Business model innovation is no longer a niche concept; it’s a critical driver of growth and sustainability for organizations across diverse sectors. This exploration delves into the core principles of business model innovation, examining successful and unsuccessful examples to illuminate best practices and potential pitfalls. We will analyze various industries, highlighting strategic approaches and the profound impact on profitability, competitive advantage, and market share.
From the revolutionary impact of the “Business Model Canvas” to the iterative nature of the “Lean Startup” methodology, we’ll uncover the methods and strategies that fuel successful innovation. Understanding the lifecycle of a business model, along with the challenges and risks involved in implementation, is crucial for effective strategic planning and execution. This comprehensive overview aims to equip readers with the knowledge and insights necessary to navigate the complexities of business model innovation and harness its transformative potential.
Defining Business Model Innovation
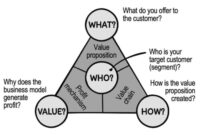
Business model innovation refers to the creation and implementation of new business models that significantly alter how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It’s not just about tweaking existing processes; it’s about fundamentally rethinking the entire way a business operates. A successful business model innovation often leads to a competitive advantage and improved profitability.
A business model comprises several core components working in synergy. These typically include the value proposition (what the business offers), the target customer segments (who the business serves), the channels used to reach customers, the customer relationships maintained, the revenue streams generated, the key activities performed, the key resources utilized, the key partnerships formed, and the cost structure. The interplay of these components defines how a company functions and creates value.
Examples of Successful Business Model Innovations
Several companies have demonstrated the power of business model innovation. Netflix, for instance, transitioned from a DVD-rental-by-mail service to a streaming giant, fundamentally altering its value proposition and revenue model. This involved significant changes in its infrastructure, content acquisition, and customer interaction. Similarly, Airbnb disrupted the hospitality industry by creating a platform connecting homeowners with travelers, effectively creating a new market and revenue stream based on sharing economy principles. Spotify revolutionized the music industry by shifting from a purchase-based model to a subscription-based streaming service, drastically changing how music is consumed and monetized.
Incremental versus Radical Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation can be categorized as either incremental or radical. Incremental innovation involves making relatively small changes to an existing business model, such as adjusting pricing strategies or expanding into new geographic markets. For example, a coffee shop might introduce a loyalty program (incremental). Radical innovation, on the other hand, involves creating entirely new business models that disrupt existing industries. The aforementioned examples of Netflix, Airbnb, and Spotify represent radical business model innovations because they redefined entire sectors.
Examples of Failed Business Model Innovations
Not all attempts at business model innovation are successful. The failure often stems from a lack of market understanding, poor execution, or an inability to adapt to changing circumstances. Webvan, an online grocery delivery service, failed due to high operational costs and an inability to scale its operations effectively. They underestimated the logistical complexities and the high cost of last-mile delivery. Similarly, many early social networking sites failed to find sustainable revenue models, leading to their demise. These failures highlight the importance of thorough market research, careful planning, and adaptability in the face of challenges.
Comparison of Different Types of Business Model Innovation
| Type of Innovation | Description | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value Proposition Innovation | Changes to the product or service offered. | Adding a new feature to an existing product. | Increased customer satisfaction, potentially higher prices. |
| Revenue Model Innovation | Changes to how revenue is generated (e.g., subscription, freemium). | Switching from a one-time purchase to a subscription model. | Recurring revenue, potential for higher lifetime customer value. |
| Customer Segment Innovation | Targeting new customer groups. | Expanding into a new geographic market. | Increased market reach, diversification of revenue streams. |
| Channel Innovation | Changes to how products or services are delivered to customers. | Shifting from brick-and-mortar stores to online sales. | Reduced costs, increased reach, improved customer experience. |
Examples of Business Model Innovation in Different Industries
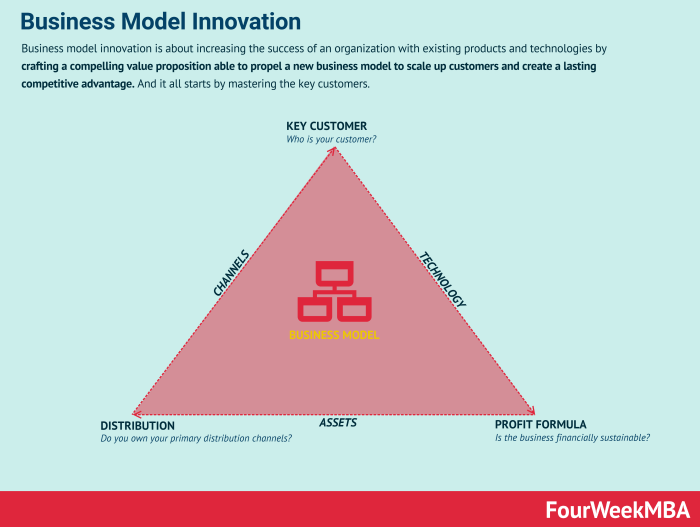
Business model innovation represents a fundamental shift in how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It’s not simply about tweaking existing processes; it’s about reimagining the core logic of the business. This section explores successful examples across various sectors, highlighting the diverse approaches companies have taken to achieve sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Business Model Innovation in the Technology Sector
The technology sector is a breeding ground for business model innovation. Companies constantly disrupt existing markets and create entirely new ones. A prime example is the shift from selling software licenses to offering Software as a Service (SaaS). Instead of a one-time purchase, customers pay a recurring subscription fee for access to software, creating a predictable revenue stream for companies like Salesforce and Adobe. Another significant innovation is the freemium model, where basic services are offered for free, while premium features are available through paid subscriptions. This model, successfully employed by companies like Spotify and Dropbox, allows for rapid user acquisition and subsequent monetization. The rise of the app store economy, pioneered by Apple and Google, also represents a transformative business model innovation, creating entirely new distribution channels and revenue streams for developers.
Business Model Innovations in the Retail Industry
The retail industry has witnessed significant disruption through business model innovation. The rise of e-commerce giants like Amazon fundamentally changed how consumers shop, shifting from brick-and-mortar stores to online marketplaces. Amazon’s success stems not only from its vast product selection but also from its innovative logistics and fulfillment network, enabling fast and reliable delivery. Another significant innovation is the subscription box model, which offers curated selections of products delivered regularly to subscribers. Companies like Birchbox and Dollar Shave Club have successfully leveraged this model to build recurring revenue and foster customer loyalty. The omnichannel approach, integrating online and offline shopping experiences seamlessly, also represents a key business model innovation in the retail sector.
Successful Business Model Innovations in the Food and Beverage Industry
The food and beverage industry has embraced several innovative business models. The rise of meal kit delivery services, such as Blue Apron and HelloFresh, represents a significant shift, providing convenience and customization to consumers. These companies have successfully disrupted traditional grocery shopping by delivering pre-portioned ingredients and recipes directly to customers’ homes. Another noteworthy innovation is the growth of direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands, bypassing traditional retail channels and building relationships directly with consumers through online platforms and social media. Companies like Death Wish Coffee and many craft breweries have leveraged this approach to build brand loyalty and control their pricing and distribution. Furthermore, the expansion of food delivery platforms, such as Uber Eats and DoorDash, has fundamentally changed how consumers access food, creating new revenue streams for restaurants and delivery drivers.
Business Model Innovations in the Healthcare and Education Sectors: A Comparison
Both the healthcare and education sectors are undergoing significant transformations driven by business model innovation. In healthcare, the shift towards value-based care, where providers are reimbursed based on patient outcomes rather than the volume of services provided, represents a fundamental change. Telemedicine, enabling remote consultations and monitoring, has also emerged as a significant innovation, improving access to care and reducing costs. In education, the rise of online learning platforms like Coursera and edX has democratized access to higher education, offering courses from leading universities to a global audience. While both sectors are seeing innovations focused on accessibility and efficiency, the healthcare sector’s innovations are often driven by regulatory changes and cost pressures, while the education sector’s innovations are more driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. The core difference lies in the regulatory environment and the nature of the service provided.
Key Features of Diverse Business Model Innovations
The following examples illustrate the diverse nature of business model innovation:
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Recurring revenue, scalable infrastructure, reduced upfront costs for customers.
- Freemium Model: Rapid user acquisition, conversion of free users to paying customers, potential for viral growth.
- Subscription Box Model: Recurring revenue, customer loyalty, curated product experience.
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Model: Increased brand control, direct customer relationships, enhanced customer data collection.
- Value-Based Care (Healthcare): Focus on patient outcomes, improved efficiency, potential for cost savings.
Methods and Strategies for Business Model Innovation
Developing innovative business models requires a structured approach. Several methodologies and tools can significantly aid in this process, fostering creativity and ensuring a practical, market-validated outcome. This section will explore some of the most effective methods and strategies.
Business Model Canvas and its Application in Innovation
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management and lean startup template for developing new or documenting existing business models. It’s a visual chart with elements describing a firm’s or product’s value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances. Its nine building blocks—Customer Segments, Value Propositions, Channels, Customer Relationships, Revenue Streams, Key Activities, Key Resources, Key Partnerships, and Cost Structure—provide a comprehensive overview, allowing for easy identification of areas needing improvement or innovation. By systematically examining each block, businesses can pinpoint weaknesses and explore opportunities for enhancement, leading to a more robust and competitive model. For example, a company might use the canvas to analyze its customer segments, identifying underserved niches or opportunities to expand into new markets. Simultaneously, they might examine their revenue streams, exploring alternative pricing models or adding new revenue sources. The visual nature of the canvas facilitates collaborative brainstorming and allows for rapid iteration and experimentation.
Lean Startup Methodology and its Relevance to Business Model Innovation
The Lean Startup methodology emphasizes building a minimum viable product (MVP) and iteratively developing it based on customer feedback. This approach is highly relevant to business model innovation because it minimizes risk and allows for rapid adaptation. Instead of investing heavily in a fully developed product or service before testing the market, the Lean Startup approach focuses on validating core assumptions early and often. This involves developing a simple prototype, gathering customer feedback, and iteratively refining the product and the business model itself based on that feedback. For instance, a company developing a new subscription service might launch a basic version with limited features, gather customer feedback on the pricing, features, and overall value proposition, and then adjust the business model accordingly before a full-scale launch. This iterative process allows for course correction and avoids costly mistakes associated with launching a product that doesn’t meet market demands.
Customer Development and its Role in Identifying Opportunities for Innovation
Customer development is a process of deeply understanding customer needs, pain points, and desires. It involves direct interaction with potential customers through interviews, surveys, and observations. This deep understanding is crucial for identifying opportunities for business model innovation. By engaging directly with customers, businesses can uncover unmet needs and identify areas where their existing business model falls short or where there’s an opportunity to create a completely new model. For example, a company might discover through customer interviews that their current product is too complex to use, leading them to redesign the user interface and potentially create a simpler, more intuitive version, thus improving the overall customer experience and creating a more successful business model.
Design Thinking Applied to Business Model Innovation
Design thinking, a human-centered problem-solving approach, emphasizes empathy, experimentation, and iteration. It’s particularly effective for business model innovation because it focuses on understanding the user’s needs and developing solutions tailored to those needs. The process typically involves five stages: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. In the context of business model innovation, design thinking might involve conducting user research to understand their challenges, defining the problem the business model aims to solve, brainstorming potential solutions, creating prototypes of the new business model, and testing them with potential customers. For instance, a company might use design thinking to develop a subscription box service tailored to a specific niche market, testing different product combinations and pricing models before launching the final product.
Step-by-Step Guide for Developing a New Business Model
Developing a new business model is an iterative process. A structured approach can significantly increase the chances of success. The following steps provide a framework:
- Analyze the Existing Business Model: Identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. Use tools like the Business Model Canvas to visualize the current model.
- Identify Customer Needs and Pain Points: Conduct thorough customer research to understand their needs, preferences, and challenges.
- Brainstorm Potential Business Model Innovations: Explore alternative revenue models, value propositions, and customer segments.
- Develop a Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Create a basic version of the new business model to test key assumptions.
- Test and Iterate: Gather customer feedback and refine the business model based on the results. Use the Lean Startup methodology to iterate quickly and efficiently.
- Scale and Refine: Once the business model has been validated, scale the operation and continue to refine it based on ongoing customer feedback and market conditions.
Analyzing the Impact of Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation significantly impacts a company’s performance across various metrics, influencing its profitability, competitive standing, market share, and long-term sustainability. Understanding these impacts is crucial for businesses seeking to leverage innovation for growth and resilience.
Business Model Innovation’s Impact on Profitability
A successful business model innovation can dramatically boost profitability. By streamlining operations, reducing costs, or creating new revenue streams, companies can see a substantial increase in their profit margins. For instance, Netflix’s shift from a DVD rental model to a streaming subscription model significantly reduced its operational costs associated with shipping and inventory management, leading to higher profitability. Conversely, a poorly executed innovation can lead to decreased profitability due to increased expenses or reduced customer demand. The key lies in carefully analyzing potential cost reductions and revenue generation opportunities before implementing any changes.
Business Model Innovation’s Influence on Competitive Advantage
Business model innovation is a powerful tool for establishing and maintaining a competitive advantage. By offering unique value propositions, accessing new markets, or disrupting existing industry structures, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors and gain a significant edge. Consider the example of Dollar Shave Club, which disrupted the traditional razor market with its subscription-based model and direct-to-consumer approach, effectively bypassing established retailers and offering a lower-priced, convenient alternative. This innovative business model created a strong competitive advantage, attracting a large customer base and challenging the dominance of traditional players.
Business Model Innovation’s Effects on Market Share
A successful business model innovation can lead to a substantial increase in market share. By addressing unmet customer needs, providing a superior customer experience, or creating a more efficient and effective approach, innovative businesses can attract new customers and win over existing ones from competitors. For example, Spotify’s introduction of a freemium model significantly increased its market share in the music streaming industry by providing a free, ad-supported tier alongside a premium subscription option, attracting a wider range of users than competitors offering only paid subscriptions. Conversely, failure to adapt to changing market dynamics and technological advancements through business model innovation can result in a decline in market share.
The Relationship Between Business Model Innovation and Sustainability
Increasingly, businesses are recognizing the importance of integrating sustainability into their business models. Innovations focused on reducing environmental impact, promoting ethical sourcing, or developing circular economy approaches can not only enhance a company’s reputation but also contribute to long-term financial success. Companies like Patagonia, known for their commitment to environmental sustainability and fair labor practices, have demonstrated that incorporating sustainability into their business model can be a source of competitive advantage and attract environmentally conscious consumers. This approach also helps to mitigate risks associated with resource depletion and changing regulations.
Lifecycle of a Successful Business Model Innovation
Imagine a graph charting the progress of a business model innovation. The initial phase is characterized by ideation and development, a period of slow growth and investment. This is followed by a period of rapid growth and market penetration as the innovation gains traction. Maturity sees a leveling off of growth as the market becomes saturated. Eventually, decline may occur if the business model fails to adapt to changing market conditions or technological advancements, or if a new disruptive innovation emerges. This cyclical pattern highlights the need for continuous innovation and adaptation to maintain long-term success. The graph would visually represent this as an upward sloping curve, reaching a peak, and then gradually declining.
Challenges and Risks of Business Model Innovation

Business model innovation, while potentially highly rewarding, is not without its significant challenges and risks. Undertaking radical changes to a company’s core operations, revenue streams, and customer relationships inherently involves uncertainty and the potential for setbacks. Successfully navigating these challenges requires careful planning, robust execution, and a deep understanding of the organizational context.
Potential Risks Associated with Radical Business Model Changes
Radical business model changes often disrupt existing operations and can lead to unforeseen consequences. The most significant risk is failure. A poorly conceived or poorly executed innovation can lead to significant financial losses, damage to brand reputation, and even the demise of the company. Other risks include the loss of key employees who are resistant to change, the inability to attract and retain customers accustomed to the old model, and the emergence of unexpected competition exploiting weaknesses in the new model. For example, the transition to a subscription-based model can fail if the pricing is not competitive or if the value proposition doesn’t resonate with customers. Similarly, a shift to a digital-first strategy might backfire if the company underestimates the technical challenges or the need for substantial investment in digital infrastructure and expertise.
Challenges of Implementing New Business Models within Established Organizations
Implementing new business models within established organizations presents a unique set of hurdles. Established companies often have entrenched processes, cultures, and power structures that can resist change. Inertia, resistance from employees who fear job losses or changes in their roles, and conflicts between different departments are common obstacles. Furthermore, legacy systems and technologies may not be compatible with the new model, requiring significant investment in upgrades or replacements. Companies may also struggle to allocate resources effectively, balancing the needs of the new business model with the demands of existing operations. Consider a traditional brick-and-mortar retailer attempting to transition to an omnichannel strategy; they might face resistance from store managers accustomed to traditional sales methods and struggle to integrate online and offline operations seamlessly.
Importance of Organizational Culture in Supporting Business Model Innovation
A supportive organizational culture is crucial for successful business model innovation. A culture that embraces experimentation, tolerates failure, and encourages collaboration is essential for fostering creativity and driving innovation. Employees need to feel empowered to challenge existing practices, propose new ideas, and take calculated risks. Conversely, a rigid, risk-averse culture can stifle innovation and prevent the successful implementation of new business models. Organizations that successfully implement business model innovations often have a culture of continuous learning, adaptation, and feedback. They actively seek input from employees, customers, and other stakeholders to refine their approach and ensure the new model is meeting its objectives.
Strategies for Mitigating the Risks of Business Model Innovation
Several strategies can help mitigate the risks associated with business model innovation. These include thorough market research to validate the viability of the new model, phased implementation to minimize disruption and allow for adjustments along the way, robust testing and prototyping to identify and address potential flaws before full-scale launch, and clear communication and engagement with employees to address concerns and build buy-in. Furthermore, investing in the necessary skills and technologies, building strong partnerships, and establishing clear metrics to track progress and measure success are all essential steps. For example, a company launching a new platform-based business model might start with a minimum viable product (MVP) to test its core features before investing heavily in scaling the platform.
Common Challenges and Potential Solutions Related to Business Model Innovation
| Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Resistance to change from employees | Clear communication, employee training, and incentives for adoption. |
| Lack of resources | Prioritization, phased implementation, and securing external funding. |
| Incompatible legacy systems | System upgrades, integration with new technologies, and phased migration. |
| Market uncertainty | Thorough market research, agile development, and continuous monitoring. |
Conclusion

Ultimately, mastering business model innovation requires a strategic blend of creativity, analytical rigor, and a deep understanding of market dynamics. By carefully studying successful examples, learning from failures, and employing proven methodologies, organizations can position themselves for sustained growth and competitive dominance. The journey may be challenging, but the rewards of a successfully innovated business model are undeniable, leading to increased profitability, enhanced market share, and a more resilient future. This exploration serves as a valuable resource for entrepreneurs, executives, and anyone seeking to understand and leverage the power of business model innovation.
FAQ Corner
What is the difference between incremental and radical business model innovation?
Incremental innovation involves making small, iterative changes to an existing business model, while radical innovation involves a complete overhaul or fundamental shift in the business model.
How can I identify opportunities for business model innovation in my industry?
Conduct thorough market research, analyze competitor strategies, identify unmet customer needs, and explore emerging technologies.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid during business model innovation?
Ignoring customer feedback, underestimating implementation challenges, and lacking organizational support are key pitfalls.
How can I measure the success of a business model innovation?
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as revenue growth, customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and market share.