Mastering personal finances can feel daunting, but effective budgeting is key to achieving financial freedom. Fortunately, a plethora of budgeting apps exist, each offering unique features and approaches to help manage your money. This comparison explores the best budgeting apps, examining their core functionalities, security measures, integration capabilities, user experiences, and cost-effectiveness to help you choose the perfect tool for your financial journey.
From zero-based budgeting to envelope systems, these apps cater to diverse budgeting styles. We’ll delve into the specifics of popular choices, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to equip you with the knowledge needed to make an informed decision. This guide aims to demystify the world of budgeting apps, empowering you to take control of your finances with confidence.
Introduction to Budgeting Apps
Budgeting apps have revolutionized personal finance management, offering a convenient and accessible way to track income, expenses, and savings goals. These apps provide a centralized platform to monitor financial health, offering insights and tools to improve financial well-being. They are designed to simplify the often-complex process of budgeting, making it manageable for individuals of all financial literacy levels.
Budgeting apps offer numerous benefits for personal finance management. They provide a clear picture of spending habits, allowing users to identify areas where they can cut back. Features like automated transaction categorization and visual representations of spending patterns make it easier to understand where money is going. Many apps also offer goal-setting tools, helping users track progress towards financial objectives such as saving for a down payment or paying off debt. The convenience of accessing financial information anytime, anywhere, contributes significantly to consistent budgeting and financial awareness. Furthermore, some apps offer features like bill reminders and debt tracking tools, enhancing overall financial organization.
Budgeting Methods Supported by Budgeting Apps
Various budgeting apps support different budgeting methods, catering to diverse financial styles and preferences. Understanding these methods is crucial for selecting an app that aligns with individual needs and financial goals. Popular methods include zero-based budgeting and the envelope system, each offering a unique approach to managing finances.
Zero-based budgeting involves allocating every dollar of income to a specific expense category or savings goal, ensuring that all income is accounted for. This method often leads to a more conscious approach to spending, promoting financial discipline. For example, an individual using a zero-based budgeting app might allocate specific amounts to housing, groceries, transportation, entertainment, and savings. Any remaining funds are then directed towards debt repayment or additional savings.
The envelope system, a more traditional method, involves dividing cash into different envelopes, each representing a specific expense category. While not all budgeting apps directly replicate the physical envelope system, many incorporate the concept by allowing users to digitally allocate funds to specific categories. This approach can help visualize spending limits and avoid overspending in particular areas. For example, someone using an app that mirrors the envelope system might allocate a certain amount to groceries, entertainment, and gas, digitally tracking spending within those predetermined limits.
Key Features Comparison

Choosing the right budgeting app depends heavily on individual needs and preferences. This section compares the core features of five popular budgeting apps, considering pricing, user interface, and unique functionalities to help you make an informed decision. We’ll explore how each app caters to both novice and experienced budgeters.
Budget App Feature Comparison
The following table summarizes key features, pricing, and user interface ratings (1-5 stars) for five popular budgeting apps: Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget), Personal Capital, EveryDollar, and PocketGuard. These ratings are based on general user feedback and reviews. Individual experiences may vary.
| App Name | Key Features | Pricing Model | User Interface Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mint | Account aggregation, spending tracking, budgeting tools, bill payment reminders, credit score monitoring. | Free (with ads) | 4 |
| YNAB (You Need A Budget) | Zero-based budgeting, goal setting, debt tracking, detailed reporting, strong community support. | Subscription-based | 3.5 |
| Personal Capital | Comprehensive financial planning tools, investment tracking, retirement planning, net worth tracking. | Free (with premium features available) | 4.5 |
| EveryDollar | Envelope budgeting system, detailed expense tracking, debt reduction tools, guided budgeting tutorials. | Free (with premium features available) | 4 |
| PocketGuard | Spending tracking, budgeting based on available funds, automatic savings suggestions, debt payoff tools. | Free (with premium features available) | 3.5 |
App-Specific Functionalities and Unique Selling Points
Each app offers a unique approach to budgeting. Mint excels at its ease of use and comprehensive account aggregation, making it ideal for beginners. YNAB’s zero-based budgeting method, while requiring more initial setup, is highly effective for those seeking more control over their finances. Personal Capital stands out with its robust investment tracking and financial planning features, making it attractive to users with more complex financial needs. EveryDollar’s simple envelope budgeting system appeals to users who prefer a visual and structured approach. PocketGuard’s focus on remaining funds and automatic savings suggestions is particularly beneficial for those who want to prioritize saving.
Ease of Use and User Experience
For beginners, Mint and EveryDollar provide intuitive interfaces and straightforward budgeting tools. Their simpler setups and guided tutorials make them accessible for those new to budgeting. Experienced budgeters might find YNAB’s more advanced features and customizable options more appealing, allowing for greater control and personalized financial management. Personal Capital’s comprehensive features cater to users with more advanced financial knowledge and goals. PocketGuard’s simplicity and focus on readily available funds can be beneficial for all user experience levels.
Security and Privacy Considerations

Choosing a budgeting app involves entrusting your financial data to a third-party service. Therefore, understanding the security and privacy measures implemented by each app is crucial. This section compares the security features and privacy practices of several popular budgeting apps, highlighting key differences to help you make an informed decision.
Protecting your financial information requires a multi-layered approach. Different apps employ various techniques, from robust encryption to stringent authentication protocols and transparent privacy policies. Analyzing these elements allows for a comprehensive assessment of each app’s commitment to user security.
Data Encryption Methods
Many budgeting apps utilize encryption to protect your data both in transit and at rest. This means your data is scrambled during transmission between your device and the app’s servers, and it remains encrypted while stored on their servers. The strength of the encryption varies, however. Some apps might use AES-256 encryption, considered a highly secure standard, while others may use less robust methods. Knowing the specific encryption algorithm used by each app is important for evaluating its security. For example, Mint uses industry-standard encryption protocols to protect user data, while Personal Capital employs robust security measures including encryption and secure data centers. A detailed comparison of encryption methods would need to be sourced directly from each app’s security documentation or through independent security audits.
User Authentication and Access Controls
Strong user authentication is another critical aspect of security. This typically involves password protection, often supplemented by multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a one-time code sent to your phone or email, in addition to your password. The availability and types of MFA options differ between apps. Some apps may offer biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition), while others might rely solely on password-based logins. A robust password policy, including minimum length and complexity requirements, also plays a significant role in preventing unauthorized access.
Privacy Policies and Data Handling
Each budgeting app has a privacy policy outlining how it collects, uses, and shares your data. It’s essential to review these policies carefully to understand what information is collected, with whom it might be shared (e.g., third-party advertising partners or financial institutions), and what controls you have over your data. Some apps may be more transparent about their data practices than others. Look for apps with clear and concise privacy policies that are easily accessible and understandable. Pay close attention to sections regarding data retention, data breaches, and user rights regarding data access, correction, and deletion.
Comparative Table of Security Features and Privacy Practices
| App Name | Data Encryption | User Authentication | Privacy Policy Transparency | Data Sharing Practices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mint | Industry-standard encryption (details not publicly specified) | Password, potentially MFA (details vary by device and setup) | Detailed, readily accessible | Shares data with Intuit family of products; details Artikeld in privacy policy |
| Personal Capital | Robust security measures including encryption (specific details not publicly specified) | Password, MFA options available | Detailed, readily accessible | Data sharing practices Artikeld in privacy policy |
| YNAB (You Need A Budget) | Encryption used (specific details not publicly specified) | Password, MFA options available | Detailed, readily accessible | Data sharing practices Artikeld in privacy policy |
| EveryDollar | Encryption used (specific details not publicly specified) | Password | Detailed, readily accessible | Data sharing practices Artikeld in privacy policy |
Integration with Other Financial Tools
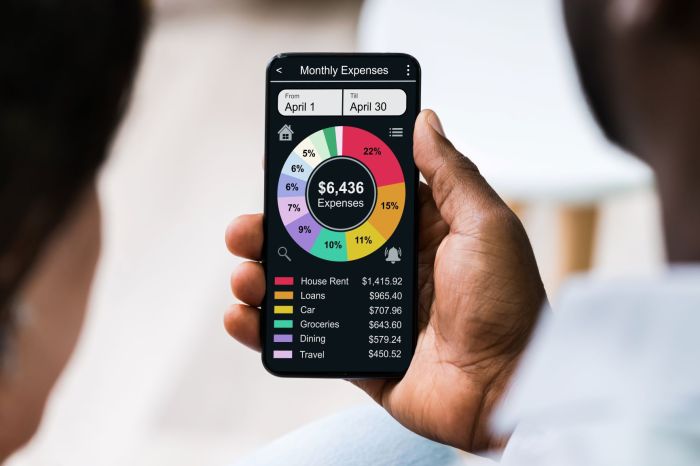

Seamless integration with other financial tools is a crucial feature for any budgeting app. The ability to connect your bank accounts, credit cards, and investment accounts allows for a comprehensive overview of your finances, simplifying the budgeting process and providing a more accurate picture of your financial health. The level of integration varies significantly between apps, impacting both convenience and the accuracy of your budget.
The convenience of automated transaction importing is undeniable. It saves users significant time and effort, eliminating the need for manual data entry. However, this automation also presents potential drawbacks, including the risk of inaccurate data import due to miscategorization or errors in the source data. Regular review and reconciliation of imported transactions are essential to maintain accuracy.
Automated Transaction Importing: Benefits and Drawbacks
Automated transaction importing offers considerable benefits, primarily time savings and reduced manual effort. Users can focus on analyzing their finances rather than spending time inputting data. This automation also contributes to a more complete and up-to-date financial picture, enabling better budgeting decisions. However, reliance on automated imports can lead to inaccuracies if the app miscategorizes transactions or if the source data from the financial institution contains errors. This highlights the need for users to regularly review and correct any discrepancies. For example, if an app consistently miscategorizes restaurant purchases as “Groceries,” the budget will be skewed, leading to inaccurate financial projections. Therefore, a degree of manual oversight is still necessary to ensure data accuracy.
App-Specific Integration Capabilities
The following list details the integration capabilities of several popular budgeting apps. Note that these integrations are subject to change, and it’s always advisable to check the app’s website for the most up-to-date information.
- Mint: Integrates with a wide range of banks, credit cards, and investment accounts. Supports automated transaction importing, but requires manual categorization adjustments. Offers limited integration with loan accounts.
- YNAB (You Need A Budget): Primarily focuses on manual data entry, though it does offer limited automated import capabilities. This allows for greater control over categorization and ensures accuracy. It lacks direct integration with investment platforms.
- Personal Capital: Offers comprehensive integration with bank accounts, credit cards, investment accounts (including brokerage accounts and retirement accounts), and loan accounts. Automated importing is a key feature, but users should review the imported data for accuracy.
- PocketGuard: Integrates with various bank accounts and credit cards, enabling automated transaction importing. It offers a simplified interface, prioritizing ease of use over extensive integration with investment platforms.
User Reviews and Ratings
Understanding user reviews and ratings is crucial for selecting a budgeting app that truly meets your needs. These provide valuable insights into the real-world experiences of other users, supplementing the technical specifications and features we’ve already discussed. Analyzing this feedback allows for a more holistic assessment of each app’s strengths and weaknesses.
User reviews and ratings from major app stores like Google Play and the Apple App Store reveal a mixed bag of opinions across different budgeting apps. While some consistently receive high praise for their intuitive interfaces and effective features, others face criticism regarding usability issues, technical glitches, or insufficient customer support. Aggregating this feedback gives a clearer picture of user satisfaction and identifies potential red flags.
Average User Ratings Visualization
A bar chart effectively visualizes the average user ratings for each app. The horizontal axis would list the names of the budgeting apps being compared (e.g., Mint, YNAB, Personal Capital, EveryDollar). The vertical axis would represent the average star rating, ranging from 1 to 5 stars. Each app would be represented by a bar whose height corresponds to its average rating. For example, if Mint had an average rating of 4.5 stars, its bar would reach the 4.5 mark on the vertical axis. Similarly, if YNAB had an average rating of 4.2 stars, its bar would be shorter. Data points would be clearly labeled above each bar, indicating the precise average rating. This visual representation allows for a quick and easy comparison of user satisfaction across different apps.
Potential Biases in User Reviews
It’s important to acknowledge that user reviews are not always objective. Several biases can influence ratings and feedback. For example, users who have had negative experiences are often more likely to leave a review than those who are satisfied. This creates an overrepresentation of negative feedback. Furthermore, reviews can be influenced by personal preferences and technical expertise. A user comfortable with complex financial tools might rate a sophisticated app highly, while a user seeking simplicity might find the same app frustrating. Finally, paid reviews or those incentivized in other ways can artificially inflate or deflate ratings, skewing the overall perception of an app. Considering these potential biases is essential for a balanced evaluation of user feedback.
Cost and Value Proposition

Choosing a budgeting app often involves weighing its cost against the benefits it offers. Many apps operate on a freemium model, providing basic functionality for free while charging for premium features or through subscription services. Understanding the pricing structures and the value each tier provides is crucial for making an informed decision.
The pricing models vary significantly across different budgeting apps. Some apps remain entirely free, supported by advertising or affiliate marketing. Others offer a basic free plan with limited features, encouraging users to upgrade to a paid subscription for access to more advanced tools and capabilities. Paid subscriptions typically range from a few dollars to upwards of $10 per month, sometimes offering annual subscriptions at a discounted rate. Finally, some apps utilize in-app purchases, allowing users to pay for specific features or add-ons individually, rather than committing to a recurring subscription.
Pricing Models and Feature Sets
The features included in each pricing tier directly impact the value proposition. Free plans generally offer core budgeting functions such as tracking income and expenses, creating simple budgets, and generating basic reports. However, paid subscriptions often unlock more advanced features like: detailed financial analysis tools, automated budgeting suggestions, debt management tools, investment tracking, and more robust reporting and visualization capabilities. For instance, a free plan might limit the number of accounts you can connect, while a paid subscription removes this limitation. Similarly, a paid plan may offer personalized financial advice or insights unavailable in the free version. In-app purchases typically offer a single, specific feature enhancement, like a premium report template or access to a specific data integration.
Value Proposition Analysis
Determining the value proposition requires comparing the cost of the app against the benefits it offers relative to the user’s individual needs and financial situation. A free app might suffice for someone with simple financial needs and a high comfort level with manual data entry. However, for users with complex financial situations or a preference for automation, the cost of a premium subscription might be easily justified by the time saved and improved financial insights. For example, an app with automated budgeting features could save users significant time compared to manually categorizing transactions. Similarly, sophisticated financial analysis tools can offer valuable insights that could lead to better financial decisions and improved savings. The key is to assess whether the additional features and capabilities offered by a paid plan justify the increased cost based on your individual circumstances.
Platform Compatibility and Accessibility
Choosing a budgeting app often hinges on its compatibility with your devices and its ability to cater to diverse user needs, including those with disabilities. A seamless user experience across platforms and robust accessibility features are crucial for widespread adoption and inclusivity. This section examines the platform compatibility and accessibility features of several popular budgeting apps.
App developers are increasingly prioritizing accessibility, recognizing the importance of creating inclusive financial management tools. This involves incorporating features that cater to users with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments. The impact of these features is significant, empowering users with disabilities to manage their finances independently and effectively.
Operating System and Device Support
Understanding which operating systems and devices are supported by each app is vital for users to determine compatibility with their existing technology. This information allows users to make informed decisions, ensuring the chosen app seamlessly integrates into their digital ecosystem.
| App Name | iOS Support | Android Support | Web Support | Other Supported Devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example App 1 | Yes | Yes | Yes | None |
| Example App 2 | Yes | Yes | No | None |
| Example App 3 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Apple Watch, Wear OS |
Accessibility Features for Users with Disabilities
Many budgeting apps now incorporate a range of accessibility features designed to enhance usability for people with disabilities. These features significantly improve the user experience, promoting financial independence and inclusivity.
- Screen reader compatibility: Apps compatible with screen readers (like VoiceOver on iOS and TalkBack on Android) allow users with visual impairments to navigate the app and access information through auditory cues.
- Adjustable text size and font: The ability to increase text size and choose different fonts accommodates users with low vision or visual impairments, making information clearer and easier to read.
- High contrast mode: This feature enhances the visual distinction between text and background colors, improving readability for users with visual impairments or photosensitivity.
- Keyboard navigation: Full keyboard navigation allows users with motor impairments to control the app without relying on touch input.
- Voice control: Some apps offer voice control features, enabling users with motor impairments to interact with the app using voice commands.
Impact of Accessibility Features on User Experience
The implementation of accessibility features directly impacts the user experience, making budgeting apps more inclusive and user-friendly for everyone. These features go beyond mere compliance; they represent a commitment to creating a positive and empowering experience for all users.
For example, a user with low vision who can adjust the text size to a comfortable level will have a much more positive experience compared to a user who struggles to read the small default text. Similarly, a user with motor impairments who can navigate the app using a keyboard will find the app far more accessible and usable than one relying solely on touch input. These improvements lead to increased user satisfaction, improved financial literacy, and greater independence in managing personal finances.
Epilogue

Ultimately, the best budgeting app depends on your individual needs and preferences. While some prioritize sleek interfaces and advanced analytics, others focus on simplicity and ease of use. By carefully considering the factors Artikeld in this comparison—security, integration, user reviews, cost, and platform compatibility—you can confidently select a budgeting app that aligns with your financial goals and enhances your journey toward financial well-being. Remember to always prioritize security and read user reviews to gauge real-world experiences.
Helpful Answers
What data do budgeting apps typically access?
Most budgeting apps require access to your bank accounts and credit cards to automatically import transaction data. The level of access varies depending on the app and your permissions.
Are budgeting apps secure?
Reputable budgeting apps employ robust security measures, including encryption and multi-factor authentication. However, it’s crucial to choose apps with strong privacy policies and positive security reviews.
Can I use a budgeting app if I don’t have a smartphone?
Many budgeting apps offer web-based access, allowing you to manage your budget from a computer or tablet, even without a smartphone.
What if I switch banks or credit cards?
Most apps seamlessly integrate with new accounts once you update your linked financial institutions within the app’s settings.