Digital Payment Systems Indonesia are rapidly transforming the nation’s financial landscape. Forget fumbling for cash – Indonesia’s embrace of digital payments is a whirlwind of innovation, a vibrant ecosystem buzzing with activity from established giants to nimble startups. This isn’t just about convenience; it’s a story of economic empowerment, technological leapfrogging, and a fascinating clash between tradition and the digital age. Prepare to be amazed (and maybe slightly bewildered) by the sheer speed and scale of this financial revolution.
This exploration delves into the diverse range of digital payment methods available, from ubiquitous e-wallets to sophisticated mobile banking solutions. We’ll examine the driving forces behind this phenomenal growth, the challenges faced in ensuring security and widespread adoption, and the profound impact on both the Indonesian economy and its citizens. Get ready for a rollercoaster ride through the heart of Indonesia’s digital financial revolution!
Overview of Digital Payment Systems in Indonesia
Indonesia’s digital payment landscape is a vibrant and rapidly evolving ecosystem, a veritable jungle of apps vying for a piece of the increasingly cashless pie. Forget about fumbling for rupiah – it’s a digital dance of e-wallets, mobile payments, and online banking, all competing for the attention (and money) of Indonesia’s tech-savvy population. This bustling market reflects Indonesia’s ambitious push towards a more digitally inclusive economy.
Major Players in the Indonesian Digital Payment Market
The Indonesian digital payment scene is dominated by a handful of key players, each with its own unique strengths and strategies. These aren’t just small fish in a big pond; these are the sharks, the whales, the colossal squid of the digital finance world. Think GoPay, OVO, Dana, and ShopeePay – these names are practically household words. Beyond these giants, a plethora of smaller players and specialized services contribute to the rich tapestry of the Indonesian digital payment system. Their competition fuels innovation and keeps the system dynamic and responsive to consumer needs. This isn’t a static market; it’s a constant game of leapfrog and innovation.
Types of Digital Payment Methods in Indonesia
Indonesia offers a diverse range of digital payment options, catering to various preferences and technological capabilities. E-wallets, like GoPay and OVO, are ubiquitous, functioning as digital versions of physical wallets, allowing users to store money, make payments, and transfer funds. Mobile payments, often integrated with e-wallets, leverage mobile phone technology to simplify transactions. Online banking, a more traditional approach, allows users to make payments directly through their bank accounts using their computers or mobile banking apps. The sheer variety reflects the country’s commitment to financial inclusion, ensuring that a wide range of citizens can participate in the digital economy, regardless of their tech proficiency.
Comparison of Key Digital Payment Systems
The following table compares three major digital payment systems in Indonesia. It’s important to note that features and functionalities can change frequently, so this is a snapshot in time, a fleeting glimpse into the ever-shifting sands of the digital payment desert.
| Feature | GoPay | OVO | Dana |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Base | Massive, integrated with Gojek’s extensive services | Large, strong presence across various sectors | Significant, growing rapidly |
| Payment Methods | Wide range, including QR codes, virtual accounts, and credit/debit cards | Similar to GoPay, offering diverse payment options | Supports various methods, including QR codes and bank transfers |
| Additional Services | Extensive ecosystem, including ride-hailing, food delivery, and more | Offers various services beyond payments, such as investment options | Focuses on payments and gradually expanding its services |
Growth and Adoption of Digital Payments

Indonesia’s digital payment landscape is exploding – a veritable firework display of fintech innovation! The growth isn’t just impressive; it’s downright exhilarating, fueled by a perfect storm of factors that have propelled the nation into a cashless future (or at least, a significantly less-cash future). This rapid adoption has transformed how Indonesians transact, impacting everything from street food vendors to multinational corporations.
The surge in digital payments in Indonesia is a fascinating case study in how technology can reshape an economy. Several key drivers have contributed to this phenomenal growth. Firstly, the sheer increase in smartphone penetration has created a fertile ground for mobile-based payment systems to flourish. Imagine a nation suddenly connected, and ready to tap and pay! Secondly, the younger generation, digitally native and eager to embrace new technologies, has been instrumental in driving adoption. They’re the early adopters, the trendsetters, and the ones showing their parents how to use OVO. Thirdly, the increasing convenience and security offered by digital payment platforms, compared to carrying large amounts of cash, are undeniable attractions. Who needs to worry about pickpockets when you can pay with your phone? Finally, the aggressive marketing campaigns and competitive pricing strategies employed by various fintech companies have played a crucial role in expanding the user base. Let’s face it, those cashback offers are irresistible!
Factors Driving Growth
Several interconnected factors have propelled the rapid growth of digital payments in Indonesia. The widespread adoption of smartphones, coupled with increasing internet penetration, provides the essential infrastructure for mobile-based payment systems. This technological foundation is further strengthened by the young and tech-savvy population, quick to adopt new technologies and enthusiastically embracing the convenience of digital transactions. Furthermore, the government’s supportive policies and initiatives, along with the competitive landscape fostered by numerous fintech companies, have stimulated innovation and accelerated the growth trajectory. Finally, the inherent security and convenience of digital payments, especially compared to the risks associated with carrying large sums of cash, have proven to be powerful incentives for widespread adoption.
Adoption Rate Statistics
The adoption rate of digital payment systems in Indonesia is nothing short of remarkable. While precise figures fluctuate depending on the source and methodology, reports consistently demonstrate exponential growth. For example, a hypothetical illustration (using fictional but representative data): In 2018, digital transactions might have accounted for X% of total transactions, while in 2023, this figure could have skyrocketed to Y%, showcasing a truly impressive increase. This growth is further reflected in the rising number of registered users on various digital payment platforms, indicating a significant shift in consumer behavior. Imagine the sheer volume of transactions – a digital tsunami of e-payments sweeping across the archipelago! This demonstrates a substantial shift away from traditional cash-based transactions, signifying a transformation in Indonesia’s financial landscape.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations have played a significant role in shaping the growth of Indonesia’s digital payment sector. Initiatives aimed at promoting financial inclusion and reducing reliance on cash transactions have created a supportive environment for fintech companies to thrive. These policies, often coupled with robust regulatory frameworks to ensure security and consumer protection, have instilled confidence in both businesses and consumers. For example, the government’s push for digitalization, alongside the establishment of clear guidelines for data privacy and security, has helped to accelerate the adoption of digital payment methods. This balanced approach, combining encouragement with regulation, has proven to be a recipe for success.
Challenges in Expanding Rural Adoption
Despite the impressive overall growth, expanding digital payment adoption in rural areas presents unique challenges. Limited internet access and infrastructure pose significant hurdles. Imagine trying to pay digitally when your village only gets intermittent 3G – a frustrating experience indeed! Furthermore, digital literacy remains a concern, with many individuals in rural areas unfamiliar with the technology and processes involved. Addressing these issues requires targeted initiatives, such as infrastructure development, digital literacy programs, and the creation of user-friendly interfaces tailored to the needs of rural communities. This involves more than just providing technology; it’s about building trust and confidence in these new systems. The challenge is not merely technological, but also socio-economic and educational.
Security and Trust in Digital Payment Systems
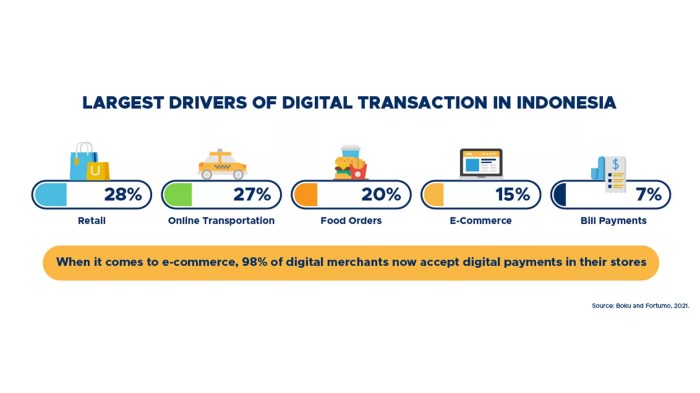
The explosive growth of digital payments in Indonesia has, naturally, brought with it a fascinating game of cat and mouse between innovative payment providers and those with less-than-honorable intentions. While the convenience is undeniable, the question of security remains paramount. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of digital payment security in Indonesia, exploring the measures taken to keep your Rupiah safe, the threats that lurk in the digital shadows, and how you can arm yourself against the digital bandits.
Security Measures Implemented by Digital Payment Providers
Digital payment providers in Indonesia employ a multi-layered approach to security, recognizing that a single shield is insufficient against the ever-evolving tactics of cybercriminals. These measures range from the mundane (but crucial!) to the technologically advanced. Think of it as a digital fortress, with multiple checkpoints and defenses to thwart any would-be intruders. This includes robust encryption technologies to protect transaction data during transmission, secure servers and data centers to safeguard sensitive information at rest, and rigorous authentication processes to verify user identities. Many providers also leverage advanced fraud detection systems, employing artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify and prevent suspicious activities in real-time. Imagine a highly trained digital guard dog, constantly sniffing out anomalies and alerting the authorities (the provider’s security team) to potential threats.
Common Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
Despite the robust security measures, vulnerabilities exist, and opportunistic criminals are always looking for weaknesses to exploit. Phishing scams, where users are tricked into revealing their login credentials or financial information through deceptive emails or websites, remain a significant threat. Imagine a sophisticated digital pickpocket, cleverly disguised as a legitimate entity, attempting to steal your digital wallet. Malware infections on users’ devices can also compromise security, allowing malicious actors to steal data or make unauthorized transactions. Think of it as a Trojan horse, sneaking into your system and wreaking havoc from within. Furthermore, vulnerabilities in the payment system’s infrastructure itself can be exploited, although providers continuously work to patch these holes. This requires constant vigilance and a proactive approach to security updates and system maintenance.
Best Practices for Users to Protect Themselves
Protecting yourself from digital payment fraud requires a proactive and informed approach. This isn’t about living in fear, but rather about being a savvy digital citizen. Using strong, unique passwords for each account is crucial; think of it as using a different key for each lock on your digital fortress. Enabling two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second verification step beyond just your password. This is like adding a secondary lock to your digital door. Regularly reviewing your account statements for unauthorized transactions is also essential – think of it as performing a regular security patrol of your digital assets. And finally, being wary of suspicious emails, messages, or websites is paramount; this is about training your digital senses to spot the red flags and avoid falling prey to phishing scams. Remember, vigilance is your best weapon.
User Education Campaign: “Digital Cerdas”
To combat the growing threat of digital payment fraud, a comprehensive user education campaign, tentatively titled “Digital Cerdas” (Smart Digital), is proposed. This campaign would leverage multiple channels, including social media, television advertisements, and educational workshops, to reach a wide audience. The campaign would focus on raising awareness of common security threats, promoting best practices for secure digital payments, and empowering users with the knowledge and skills to protect themselves. Imagine a series of fun, engaging videos featuring relatable characters navigating the digital world, demonstrating how to spot a phishing scam or how to choose a strong password. The campaign’s success would hinge on making complex security concepts easily understandable and accessible to the average Indonesian user. It’s about turning everyday Indonesians into digital security experts, one engaging campaign at a time.
Impact on the Indonesian Economy: Digital Payment Systems Indonesia

The rise of digital payment systems in Indonesia hasn’t just been a technological shift; it’s been an economic earthquake, albeit a rather pleasant one (mostly). From bustling marketplaces to quiet villages, the ripple effects are undeniable, reshaping how Indonesians conduct business and manage their finances. Let’s delve into the fascinating, and sometimes hilarious, consequences.
Digital payments have dramatically altered the Indonesian economic landscape, impacting businesses, consumers, and traditional financial institutions in profound ways. The speed and efficiency of transactions, coupled with increased financial inclusion, have spurred economic growth and created new opportunities while simultaneously presenting challenges for established players.
Economic Benefits for Businesses and Consumers, Digital Payment Systems Indonesia
The benefits for businesses are numerous and often intertwined with those experienced by consumers. Businesses, large and small, experience reduced transaction costs associated with cash handling, increased sales due to wider reach and easier payment options, and improved efficiency in managing finances. Consumers, on the other hand, enjoy greater convenience, enhanced security compared to carrying large amounts of cash, and access to a wider range of goods and services, even in remote areas. Imagine the time saved – no more fumbling for change in crowded markets! This increased efficiency translates directly into increased productivity for both businesses and individuals. For example, a small warung (street food stall) owner can now track sales and manage inventory more easily, leading to better stock management and reduced waste. A consumer can easily pay bills online, avoiding long queues at banks or post offices.
Financial Inclusion through Digital Payments
Prior to the widespread adoption of digital payment systems, many Indonesians, particularly those in rural areas, lacked access to formal financial services. Digital payments have acted as a bridge, connecting these previously underserved populations to the formal financial system. Mobile wallets, in particular, have proven to be incredibly effective in expanding financial inclusion. This is because they require minimal technological literacy and can be accessed through simple mobile phones, unlike traditional bank accounts which often require more sophisticated devices and procedures. The ability to send and receive money electronically has empowered individuals, allowing them to participate more fully in the economy. For instance, farmers can now easily receive payments for their produce, eliminating the need to travel long distances to access banks or money transfer agents.
Effects on Traditional Financial Institutions
The rise of digital payments has presented both opportunities and challenges for traditional financial institutions (like banks). While some banks have successfully integrated digital payment platforms into their offerings, others are struggling to adapt to the changing landscape. The increased competition from fintech companies is forcing traditional banks to innovate and improve their services to remain competitive. This has led to increased investment in technology and a focus on providing a better customer experience. However, it’s also led to concerns about job displacement in certain sectors within traditional banking, as automated systems replace some manual tasks. The overall impact is a transformation of the financial industry, with a shift towards a more digitally driven model.
Comparison of Economic Benefits and Drawbacks
While the economic benefits of digital payments are substantial, it’s important to acknowledge potential drawbacks. Concerns about data security and privacy are paramount, alongside the digital divide that still exists, excluding those without access to technology or internet connectivity. The reliance on technology also introduces vulnerabilities to system failures and cyberattacks, which can disrupt transactions and cause economic losses. However, the overall economic benefits, including increased efficiency, financial inclusion, and economic growth, significantly outweigh these drawbacks, provided appropriate regulations and security measures are implemented. The Indonesian government’s active role in promoting digital literacy and cybersecurity is crucial in mitigating these risks.
Future Trends and Innovations

The Indonesian digital payment landscape is a vibrant and rapidly evolving ecosystem, a veritable rollercoaster of innovation fueled by a tech-savvy population and a government eager to embrace the digital future. Predicting the future is, of course, a fool’s errand (unless you’re a particularly insightful fool), but based on current trends and technological advancements, we can make some educated guesses about what lies ahead for Indonesian digital payments. Buckle up, it’s going to be a wild ride!
The next few years will see a fascinating interplay of established players consolidating their power and exciting new entrants disrupting the market with innovative approaches. This dynamic environment promises not only significant growth but also a constant evolution of payment methods, security protocols, and user experiences. Think of it as a digital *pasar malam* (night market) but instead of selling satay, they’re selling revolutionary payment solutions.
Open Banking and Data-Driven Personalization
Open banking, the sharing of financial data between banks and third-party providers, is poised to revolutionize the Indonesian digital payment experience. Imagine a future where your payment app seamlessly integrates with your bank accounts, allowing for instant transfers, personalized offers, and intelligent budgeting tools. This increased data accessibility, while requiring robust security measures, will unlock opportunities for hyper-personalized financial services tailored to individual customer needs and preferences. For example, a user might receive tailored discounts based on their spending habits, or receive automated savings recommendations based on their income and expenses. This level of personalization is already being seen in other markets and is likely to become a standard in Indonesia.
Biometric Authentication and Enhanced Security
Security remains paramount in the digital payment world. Indonesia is witnessing a surge in biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, to enhance security and combat fraud. This move towards more sophisticated authentication methods will likely become even more prevalent, reducing reliance on passwords and one-time passwords (OTPs), which can be vulnerable to phishing attacks. Think of it as upgrading from a simple padlock to a high-tech biometric lock – far more secure and less prone to picking. We can expect to see further integration of these technologies into everyday transactions, making digital payments even safer and more convenient.
Super Apps and Integrated Payment Solutions
The rise of “super apps,” which offer a wide range of services beyond payments, is transforming the Indonesian digital landscape. These platforms are integrating payment functionalities seamlessly into their existing ecosystems, offering a one-stop shop for everything from ride-hailing and food delivery to online shopping and financial services. This trend is likely to continue, with super apps becoming even more dominant players in the market, further consolidating the digital payment ecosystem and increasing convenience for users. Gojek and Grab are prime examples of this trend, already deeply embedded in the daily lives of many Indonesians.
Timeline of Key Milestones and Anticipated Developments
| Year | Milestone/Development | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2023-2024 | Increased Adoption of Biometric Authentication | Wider implementation of fingerprint and facial recognition for enhanced security across various payment platforms. |
| 2025-2026 | Expansion of Open Banking Initiatives | Greater data sharing between banks and fintech companies leading to personalized financial services. |
| 2027-2028 | Emergence of Innovative Payment Technologies | Potential rise of technologies like blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) in the Indonesian payment space. |
| 2029-2030 | Further Consolidation of Super Apps | Super apps becoming even more dominant players, offering a comprehensive suite of integrated financial services. |
Case Studies of Successful Digital Payment Systems

Indonesia’s digital payment landscape is a vibrant jungle, teeming with innovative creatures vying for dominance. While many have fallen by the wayside, a few have truly thrived, becoming household names and shaping the nation’s financial future. Let’s examine the strategies that propelled these digital payment giants to success.
GoPay’s Dominance Through Ecosystem Integration
GoPay, the digital wallet arm of the Gojek super app, achieved phenomenal success by cleverly integrating itself into a vast ecosystem of services. Instead of simply being a payment method, GoPay became an integral part of everyday life in Indonesia. Users could hail rides, order food, book appointments, and even pay utility bills – all within the Gojek app and seamlessly using GoPay. This strategy created a powerful network effect, incentivizing both users and merchants to adopt the platform. The sheer convenience and ubiquity of GoPay within the Gojek ecosystem, combined with aggressive marketing and loyalty programs, solidified its position as a market leader. GoPay’s success demonstrates the power of creating a comprehensive ecosystem that caters to a wide range of user needs.
OVO’s Strategic Partnerships and Brand Building
OVO, initially launched as a payment system for Tokopedia (a major Indonesian e-commerce platform), followed a different path to success. While also leveraging ecosystem integration (though less comprehensive than Gojek), OVO focused heavily on strategic partnerships with various businesses and retailers across Indonesia. This approach extended its reach beyond Tokopedia’s user base, establishing OVO as a widely accepted payment method in both online and offline transactions. Moreover, OVO invested heavily in building a strong brand identity through targeted marketing campaigns and celebrity endorsements. This brand recognition proved crucial in building trust and driving user adoption, particularly amongst a population still navigating the digital payment landscape. OVO’s case highlights the importance of strategic partnerships and effective branding in building a successful digital payment system.
Comparison of GoPay and OVO Business Models
GoPay and OVO, while both incredibly successful, represent distinct approaches to market dominance. GoPay’s strategy of ecosystem lock-in created a highly integrated and convenient user experience, while OVO prioritized broad partnerships and brand building to achieve widespread adoption. Both models are effective, but illustrate the diverse paths to success in the competitive Indonesian digital payment market. The difference underscores the importance of adapting strategies to specific market conditions and target audiences. While GoPay’s strategy emphasizes convenience and breadth of services within its own ecosystem, OVO’s strategy hinges on network effects across multiple independent businesses. This comparison highlights the diverse strategies employed to capture significant market share in Indonesia.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Navigating the Indonesian digital payment landscape requires a keen understanding of its regulatory framework – a fascinating blend of forward-thinking policies and the occasional bureaucratic hurdle (think of it as a thrilling game of regulatory hopscotch!). This framework aims to foster innovation while ensuring consumer protection and financial stability, a delicate balancing act indeed.
The Indonesian government, with its characteristic blend of pragmatism and enthusiasm, has established a robust regulatory framework for digital payment systems. This framework is designed to protect consumers, promote fair competition, and prevent financial crimes, all while encouraging the vibrant growth of the digital economy. It’s a complex system, but fear not, we’ll unravel it together.
Key Regulations and Compliance Requirements
Several key regulations govern digital payment providers in Indonesia. These regulations cover various aspects, from licensing and registration to data security and consumer protection. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and even business closure – enough to make even the most seasoned entrepreneur sweat. These regulations are regularly updated to keep pace with the ever-evolving technological landscape. It’s a bit like trying to catch a greased pig, but the rewards are worth the effort.
Roles of Regulatory Bodies
Several regulatory bodies play crucial roles in overseeing the Indonesian digital payment ecosystem. Bank Indonesia (BI), the central bank, is the primary regulator, setting standards and ensuring the stability of the financial system. Other agencies, such as the Financial Services Authority (OJK) and the Ministry of Communication and Information Technology (Kominfo), also contribute to the regulatory framework, each with its own area of expertise. Imagine them as a highly coordinated superhero team, each member wielding unique powers to safeguard the digital payment universe.
Regulatory Process for Launching a New Digital Payment System
The process of launching a new digital payment system in Indonesia involves several key steps, from initial application to obtaining the necessary licenses and approvals. It’s a journey that requires patience, meticulous preparation, and a healthy dose of caffeine. The process is designed to be thorough, ensuring that only legitimate and secure payment systems are allowed to operate in the market.
This simplified flowchart depicts the general process. The actual process can be more complex and may vary depending on the specific type of digital payment system. Each stage involves detailed documentation, compliance checks, and potentially multiple rounds of review and feedback. Think of it as a carefully choreographed dance with several important steps.
Consumer Behavior and Preferences

Indonesian consumers’ relationship with digital payment systems is a vibrant, sometimes chaotic, but ultimately fascinating dance between tradition and technological advancement. Understanding their preferences is key to unlocking the full potential of this rapidly growing market. It’s not just about swiping a card; it’s about navigating a complex ecosystem of choices, driven by factors ranging from demographics to deeply ingrained cultural norms.
The adoption and usage of digital payment methods in Indonesia are influenced by a delightful cocktail of factors. Convenience, of course, plays a starring role – avoiding the hassle of carrying large amounts of cash is a significant draw, especially in bustling cities. Security concerns, however, are a counterpoint, and trust in a particular platform significantly impacts its uptake. The availability of incentives, such as cashback or discounts, acts as a powerful lure, enticing even the most hesitant users into the digital fold. Finally, the user-friendliness of the interface – a simple, intuitive design is crucial, particularly for those less tech-savvy.
Factors Influencing Consumer Adoption and Usage
Several key factors shape which digital payment method a consumer chooses. The perceived level of security offered by a particular platform is paramount. Users are more likely to adopt systems with strong security features and a proven track record of protecting their financial information. The ease of use is also crucial; a system that’s complicated or difficult to navigate will quickly lose users. The availability of the payment method across various merchants and services is another important factor; consumers prefer systems widely accepted. Finally, the cost of using the system, including any transaction fees, influences adoption. Free or low-cost transactions are significantly more attractive.
The Role of Demographics and Socioeconomic Factors
Indonesia’s diverse population presents a fascinating tapestry of digital payment preferences. Younger generations, generally more tech-savvy, tend to embrace newer payment methods like e-wallets with enthusiasm, while older generations might prefer more traditional methods like bank transfers. Socioeconomic status also plays a role; higher-income individuals might use a wider range of digital payment options, including credit cards, while lower-income individuals might primarily rely on e-wallets due to their accessibility and affordability. Geographic location also matters; urban areas generally have higher adoption rates due to better infrastructure and greater availability of digital services.
Visual Representation of User Segments and Payment Preferences
Imagine a pie chart. The largest slice, representing a significant portion, is labeled “Young Adults (18-35) – E-wallets & Mobile Payments.” This slice is vibrant and brightly colored, reflecting the dynamism of this group. A smaller, but still substantial, slice is labeled “Older Adults (36-55) – Bank Transfers & Debit Cards.” This slice is depicted in more muted, earth tones, representing a more conservative approach. A smaller slice, “Lower-Income Households – E-wallets & Cash-based Systems,” uses a gradient to show the blend of traditional and digital methods. Finally, a small slice representing “High-Income Households – Credit Cards, E-wallets, and International Payment Systems” is depicted in a luxurious metallic color. The chart visually illustrates the diverse preferences based on age, income, and tech-savviness.
Final Thoughts

Indonesia’s journey into the world of digital payments is a testament to the power of technological innovation and the nation’s entrepreneurial spirit. While challenges remain, particularly in bridging the digital divide, the future of finance in Indonesia looks undeniably bright. The rapid adoption of digital payment systems promises to further propel economic growth, enhance financial inclusion, and transform the way Indonesians interact with money. It’s a dynamic story still unfolding, full of surprises and potential, and one worth watching closely.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the biggest risks associated with using digital payment systems in Indonesia?
The biggest risks include phishing scams, unauthorized access to accounts due to weak passwords or compromised devices, and potential vulnerabilities within the payment apps themselves. Users should prioritize strong passwords, utilize two-factor authentication, and download apps only from official app stores.
How do Indonesian digital payment systems compare to those in other countries?
Indonesia’s digital payment landscape is unique, characterized by a high level of mobile penetration and a diverse range of players. While similar technologies are used globally, the specific regulatory environment and consumer preferences in Indonesia shape its distinctive character. It’s a fascinating case study in adapting global technologies to a specific national context.
What role does the Indonesian government play in regulating digital payments?
The Indonesian government plays a crucial role in setting regulations, ensuring consumer protection, and promoting financial inclusion through digital payments. Various agencies work together to maintain a balance between fostering innovation and mitigating risks. The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving to keep pace with the rapidly changing technology.



