are powerful tools for enhancing comprehension and engagement. They transform complex data into easily digestible information. Think of them as the garnishes on your cake – they add visual appeal and enhance the overall experience.
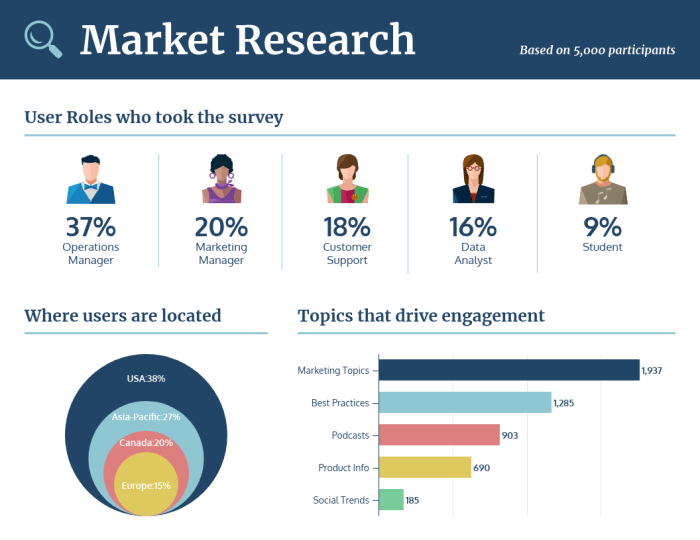
- Charts and Graphs: Bar charts effectively compare categories, while pie charts illustrate proportions. Line graphs showcase trends over time. For example, a line graph could display sales figures over a year, clearly showing growth or decline.
- Tables: Tables are excellent for presenting detailed numerical data in an organized manner. For instance, a table could compare the market share of different competing brands.
- Images and Photographs: Relevant images can add visual interest and help illustrate key concepts. For example, a photograph of a product could be used to illustrate a point about its design or appeal.
Formatting Conventions and Best Practices
Consistency is key to a professional report. Use a consistent font, font size, and spacing throughout. Headings and subheadings should be clearly defined, and the use of bullet points and numbered lists improves readability. Imagine a perfectly iced cake – the smooth, consistent frosting is the equivalent of consistent formatting. Using a professional template can ensure a consistent and polished look. Furthermore, incorporating page numbers and a table of contents allows for easy navigation. Finally, proofreading and editing are crucial for eliminating errors and ensuring a polished final product.
Interpreting and Applying Findings from Sample Reports
So, you’ve wrestled with the data, charted the trends, and now you’re staring at a mountain of information. Don’t panic! Interpreting market research findings isn’t about decoding ancient hieroglyphs (though it can feel that way sometimes). It’s about using common sense, a dash of statistical savvy, and a healthy dose of skepticism to uncover the gold nuggets hidden within your report. Let’s transform those numbers into actionable insights.
The key to successfully interpreting sample market research reports lies in understanding the context of the data. This means carefully considering the methodology employed, the sample size, and the limitations of the study. Remember, a perfectly executed study is a unicorn – a mythical beast rarely encountered in the real world. Understanding the imperfections allows for more nuanced interpretation and prevents drawing wildly inaccurate conclusions.
Identifying Key Trends and Patterns
Identifying trends and patterns requires a keen eye and a systematic approach. Start by examining the data visually. Charts and graphs are your best friends here. Look for significant increases or decreases in key metrics, correlations between variables, and any outliers that might suggest a hidden story. For instance, a significant drop in customer satisfaction scores correlated with the launch of a new product line might indicate a problem with that product. Don’t just look at individual data points in isolation; consider the bigger picture and the relationships between different aspects of the data.
Implications of Different Data Points on Business Strategy
Different data points have varying implications for business strategy. A high customer churn rate, for example, suggests a need to improve customer retention strategies, perhaps through loyalty programs or enhanced customer service. Conversely, strong brand awareness but low conversion rates might indicate a problem with the sales funnel or pricing strategy. Each data point offers a clue, and piecing these clues together paints a more complete picture of your market position and your opportunities. Analyzing these implications requires strategic thinking and an understanding of your business goals.
Using Findings to Inform Marketing Decisions
Market research is not just an academic exercise; it’s a tool for making informed marketing decisions. The insights gained from your report should directly influence your marketing strategy. For instance, if your research reveals a strong preference for a particular product feature, you can tailor your marketing messaging to highlight that feature. Similarly, if your research identifies a new target audience, you can adjust your marketing channels and messaging to reach that audience effectively. Essentially, your research should guide your marketing efforts, ensuring that you’re targeting the right people with the right message at the right time.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Strategic Decision Based on Market Research
Let’s imagine “Floofy Friends,” a company selling plush toys, conducted market research and discovered a significant unmet need for eco-friendly plush toys made from recycled materials. Their sample report showed a strong preference for sustainable products among their target demographic (parents of young children). Based on these findings, Floofy Friends decided to invest in developing a new line of eco-friendly plush toys. This strategic decision, directly informed by their market research, allowed them to tap into a growing market segment and gain a competitive advantage. This new line of toys not only boosted their sales but also enhanced their brand image as an environmentally conscious company. The success of this new product line was directly attributable to the insights gained from the market research report, demonstrating the importance of using data-driven decision-making in a competitive marketplace.
Last Point

In conclusion, crafting a compelling sample market research report is a journey of discovery, a blend of meticulous methodology and creative storytelling. By mastering the art of data collection, analysis, and presentation, you can unlock valuable insights that inform strategic business decisions. Remember, a well-crafted report isn’t just a document; it’s a powerful tool that can transform your understanding of the market and propel your business towards success. So go forth, armed with knowledge and a healthy dose of wit, and conquer the world of market research!
Top FAQs
What’s the difference between primary and secondary data?
Primary data is collected directly from sources (surveys, interviews), while secondary data uses existing information (industry reports, publications).
How long does it typically take to create a market research report?
The timeline varies greatly depending on the scope, but expect anywhere from a few weeks to several months for comprehensive reports.
What software is best for creating market research reports?
Many options exist, from Microsoft Word and Excel to specialized statistical software like SPSS and dedicated report-writing tools.
Are there free sample market research reports available online?
While finding complete, high-quality free reports is challenging, snippets and examples of sections are readily available online for educational purposes.