Competitive Analysis Template: Unlocking the secrets to market dominance starts with understanding your rivals. This isn’t just about spying on competitors; it’s about strategically analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, and market maneuvers to inform your own business strategy. We’ll delve into practical methods for identifying competitors, dissecting their strategies, and ultimately, crafting a competitive profile that gives you a decisive edge.
This comprehensive guide walks you through the entire process, from defining your competitive landscape to developing actionable strategies based on your findings. We’ll explore various frameworks, provide practical examples, and offer a template to streamline your analysis. Prepare to transform your understanding of the competitive arena and gain a significant advantage in the marketplace.
Defining the Scope of a Competitive Landscape
Competitive analysis: it’s not just about spying on your rivals (though, let’s be honest, a little harmless peeking never hurt anyone). It’s about understanding the intricate dance of market forces and positioning your business for glorious triumph. A well-defined competitive landscape is the cornerstone of a successful strategy, a sturdy map guiding you through the treacherous terrain of the marketplace. Without it, you’re essentially navigating by the stars…while blindfolded.
A robust competitive landscape assessment is characterized by its meticulous detail and insightful analysis. It’s not just a list of names; it’s a deep dive into each competitor’s strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market share. It considers factors like their pricing, marketing tactics, product offerings, customer base, and even their corporate culture (because, let’s face it, even a company’s vibe can impact its success). Think of it as a comprehensive character profile for each player in your market’s grand drama. The more thorough the assessment, the clearer the picture, and the more effective your strategic planning.
Key Industries Requiring Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis is particularly crucial in industries characterized by high competition, rapid innovation, and significant barriers to entry. Three prime examples are the technology sector, the pharmaceutical industry, and the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) market.
In the technology sector, the pace of innovation is breakneck. New players emerge constantly, and established giants are constantly jostling for position. A robust competitive analysis is vital for identifying emerging threats, capitalizing on market opportunities, and staying ahead of the curve. Think of the smartphone market: Apple, Samsung, Google—all engaged in a constant battle for market share, each needing a precise understanding of the others’ moves.
The pharmaceutical industry is a high-stakes game of research, development, and regulatory hurdles. Competitive analysis helps companies identify promising drug candidates, assess the potential market size, and understand the competitive landscape before investing heavily in research and development. Imagine the investment needed to bring a new drug to market – understanding the competition is not merely advisable, it’s essential.
The FMCG market is all about speed and agility. New products are constantly launched, and consumer preferences are ever-shifting. A comprehensive competitive analysis helps companies understand consumer trends, identify market gaps, and adapt their product offerings and marketing strategies accordingly. Consider the cola wars between Coca-Cola and Pepsi – a classic example of intense competition fueled by meticulous competitive analysis.
Defining the Target Market for Competitive Analysis
Clearly defining the target market is paramount. It’s like focusing your binoculars: a blurry, wide view won’t help you pinpoint your rivals; a sharp, focused view will. This involves identifying specific customer segments, their needs, and their purchasing behavior. Consider factors such as demographics (age, gender, location), psychographics (lifestyle, values, interests), and buying patterns (frequency, volume, channels). Once your target market is defined, you can then identify the competitors who are actively vying for those same customers. This process involves market research, customer surveys, and analyzing sales data to get a clear picture of who you’re up against.
Methods for Identifying Competitors
Identifying competitors requires a multi-pronged approach. Different methods provide different perspectives, creating a more complete picture.
| Method | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Observation | Actively observing competitors’ activities, including marketing, pricing, and product offerings. | Provides firsthand insights. | Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. |
| Market Research Reports | Utilizing industry reports and market analysis from reputable sources. | Provides broad overview and market trends. | May not offer specific competitor details. |
| Customer Feedback | Gathering information from customers about their experiences with different brands. | Provides valuable insights into customer perceptions. | Can be subjective and biased. |
| Online Research | Analyzing competitors’ websites, social media presence, and online reviews. | Easy access to information. | Information may not be comprehensive or accurate. |
Identifying Key Competitors
Unveiling your competitors is like a thrilling detective story – except the stakes are higher than just catching a thief; they’re about securing your market share! This section will equip you with the tools and techniques to identify those sneaky rivals, both the obvious and the surprisingly hidden ones. Prepare for some serious competitive intel gathering!
Identifying your key competitors is crucial for developing effective strategies. Understanding your competitive landscape allows you to anticipate market trends, refine your offerings, and ultimately, dominate (in a friendly, business-like way, of course!). Ignoring your competitors is like playing poker with your eyes closed – you might get lucky, but the odds are stacked against you.
Methods for Identifying Direct and Indirect Competitors
Five distinct approaches can help you uncover those competitive beasts lurking in the shadows. Employing a multi-pronged strategy ensures a comprehensive understanding of the market.
- Market Research Reports: These reports, often available through subscription services or market research firms, provide a detailed overview of market segments, competitor activities, and emerging trends. Think of them as your trusty spyglass, offering a bird’s-eye view of the battlefield.
- Online Searches and Social Media Monitoring: A simple Google search or a targeted social media scan can reveal companies offering similar products or services. It’s like eavesdropping on your competitors’ conversations – but entirely legal (and much more productive!).
- Industry Events and Conferences: Attending industry gatherings provides a fantastic opportunity for networking and directly observing competitors. You’ll not only gather information but also make valuable connections. Think of it as a high-stakes cocktail party for business professionals.
- Customer Feedback and Surveys: Your customers are your best source of information. Through feedback surveys and reviews, you can uncover which competitors they consider alternatives. This is like having your own secret informant embedded within the enemy camp.
- Competitor Websites and Marketing Materials: Analyzing your competitors’ websites, marketing brochures, and social media presence can reveal their target audience, pricing strategies, and overall brand positioning. It’s like meticulously studying their playbook before the big game.
Differentiating Direct and Indirect Competitors
Knowing the difference between direct and indirect competitors is vital for tailoring your strategies. Direct competitors offer essentially the same product or service, while indirect competitors offer alternatives that satisfy the same customer need.
For example, if you sell artisanal sourdough bread, a direct competitor would be another bakery selling artisanal sourdough bread. An indirect competitor, however, might be a grocery store selling pre-packaged bread or a restaurant offering sandwiches (which, let’s be honest, are just sophisticated bread-based delivery systems for delicious fillings).
Resources for Discovering Competitor Information
The internet is a treasure trove of competitor intelligence, but knowing where to look is half the battle. Here are some resources to help you unearth the secrets of your rivals.
- IBISWorld: Provides industry reports with detailed competitor analysis.
- Hoovers: Offers company profiles, financial data, and news on public and private companies.
- LinkedIn: An excellent platform for researching individuals working at competitor companies and understanding their professional backgrounds and expertise.
- Google Finance and Yahoo Finance: Provide financial information on publicly traded companies.
- Industry-Specific Databases: Many industries have specialized databases containing information on market size, share, and key players.
Competitor Identification Flowchart
Visualizing the process can make it much easier to manage. The following flowchart illustrates a systematic approach to identifying key competitors.
Imagine a flowchart here. It would start with a box labeled “Define your product/service.” This would lead to a diamond-shaped decision box: “Are there companies offering the exact same product/service?” A “Yes” branch leads to “Identify Direct Competitors,” while a “No” branch leads to “Identify Indirect Competitors.” Both branches then converge into a box labeled “Analyze Competitors,” which leads to a final box: “Develop Competitive Strategies.”
Analyzing Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Unleashing the power of competitive analysis is like wielding a finely-honed katana – precise, effective, and potentially very embarrassing if you trip over your own feet. Understanding your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses is the key to crafting a winning strategy, avoiding disastrous blunders, and generally making your rivals look slightly less competent (a subtle, yet satisfying, victory). This section will equip you with the analytical tools to dissect your competition and emerge victorious (or at least, not completely defeated).
Five Frameworks for Assessing Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Several frameworks exist to help businesses systematically analyze their competitors. Choosing the right framework depends on the specific context and the information available. Each offers a unique perspective on competitive dynamics.
- SWOT Analysis: This classic framework examines internal Strengths and Weaknesses, alongside external Opportunities and Threats. It’s a simple yet effective way to get a holistic view of a competitor’s position.
- Porter’s Five Forces: This model analyzes the competitive intensity of an industry by examining the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors. It helps understand the overall competitive landscape rather than focusing on individual competitors in isolation.
- Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM): The CPM allows for a direct comparison of your company and its competitors across several key success factors. This framework facilitates a quick assessment of relative strengths and weaknesses.
- Value Chain Analysis: By examining each stage of a competitor’s value chain (from raw materials to final product), you can identify areas of efficiency, cost advantage, or differentiation. This detailed analysis provides a granular understanding of their operations.
- VRIO Framework: This framework analyzes whether a competitor’s resources and capabilities are Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, and Organized. It helps identify sustainable competitive advantages.
Comparing SWOT and Porter’s Five Forces
SWOT analysis provides a concise internal and external assessment of a *single* competitor, focusing on its specific characteristics. Porter’s Five Forces, on the other hand, paints a broader picture of the *entire* industry’s competitive landscape, examining the structural forces impacting *all* players. SWOT is great for detailed competitor profiling, while Porter’s Five Forces helps understand the overall competitive dynamics and potential threats or opportunities. Think of SWOT as a close-up and Porter’s Five Forces as a wide shot – both are crucial for a complete understanding.
Using SWOT Analysis to Identify Opportunities and Threats
Let’s imagine a fictional competitor, “Fluffy Clouds Inc.”, a company selling artisanal cloud-based software solutions. A SWOT analysis might reveal:
Strengths: Unique brand, strong customer loyalty, innovative product features.
Weaknesses: High pricing, limited geographic reach, dependence on a single supplier.
Opportunities: Expanding into new markets, developing complementary products, strategic partnerships.
Threats: Increasing competition, changing customer preferences, economic downturn.
By analyzing these factors, we can identify opportunities like leveraging their strong brand to enter new markets, or threats like potential price wars driven by increased competition.
Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses Table
| Competitor | Product Quality | Pricing | Marketing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluffy Clouds Inc. | High (Strength) | High (Weakness) | Strong (Strength) |
| Nimbus Nine Corp. | Average | Low (Strength) | Weak |
| Rainstorm Solutions | Low (Weakness) | Average | Strong (Strength) |
Evaluating Competitor Strategies: Competitive Analysis Template
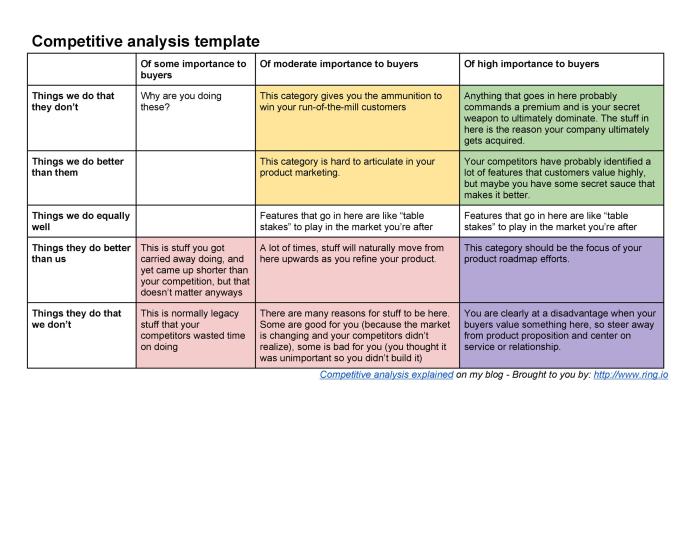
Understanding competitor strategies is like deciphering a rival’s playbook – essential for victory in the business arena. Ignoring your competitors’ moves is akin to playing chess blindfolded; you might get lucky, but your odds of success are significantly diminished. This section delves into the strategic landscape, exploring common approaches, their key elements, and their potential impact on market share. Prepare for a strategic deep dive, because this isn’t your grandma’s board game.
Three Common Competitive Strategies and Examples
Competitive strategies are the blueprints companies use to achieve their market objectives. These strategies, while varied, often fall under a few overarching umbrellas. Understanding these archetypes allows for more effective competitive analysis.
- Cost Leadership: This strategy focuses on becoming the lowest-cost producer in the industry, allowing for competitive pricing and higher profit margins. Walmart, for instance, has built its empire on this strategy, offering consistently low prices across a vast range of goods. Their relentless focus on efficiency and supply chain optimization allows them to undercut competitors.
- Differentiation: Differentiation involves creating a unique product or service that stands out from the competition. Apple, a master of this strategy, consistently commands premium prices due to its innovative design, user-friendly interface, and strong brand image. Their products are often more expensive than competitors’, yet they maintain high demand.
- Focus: This strategy targets a specific niche market segment rather than the broader market. A company specializing in organic, locally-sourced produce, for example, might focus on a customer base concerned about sustainability and ethical sourcing. This allows them to cater to a specific need and command higher prices than mass-market competitors.
Key Elements of a Successful Differentiation Strategy
A successful differentiation strategy isn’t simply about being “different”; it’s about being meaningfully different in ways that resonate with customers and justify a premium price. Several key elements contribute to this success.
- Unique Value Proposition: Clearly articulating what makes your product or service superior and addressing a specific customer need is paramount. This isn’t just about features; it’s about the benefits those features provide.
- Strong Brand Identity: A powerful brand creates an emotional connection with customers, fostering loyalty and willingness to pay more. This involves consistent messaging, visual identity, and customer experience.
- Effective Marketing and Communication: Highlighting the unique value proposition requires skillful marketing that reaches the target audience and effectively communicates the product’s differentiation.
- Sustainable Competitive Advantage: The differentiation must be difficult for competitors to imitate or replicate. This might involve patents, proprietary technology, or a deeply entrenched brand reputation.
Comparison of Marketing Strategies: Coca-Cola and Pepsi
Coca-Cola and Pepsi, two titans of the soft drink industry, employ distinct marketing strategies despite operating in the same market. Coca-Cola often focuses on evoking nostalgia and a sense of shared experience, employing sentimental campaigns that tap into cultural moments. Pepsi, on the other hand, frequently uses celebrity endorsements and a more youthful, edgy approach to appeal to a younger demographic. This contrasting approach highlights how even companies offering similar products can differentiate themselves through marketing.
Potential Implications of Different Competitor Strategies on Market Share
The impact of a competitor’s strategy on market share can be significant, leading to various outcomes.
- Cost Leadership: May lead to increased market share through lower prices, potentially squeezing profits for competitors. However, it can also lead to a price war, reducing profitability for all involved.
- Differentiation: Can command premium prices and increased profit margins, leading to higher market share if successful. However, failure to effectively communicate the value proposition can limit market penetration.
- Focus: Allows for specialization and capturing a niche market, potentially leading to high profit margins and a strong position within the segment. However, it limits the overall market reach and makes the company vulnerable to shifts in the targeted niche.
Developing a Competitive Profile Template
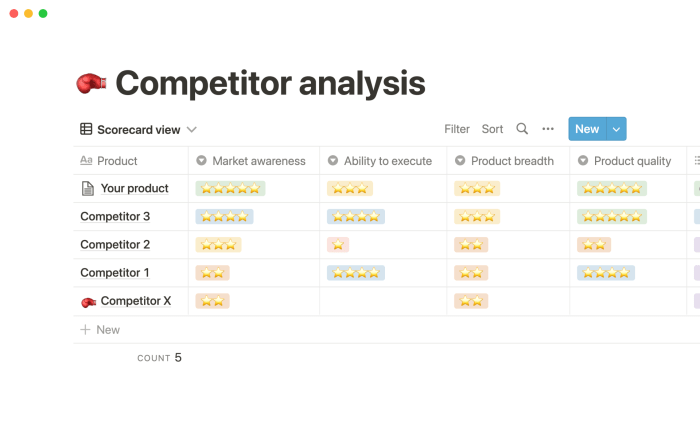
Crafting a competitive profile is like creating a meticulously detailed spy dossier, except instead of shadowy figures, you’re profiling companies. This crucial document provides a clear, concise, and – dare we say – entertaining snapshot of your competitors, allowing you to outmaneuver them in the marketplace with the grace of a seasoned chess grandmaster (or at least, a slightly above-average player).
A well-structured competitive profile template streamlines the process of gathering and organizing competitor information, preventing you from drowning in a sea of data points. Think of it as your secret weapon, a beautifully organized filing cabinet for all things competitor-related.
Competitor Profile Template Design
The design of your competitive profile template should be both informative and aesthetically pleasing. Remember, even spreadsheets can be beautiful (if you squint hard enough). The core elements should include sections for a company overview, their market positioning, and their key strategies. These sections allow for a comprehensive analysis, providing a holistic understanding of the competitor’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall market approach. Consider using a table format for clear organization and easy comparison across multiple competitors. A suggested template might include columns for: Competitor Name, Market Share, Key Products/Services, Target Audience, Pricing Strategy, Marketing Channels, and Strengths and Weaknesses.
Competitor Profile Information
Populating your competitive profile requires diligent research. Don’t just skim the surface; dive deep! For the Company Overview, include details such as company history, mission statement, organizational structure, and financial performance (if publicly available, of course – we’re not advocating for corporate espionage!). The Market Position section should detail the competitor’s market share, target audience, and overall market positioning (are they a niche player, a market leader, or somewhere in between?). Finally, the Key Strategies section should Artikel their pricing strategies, marketing approaches, product development cycles, and any other notable strategic initiatives. Think of it as a detective’s notebook, filled with clues about your opponent’s next move.
Remember to cite your sources! Plagiarism is a serious offense, even in the world of competitive analysis.
Visual Representations in a Competitive Profile
While we’re not including actual images here, let’s brainstorm some visually engaging ways to present your hard-earned data. A radar chart could effectively compare competitors across several key performance indicators (KPIs). Imagine a spiderweb of data points, each competitor represented by a unique shape, showcasing their relative strengths and weaknesses in various areas. Another option is a market share chart, a simple yet effective visual that instantly communicates market dominance (or lack thereof). A bar graph could effectively represent competitor market share, while a pie chart could showcase the breakdown of market segments. Even a simple SWOT analysis matrix can be visually appealing, and it clearly displays the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to each competitor. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, and a well-chosen chart is worth a thousand spreadsheets.
Consider your audience when selecting visual aids. A colorful infographic might be perfect for a casual presentation, while a more formal report might benefit from clean, minimalist charts.
Using the Competitive Analysis Template
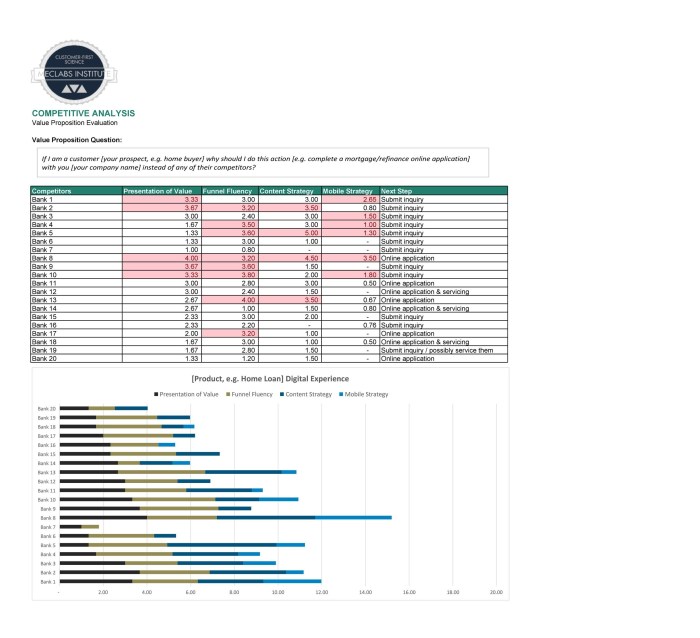
So, you’ve painstakingly gathered all this juicy intel on your competitors – now what? Don’t just let it gather dust like a forgotten tax return! This section reveals how to transform your competitive analysis into a strategic weapon, sharper than a ninja’s throwing star (and hopefully less likely to cause accidental eye injuries). We’ll show you how to use your findings to not only understand the market, but to conquer it.
Competitive Analysis Informs Business Strategy
The information gleaned from a competitive analysis acts as a roadmap for strategic decision-making. By understanding your competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, and strategies, you can identify gaps in the market, refine your own offerings, and anticipate potential threats. For example, if you discover a competitor is struggling with customer service, you can position your business as the reliable, customer-centric alternative. Conversely, if a competitor has a strong marketing campaign, you might need to rethink your own approach to ensure you’re not drowned out by their superior noise. The analysis isn’t just about copying; it’s about strategic differentiation and informed decision-making.
Using the Competitive Profile Template to Identify Market Opportunities, Competitive Analysis Template
Your meticulously crafted competitive profile template is more than just a pretty spreadsheet; it’s a treasure map to untapped market potential. By comparing your company’s strengths and weaknesses against those of your competitors, you can identify niches where you excel. Let’s say your analysis reveals that while your competitors focus on a high-price, luxury market, you possess the efficiency to deliver a comparable product at a significantly lower price point. Boom! You’ve just identified a market opportunity – the budget-conscious consumer segment. Similarly, if your competitors lack a certain feature or service that your company offers, you can highlight that unique selling proposition to attract customers seeking that specific offering.
Adapting the Template to Different Industry Contexts
The beauty of a well-designed competitive analysis template lies in its adaptability. While the fundamental principles remain the same (identifying competitors, analyzing strengths and weaknesses, etc.), the specific metrics and factors you consider will vary greatly depending on your industry. For example, a competitive analysis for a tech startup will focus on factors like technological innovation, app store rankings, and social media engagement, while a competitive analysis for a bakery might concentrate on customer reviews, ingredient sourcing, and local market share. The key is to tailor the template to include the relevant factors specific to your industry to ensure the analysis is both comprehensive and relevant.
Potential Actions Based on Competitive Analysis Findings
| Finding | Potential Action | Example | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Competitor A has superior customer service. | Improve customer service training and processes. | Implement a new CRM system and customer feedback program. | Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. |
| Competitor B dominates a specific niche. | Explore adjacent niches or develop new product features. | Introduce a new product line targeting a different customer segment. | Market expansion and diversification. |
| Competitor C has a weak online presence. | Invest in digital marketing and social media strategies. | Launch a targeted social media campaign and optimize website . | Increased brand awareness and online traffic. |
| Competitor D uses outdated technology. | Invest in R&D to develop innovative technologies. | Develop a new software platform that improves efficiency and reduces costs. | Competitive advantage and increased profitability. |
Closing Summary
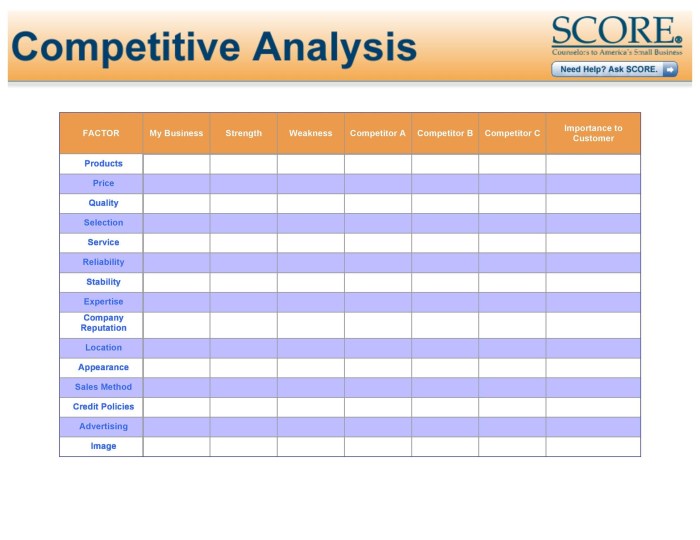
Mastering competitive analysis is no longer a luxury but a necessity for sustained business success. By systematically identifying, analyzing, and understanding your competitors, you can proactively shape your business strategy, identify lucrative opportunities, and ultimately, outmaneuver the competition. This template provides a robust framework to make that happen. So, sharpen your analytical skills, put on your detective hat, and embark on this journey to competitive mastery!
Essential Questionnaire
What if I have limited resources for competitive analysis?
Focus on your key direct competitors first. Utilize free resources like Google searches, company websites, and social media to gather initial information. Prioritize the most impactful areas of analysis.
How often should I update my competitive analysis?
Regular updates are crucial. Aim for at least quarterly reviews, or more frequently in dynamic markets. Major industry shifts or competitor actions warrant immediate reassessment.
Can I use this template for any industry?
Yes, the core principles apply across industries. However, you’ll need to adapt the specific areas of analysis (e.g., marketing channels, key performance indicators) to suit the unique characteristics of your industry.