Budgeting Apps Review Update: The landscape of personal finance management is constantly evolving, with budgeting apps playing an increasingly crucial role. This review examines the current state of the market, analyzing popular apps across key features, user experiences, security, and future trends. We delve into user reviews, highlighting both strengths and weaknesses to provide a comprehensive overview for users seeking effective financial tools.
From basic budgeting tools to sophisticated AI-powered platforms, the options available cater to a wide range of needs and technical skills. This update explores the diverse functionalities, pricing models, and integration capabilities of leading budgeting apps, providing a valuable resource for informed decision-making. We also consider crucial aspects like data security and privacy, empowering users to make choices that align with their financial goals and security preferences.
Introduction to Budgeting Apps

The budgeting app market has exploded in recent years, transforming how individuals and families manage their finances. This surge in popularity is driven by the increasing accessibility of smartphones and the desire for greater financial control in an increasingly complex economic landscape. These apps offer a convenient and often visually appealing alternative to traditional budgeting methods like spreadsheets or pen-and-paper tracking.
The evolution of budgeting apps mirrors the broader technological advancements in mobile computing. Early apps were primarily basic calculators and expense trackers. However, modern budgeting apps offer sophisticated features, including automated transaction categorization, bill reminders, savings goal tracking, and even investment management integration. This evolution has led to a much wider user base, encompassing individuals across various age groups and financial literacy levels.
Budgeting App Categories
The variety of budgeting apps available reflects the diverse needs and technological comfort levels of users. Apps can be broadly categorized based on their features and pricing models.
Basic budgeting apps typically offer core functionalities like expense tracking and simple budgeting tools. These apps are usually free or offer a limited free version with in-app purchases for premium features. Examples might include apps with simple interfaces focusing on visual representations of spending, allowing users to quickly input expenses and see their budget allocation at a glance. These apps are ideal for users who prioritize simplicity and ease of use over advanced features.
Advanced budgeting apps provide more comprehensive features, including sophisticated budgeting methods (e.g., zero-based budgeting, 50/30/20 rule), financial forecasting, debt management tools, and integration with bank accounts and credit cards. These apps often come with a subscription fee or a one-time purchase cost to unlock all features. These might include features like personalized financial advice, investment tracking, and reporting functionalities that help users analyze their spending habits over time. Users needing in-depth analysis and advanced financial planning capabilities would find these apps particularly useful.
Subscription-based budgeting apps usually offer a freemium model, providing a basic version for free while charging a recurring subscription fee for premium features and enhanced functionality. These premium features often include advanced reporting, unlimited account connections, personalized financial coaching, or access to exclusive content and resources. This model allows developers to continuously improve and expand the app’s features while providing a financially sustainable business model. Many popular budgeting apps utilize this approach, offering a range of features to suit different user needs and budgets.
Key Features of Popular Budgeting Apps
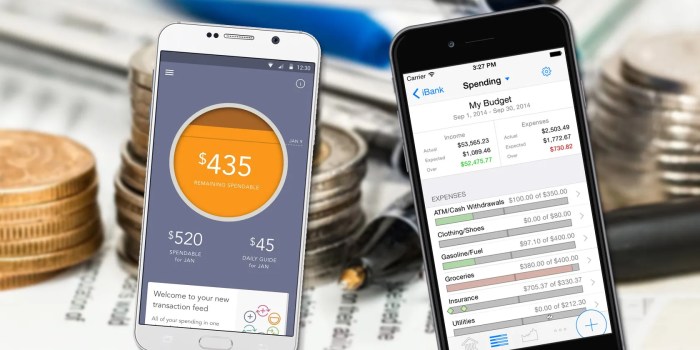
Choosing the right budgeting app can significantly impact your financial management success. This section compares and contrasts the core features of three popular budgeting apps to help you make an informed decision. We’ll examine their key features, pricing models, and user interface designs, ultimately focusing on the overall user experience.
Comparison of Popular Budgeting Apps
The following table provides a concise overview of three prominent budgeting apps: Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget), and Personal Capital. Each app offers a unique approach to budgeting, catering to different user needs and preferences.
| App Name | Key Features | Pricing Model | User Interface Design |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mint | Automated transaction tracking, spending categorization, budgeting tools, bill payment reminders, credit score monitoring. | Free (with ads), premium subscription available for additional features. | Clean and intuitive interface, easy navigation, visually appealing charts and graphs. The design prioritizes ease of use, making it accessible to users of all technical skill levels. |
| YNAB (You Need A Budget) | Zero-based budgeting, goal setting, scheduled transactions, debt tracking, detailed reporting. Emphasizes mindful spending and proactive financial planning. | Subscription-based, offering various plan options with different features and user support levels. | More complex interface than Mint, requiring a steeper learning curve. However, the design is well-organized and offers robust customization options for power users. The visual representation of budget allocation is very clear and detailed. |
| Personal Capital | Comprehensive financial dashboard, investment tracking, retirement planning tools, net worth calculation, fee analysis for investment accounts. Focuses on holistic wealth management. | Free (basic features), premium subscription unlocks advanced features such as financial advisory services. | Sophisticated and feature-rich interface, potentially overwhelming for novice users. Provides detailed insights into various aspects of personal finance. The dashboard is well-organized and provides a clear overview of the user’s financial situation, though it might feel cluttered to some. |
User Experience (UX) Aspects
The user experience varies significantly across these apps. Mint excels in its simplicity and ease of use, making it ideal for beginners. Its intuitive interface and automated features minimize the effort required for basic budgeting. YNAB, while more complex, provides a powerful framework for zero-based budgeting, empowering users to take control of their finances through detailed planning. However, this requires a higher level of engagement and understanding of its methodology. Personal Capital offers a highly comprehensive overview of one’s financial life, but its complexity can be daunting for those unfamiliar with investment management.
Strengths and Weaknesses of App Features
Mint’s strength lies in its ease of use and automated features, but its free version includes advertisements and lacks the advanced features found in paid subscriptions. YNAB’s strength is its zero-based budgeting methodology, promoting mindful spending, but its complexity can be a barrier for some users. Personal Capital offers a holistic view of finances, including investments, but its free version has limited functionality and its premium version is quite expensive. Each app balances strengths and weaknesses depending on individual user needs and priorities.
User Reviews and Ratings Analysis
Understanding user sentiment is crucial for assessing the effectiveness and overall user experience of budgeting apps. Analyzing reviews from various app stores provides valuable insights into both the strengths and weaknesses of each application. This analysis considers reviews from both the Google Play Store and the Apple App Store, categorizing them to identify prevalent themes and patterns in user feedback.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of user opinions, we categorized reviews from the Google Play Store and Apple App Store into three distinct categories: positive, negative, and neutral. Positive reviews highlighted features such as ease of use, helpful budgeting tools, and excellent customer support. Negative reviews frequently mentioned issues like glitches, limited functionality, or a confusing user interface. Neutral reviews often expressed mixed feelings, praising certain aspects while criticizing others.
Categorization of User Reviews
The review categorization process involved a team manually reviewing a significant sample of user feedback. This allowed for nuanced interpretation of reviews that might not fit neatly into a simple positive/negative binary. For example, a review mentioning both a positive experience with the budgeting features and a negative experience with the app’s syncing capabilities would be classified as neutral. The number of reviews in each category was then tallied to create a visual representation of the overall user sentiment.
Visual Representation of User Sentiment
A bar chart was created to illustrate the distribution of user sentiment across the three categories: positive, negative, and neutral. The horizontal axis represents the three categories, while the vertical axis displays the number of reviews in each category. For example, if 60% of reviews were positive, 25% negative, and 15% neutral, the bar for “Positive” would be significantly taller than the others, clearly demonstrating the overall positive user reception. The chart provides a clear and concise visual summary of the overall user experience, allowing for a quick assessment of the app’s performance based on user feedback.
Recurring Themes in User Feedback
Analysis of the categorized reviews revealed several recurring themes. Positive feedback frequently centered on the app’s intuitive interface, effective tracking features, and helpful reporting tools. Many users praised the ease of connecting bank accounts and the ability to set personalized budgets. Conversely, negative reviews commonly highlighted issues with data synchronization, occasional app crashes, and a lack of certain features, such as support for multiple accounts or advanced budgeting strategies. Neutral reviews often reflected users’ satisfaction with certain aspects but expressed dissatisfaction with others, suggesting areas for improvement.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Protecting your financial data is paramount when using budgeting apps. These apps handle sensitive information, and understanding the security measures and privacy policies is crucial for responsible usage. This section will examine the security protocols employed by popular apps and discuss potential risks and mitigation strategies.
Many budgeting apps utilize robust security measures to safeguard user data. Common practices include data encryption both in transit (using HTTPS) and at rest (using strong encryption algorithms), multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance account security, and regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities. Some apps also offer features like biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition) for added protection. However, the specific security features implemented can vary significantly between apps, so careful consideration is necessary before choosing one.
Data Encryption and Storage
The method of data encryption and storage differs across budgeting apps. Some apps might use end-to-end encryption, meaning only the user can decrypt their data. Others may use encryption at rest, protecting data stored on their servers, but not necessarily during transmission. Understanding the type of encryption used is vital, as end-to-end encryption offers the highest level of security. Users should look for transparency in the app’s security documentation regarding encryption methods employed.
Privacy Policy Comparisons
Privacy policies vary considerably among budgeting apps. Some apps might collect extensive data about user spending habits for analytical purposes or targeted advertising. Others may have a more minimalist approach, collecting only essential information for the app’s functionality. Carefully reviewing each app’s privacy policy is essential to understand what data is collected, how it’s used, and with whom it might be shared. Pay close attention to clauses regarding data sharing with third-party companies and the app’s data retention policies.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Despite security measures, risks associated with using budgeting apps still exist. Phishing attacks, malware, and data breaches are all potential threats. Users can mitigate these risks by practicing good cybersecurity habits, such as using strong, unique passwords, enabling MFA, being cautious of suspicious emails or links, and keeping the app’s software updated. Regularly reviewing account activity for any unauthorized transactions is also crucial. Choosing apps with a strong reputation for security and privacy, and a history of transparent communication regarding security incidents, will also minimize risks.
Integration with Other Financial Tools
The ability of a budgeting app to seamlessly integrate with other financial tools is a crucial factor in its overall effectiveness. A truly useful budgeting app should act as a central hub, consolidating all your financial information into one easily accessible location, rather than requiring you to manually input data from multiple sources. This integration simplifies the budgeting process and provides a more comprehensive view of your financial health.
Effective integration allows for automatic data synchronization, eliminating the need for manual entry and reducing the risk of errors. This automation saves users significant time and effort, making budgeting a more streamlined and less tedious task. However, the level of integration varies considerably between different apps, with some offering robust connections and others exhibiting limitations.
Examples of Seamless and Limited Integrations
Seamless integration typically involves real-time data synchronization with bank accounts, credit cards, investment accounts, and loan providers. For example, Mint, a popular budgeting app, offers excellent integration with many major financial institutions, automatically downloading transaction data and categorizing expenses. In contrast, some smaller or less established budgeting apps may only support a limited number of financial institutions, requiring manual data entry for accounts not included in their supported list. This limitation significantly reduces the app’s convenience and effectiveness. Another example of a limitation could be a lack of support for specific types of accounts, such as certain investment platforms or international bank accounts. This restricts the comprehensive overview of finances that a well-integrated app should provide.
Features Enhancing Integration with Other Financial Tools
The degree of integration a budgeting app offers is greatly influenced by its features. A strong emphasis on automated data imports is paramount. This eliminates manual data entry, a time-consuming and error-prone process. Beyond basic import, features that automatically categorize transactions, reconcile accounts, and generate insightful reports based on aggregated data from various sources greatly enhance the user experience. The ability to link multiple accounts, including checking, savings, credit cards, loans, and investment accounts, is also essential for a holistic financial overview. Furthermore, robust support for various financial institutions and account types is critical for broad applicability. Finally, secure API connections are essential to ensure the safe and reliable transfer of sensitive financial data between the budgeting app and other financial tools.
Future Trends in Budgeting Apps

The budgeting app market is dynamic, constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of users and leverage technological advancements. We’re seeing a shift beyond basic expense tracking towards more sophisticated tools offering personalized financial guidance and proactive financial management. This evolution is driven by the increasing availability of data, improvements in artificial intelligence, and a growing demand for user-friendly, intuitive financial tools.
The integration of advanced technologies is fundamentally reshaping the user experience and the potential for improved financial outcomes. This transformation promises to move beyond simply recording transactions to actively assisting users in achieving their financial goals.
AI-Powered Features and Personalized Financial Advice
Artificial intelligence is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of budgeting app functionality. AI algorithms can analyze spending patterns, identify areas for potential savings, and even predict future expenses based on historical data. This personalized approach goes beyond simple categorization; it provides users with actionable insights and tailored recommendations. For instance, an AI-powered app might notice a user consistently overspends on dining out and suggest a budget reduction in that category, potentially offering alternative, cost-effective solutions like meal prepping. Furthermore, AI can personalize financial advice, offering customized strategies based on individual goals, such as saving for a down payment on a house or retirement planning. This level of personalization significantly enhances user engagement and the effectiveness of the budgeting process.
Enhanced Security and Privacy Measures
With the increasing reliance on digital financial management, security and privacy are paramount. Future trends point towards the implementation of more robust security protocols, including advanced encryption and biometric authentication. Apps will likely prioritize transparent data handling practices, clearly outlining how user data is collected, used, and protected. This heightened focus on security and privacy will build user trust and encourage greater adoption of budgeting apps for sensitive financial information. For example, we can expect to see increased use of blockchain technology for secure transaction recording and improved fraud detection mechanisms.
Gamification and Behavioral Economics
Gamification techniques are increasingly being incorporated into budgeting apps to make financial management more engaging and less daunting. Features like progress bars, rewards systems, and friendly competition can incentivize users to stick to their budgets and achieve their financial goals. The application of behavioral economics principles helps design interfaces and features that nudge users towards better financial habits. For example, apps might offer rewards for consistently tracking expenses or achieving savings milestones, transforming the process from a chore into a motivating game.
Integration with Open Banking and Third-Party Services
The integration with open banking APIs allows for seamless connection with various financial institutions, providing a holistic view of a user’s financial landscape. This expanded integration facilitates automatic transaction updates, reducing manual data entry and improving accuracy. Furthermore, integrating with other third-party services, such as investment platforms or bill payment services, creates a comprehensive financial ecosystem within the app. This interconnectedness streamlines financial management and simplifies users’ overall financial lives. For instance, an app could directly link to a user’s bank account, credit card, and investment accounts, providing a unified dashboard for tracking all financial activities.
Last Recap
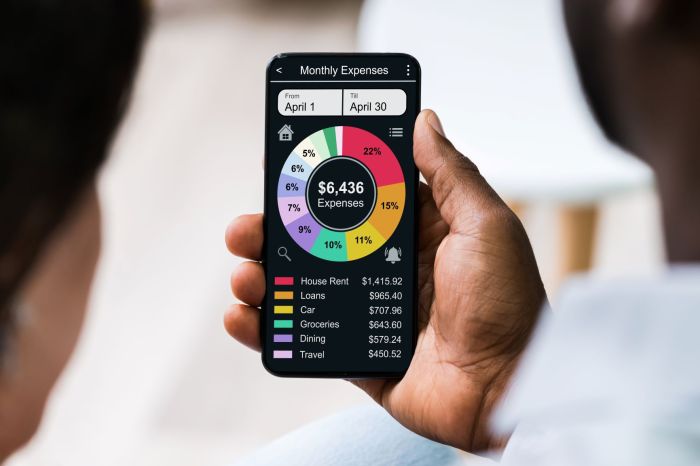

Ultimately, choosing the right budgeting app depends on individual needs and preferences. This review provides a framework for evaluating the options available, considering factors beyond mere functionality. By understanding user experiences, security measures, and future trends, individuals can select a tool that seamlessly integrates into their financial lives, promoting better budgeting habits and achieving long-term financial well-being. The ever-evolving nature of this market ensures that continuous evaluation is key to staying ahead of the curve in personal finance management.
Top FAQs
What data security measures should I look for in a budgeting app?
Look for apps that employ end-to-end encryption, two-factor authentication, and transparent privacy policies outlining data handling practices.
Are all budgeting apps free?
No, some budgeting apps offer free versions with limited features, while others operate on subscription models offering more advanced functionalities.
How do I choose the right budgeting app for my needs?
Consider your financial goals, technical comfort level, desired features (e.g., bill tracking, investment integration), and preferred user interface when selecting an app.
Can I link multiple bank accounts to one budgeting app?
Most budgeting apps allow linking multiple accounts, though the specific number and types of accounts supported vary depending on the app.



