Disaster Recovery Planning Checklist: Let’s face it, apocalypse-proofing your business isn’t exactly a picnic. But with the right plan, you can transform from a quivering wreck into a resilient, data-hoarding superhero. This checklist will guide you through the crucial steps of creating a plan that’s both comprehensive and, dare we say, slightly entertaining. We’ll tackle everything from identifying potential disasters (zombie apocalypse, anyone?) to meticulously testing your recovery strategy (because hoping for the best is a recipe for disaster).
This guide walks you through creating a robust disaster recovery plan, covering everything from defining your recovery objectives and assessing potential risks to implementing data backup strategies and failover mechanisms. We’ll explore different recovery methods, communication plans, and testing procedures, ensuring your business can weather any storm—figuratively and literally.
Defining Disaster Recovery Objectives: Disaster Recovery Planning Checklist
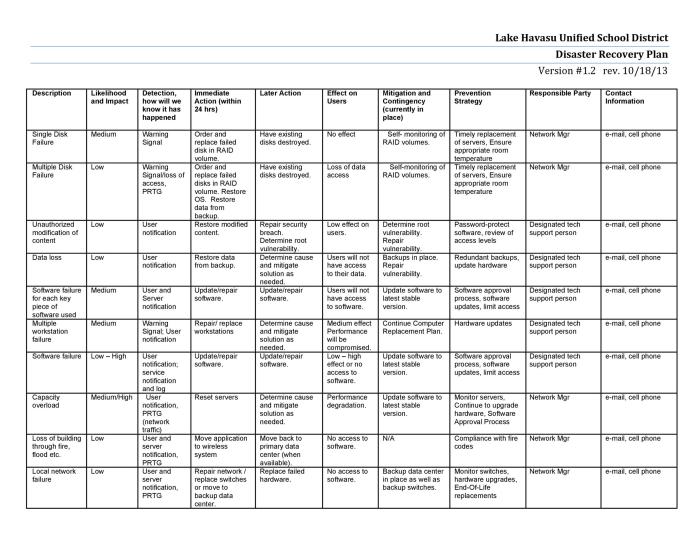
Crafting a robust disaster recovery plan isn’t just about avoiding a complete meltdown; it’s about ensuring your business survives a catastrophic sneeze – and emerges smelling like roses (or at least, like slightly less disastrous roses). A well-defined set of objectives is the cornerstone of this survival strategy, acting as your compass in the stormy seas of unforeseen events. Without clear objectives, your plan becomes a rudderless ship, adrift in a sea of panic.
The key components of a successful disaster recovery plan are intricately interwoven, much like a particularly well-made tapestry (albeit one that hopefully won’t be reduced to ashes). These components work together to ensure business continuity, minimizing downtime and data loss. They include identifying critical systems and data, establishing recovery time and point objectives (more on those delicious acronyms later), defining roles and responsibilities (so everyone knows who to blame when the fan hits the proverbial frazzle), and of course, regular testing and updates. Failure to address any of these could unravel the whole darn thing faster than a cheap sweater in a washing machine.
Critical Business Functions Requiring Prioritization
Prioritizing business functions during a disaster isn’t about playing favorites; it’s about identifying the lifeblood of your operation. Some functions are essential for immediate survival, while others can wait (a little). For example, in a financial institution, processing transactions might take precedence over updating the company blog (although, let’s be honest, the blog could probably wait). Similarly, a hospital would prioritize patient care over repainting the waiting room. The key is to categorize functions based on their impact on revenue, legal compliance, and overall business sustainability. A well-structured prioritization matrix, perhaps using a weighted scoring system, can be invaluable in this process. Think of it as a sophisticated triage system for your business.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
The RTO and RPO are the twin pillars of disaster recovery planning, providing a quantifiable measure of your recovery goals. The
Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
represents the maximum acceptable downtime after a disaster. For example, an RTO of 4 hours means your systems must be back online within 4 hours of a failure. The
Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
, on the other hand, specifies the maximum acceptable data loss. An RPO of 24 hours means you can afford to lose up to 24 hours’ worth of data. These objectives directly influence your recovery strategy and resource allocation. A low RTO and RPO will necessitate significant investment in infrastructure and redundancy, while higher values allow for a more cost-effective (but potentially riskier) approach. Consider a major e-commerce retailer: a high RTO could cost them millions in lost sales, whereas a hospital might have a lower RTO for critical patient data but a higher RTO for less critical administrative functions.
Establishing Measurable Goals for Disaster Recovery
Setting measurable goals is crucial for effective disaster recovery planning. This isn’t about vague aspirations; it’s about concrete, achievable targets. For instance, instead of saying “improve disaster recovery,” aim for “reduce RTO from 8 hours to 2 hours within the next year.” Or, instead of “better data backup,” strive for “implement a daily full backup and hourly incremental backups with a verified RPO of 1 hour.” These specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals provide a clear roadmap and allow for progress tracking. Regular reviews and adjustments based on testing and real-world scenarios are essential for keeping the plan aligned with evolving business needs and technology advancements. Think of it as setting fitness goals: “lose weight” is vague, but “lose 1 pound per week through diet and exercise” is measurable and actionable.
Risk Assessment and Identification
Let’s face it, disaster recovery planning isn’t exactly a picnic in the park. It involves staring into the abyss of potential calamities and figuring out how to not completely fall in. But fear not, intrepid planner! This section will guide you through a systematic risk assessment, transforming your apprehension into a well-structured, action-oriented plan. Think of it as a preemptive strike against chaos – only instead of ninjas, we’re using spreadsheets.
A thorough risk assessment is the bedrock of any effective disaster recovery plan. It’s the process of identifying potential threats, evaluating their likelihood, and determining their potential impact on your organization. This isn’t about predicting the future (though we wish we could!), but about understanding the range of possibilities and prioritizing accordingly. Imagine it as a highly sophisticated game of “what if?” with significantly higher stakes than Monopoly.
Potential Disaster Scenarios
Identifying potential disaster scenarios requires a broad perspective, encompassing both the predictable and the utterly unexpected. Think beyond the obvious – a hurricane might be on your radar, but have you considered a rogue employee deleting critical data? Or a sudden and inexplicable influx of adorable kittens overwhelming your server room? (Okay, maybe not the kittens, but you get the idea). The goal is to paint a comprehensive picture of potential disruptions.
- Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, wildfires – the usual suspects. Consider the geographical location of your organization and its vulnerability to specific natural events.
- Cyberattacks: Ransomware, phishing scams, denial-of-service attacks – the digital dark arts are always lurking. Evaluate your organization’s cybersecurity posture and identify potential weaknesses.
- Human Error: Accidental data deletion, misconfiguration of systems, and other human-induced calamities are surprisingly common. Think about your employee training and internal controls.
- Technological Failures: Hardware malfunctions, software glitches, power outages – the technological gremlins are always at work. Assess the reliability of your infrastructure and backup systems.
- Other Disasters: Consider less common but still impactful events like pandemics, civil unrest, or even a rogue meteor strike (it’s always a possibility, right?).
Likelihood and Impact Assessment
Once you’ve identified potential disasters, it’s time to quantify their likelihood and potential impact. This is where you’ll need to apply some critical thinking and, perhaps, a little bit of educated guesswork. The goal is to assign a probability and a severity score to each scenario, allowing for a more objective prioritization process.
| Disaster Scenario | Likelihood (1-5, 1 being unlikely, 5 being very likely) | Impact (1-5, 1 being minimal, 5 being catastrophic) |
|---|---|---|
| Power Outage | 3 | 4 |
| Ransomware Attack | 2 | 5 |
| Hurricane | 1 | 5 |
Risk Prioritization
Prioritizing risks is crucial for efficient resource allocation. A simple method involves multiplying the likelihood and impact scores from the previous step. The resulting number represents the overall risk score. Higher scores indicate higher-priority risks that should receive immediate attention. This isn’t about ignoring low-risk scenarios entirely, but about focusing your efforts on the most pressing threats first. Think of it as triage for your disaster recovery plan.
Risk Score = Likelihood x Impact
Risk Assessment Report
Finally, organize your findings into a concise and easily understandable report. This document should clearly Artikel all identified risks, their likelihood and impact scores, the calculated risk scores, and any recommended mitigation strategies. This report will serve as a crucial reference point throughout the development and implementation of your disaster recovery plan. Think of it as your organization’s survival guide for the apocalypse – only hopefully, a little less dramatic.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Let’s face it, data loss is the stuff of nightmares – especially for those of us who haven’t yet achieved digital immortality (still working on that one). A robust data backup and recovery strategy isn’t just a good idea; it’s the difference between a mildly inconvenient hiccup and a full-blown existential crisis for your business. Think of it as your digital life raft – you hope you never need it, but you’ll be awfully glad it’s there if things go south.
Data backup methods are varied, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, much like superheroes – some are all brawn, others all brains, and some are just plain weird. Choosing the right strategy depends on your specific needs and tolerance for risk (and the size of your data).
Data Backup Methods: Full, Incremental, and Differential Backups
Full backups, as the name suggests, copy *everything*. Think of it as a complete snapshot of your data at a specific point in time. Simple, straightforward, and easily restorable, but it’s also incredibly time-consuming and resource-intensive. Incremental backups, on the other hand, only copy the data that has *changed* since the last backup – whether full or incremental. This makes them faster and more efficient, but restoring data requires piecing together multiple backups, which can be a bit like assembling a particularly frustrating jigsaw puzzle. Differential backups, a happy medium, copy all data that has changed since the *last full backup*. This offers a balance between speed and restoration simplicity. Imagine it as a more organized jigsaw puzzle, where you only need to find the pieces missing from the last complete image.
Regular Data Backups and Offsite Storage Procedures
Regular backups are crucial – think of them as your daily vitamins for data health. The frequency depends on how much your data changes, but daily or at least weekly backups are generally recommended for mission-critical data. Offsite storage is equally vital. Imagine your office building catching fire. You’ve got a perfectly good backup… sitting in the incinerated server room. Not ideal. Offsite storage can be cloud-based, a separate physical location, or even a friend’s basement (though we wouldn’t recommend the last option for sensitive data). The key is redundancy – having your backups safely tucked away somewhere else entirely. A good procedure involves automated backups scheduled at regular intervals, followed by immediate transfer of the backups to an offsite location. This could be achieved through a combination of cloud storage and physical media shipped regularly.
Data Restoration from Backups: A Step-by-Step Guide
Data restoration is the moment of truth, when your carefully crafted backup strategy is put to the test. While the exact steps vary based on your backup software and storage method, the general process involves identifying the necessary backup, verifying its integrity (because corrupted backups are the bane of existence), selecting the data to restore, and then initiating the restoration process. Thorough testing after restoration is essential to ensure data integrity and functionality. This includes checking critical system files, application functionality, and data accuracy. A detailed procedure should be documented and regularly tested as part of disaster recovery drills.
Comparison of Data Recovery Solutions
Choosing the right data recovery solution is like choosing the right superhero for the job. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, but can be vulnerable to internet outages and security breaches. On-premise solutions offer more control and security but require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Let’s compare them side-by-side:
| Feature | Cloud-Based | On-Premise | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Subscription-based, potentially lower upfront cost | High upfront investment, ongoing maintenance costs | Balanced cost, depending on the split |
| Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere with internet access | Limited to the on-site location | Accessibility varies depending on the split |
| Security | Relies on the cloud provider’s security measures | Greater control over security measures | Security measures vary depending on the split |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to meet changing needs | Scalability can be challenging and expensive | Scalability depends on the cloud and on-premise components |
System Recovery and Failover Mechanisms
Ah, system recovery – the art of bringing your digital kingdom back from the brink of utter chaos. It’s less about battling dragons and more about battling… well, still dragons, but digital ones. Think rogue code, hardware meltdowns, and the occasional meteor strike (we’ve all been there, right?). Proper planning here isn’t just prudent; it’s the difference between a mildly inconvenient hiccup and a full-blown business apocalypse.
System recovery methods are like choosing your superhero: each has strengths and weaknesses. The key is understanding your organization’s needs and selecting the right approach. Failing to plan is planning to fail, as the old saying (probably) goes. So let’s dive into the details and avoid that fiery pit of despair.
Hot Site Recovery
A hot site is like having a fully equipped backup office, ready to go at a moment’s notice. Think of it as your organization’s emergency escape pod, fully stocked with all the necessary hardware, software, and even (ideally) your favorite ergonomic chair. Data is constantly replicated to the hot site, ensuring near-zero downtime. The cost? Steep, but the speed and minimal disruption often make it worth it for mission-critical systems. Imagine a major bank; they’d likely opt for a hot site to minimize disruption to customer transactions.
Cold Site Recovery
A cold site is the opposite: a bare-bones facility that provides only basic infrastructure (power, network connectivity, and maybe a coffee machine). It’s like having a pre-fab house waiting to be furnished; it’s there, but it needs significant setup before it’s operational. Data recovery relies on backups, and restoration can take days, even weeks. This approach is far cheaper than a hot site, making it suitable for organizations with lower recovery time objectives (RTOs). A smaller non-profit organization might find this a more financially feasible option.
Warm Site Recovery
The warm site is a happy medium – a compromise between the speed of a hot site and the cost-effectiveness of a cold site. It provides essential infrastructure plus some pre-configured hardware and partially replicated data. Think of it as a partially furnished apartment; you can move in quickly, but there’s still some unpacking and setting up to do. Warm sites offer a faster recovery than cold sites but at a lower cost than hot sites, making them a good balance for many businesses. A mid-sized company might choose this approach to strike a balance between cost and recovery time.
Failover Mechanisms Implementation
Implementing failover mechanisms involves creating a well-defined plan that Artikels the steps to switch to backup systems when primary systems fail. This plan should be rigorously tested to ensure its effectiveness. The plan needs to cover every aspect of the transition, from data synchronization to staff communication. Consider using automated tools to streamline the failover process, reducing the chances of human error during stressful situations. A well-executed failover plan should minimize disruption and ensure business continuity. Think of it as a carefully choreographed dance, where every step is crucial to a successful performance.
Failover Plan Design
A robust failover plan includes detailed steps for switching to backup systems, encompassing system shutdown procedures, data synchronization, and the activation of backup systems. This plan should be documented and regularly reviewed to ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness. The plan should also include communication protocols for informing stakeholders and customers of the disruption and the anticipated recovery time. A clear and concise plan minimizes confusion and ensures a smooth transition during a crisis. Consider using a flowchart or decision tree to visualize the process. This will make it easier to understand and follow during a stressful event.
Failover Mechanism Testing Procedures
Testing failover mechanisms is crucial for verifying their effectiveness and identifying potential weaknesses. Regular testing should simulate various failure scenarios to ensure the plan works as intended. This involves testing the entire process, from detecting the failure to restoring operations on the backup systems. The results of these tests should be documented and used to improve the plan over time. Think of it as a dress rehearsal for a play; the more you practice, the smoother the performance will be when the lights come on. Don’t just test the technical aspects; test the human element too. How well does your team respond under pressure?
Communication and Coordination Plan

A well-oiled communication machine is the lifeblood of any successful disaster recovery. Without clear, consistent, and (let’s be honest) slightly dramatic communication, your recovery efforts will resemble a flock of confused pigeons trying to find a crumb. Think organized chaos, but with less cooing and more frantic phone calls.
Effective communication during a disaster isn’t just about keeping everyone informed; it’s about coordinating actions, preventing duplicated efforts, and ultimately, saving your bacon (and your data). We’re talking about preventing the kind of situation where five teams are simultaneously trying to restore the same server, resulting in a spectacular digital traffic jam.
Stakeholder Notification Procedures
Establishing a clear communication tree is crucial. This involves identifying all stakeholders – from the CEO panicking in their penthouse suite to the intern frantically Googling “how to restore a server” – and determining how and when they will be notified. Consider using a multi-pronged approach: automated email alerts, SMS messages for immediate updates, and perhaps even a dedicated disaster recovery hotline (because sometimes, a good old-fashioned phone call provides that extra touch of reassuring panic). A detailed contact list, regularly updated, is absolutely non-negotiable. Imagine the chaos if your CEO’s contact information is still from his last job at a mime troupe.
Team Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are paramount. This prevents the dreaded “It’s not my job!” syndrome, which, during a disaster, can be as deadly as a rogue server. A well-defined responsibility matrix, assigning specific tasks to specific individuals, will prevent confusion and ensure everyone knows their place in the recovery orchestra. Consider incorporating a backup person for each role; because even the most dedicated tech wizard needs a bathroom break (or a stiff drink). This matrix should be readily accessible, perhaps displayed prominently on a giant screen in the emergency command center (with enough caffeine for everyone).
Tracking Recovery Progress
A robust tracking system is essential for monitoring the progress of recovery efforts. This could involve a centralized dashboard displaying the status of each task, regular status reports, or even a dedicated project management software. This allows you to identify bottlenecks, re-allocate resources, and maintain a clear picture of the recovery’s trajectory. Think of it as a digital war room, complete with flashing lights and possibly a miniature model of your data center (for dramatic effect). Without it, your recovery efforts could easily devolve into a game of digital whack-a-mole.
Examples of Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication during a crisis demands clarity, conciseness, and a touch of empathy. Consider using pre-written templates for common scenarios (e.g., server outage, data loss). Regular updates, even if they contain only reassuringly repetitive information, can prevent rumors from spreading faster than wildfire. During the infamous “Great Server Meltdown of 2023” (a hypothetical event, of course), one company successfully used a combination of automated emails, SMS messages, and a dedicated blog to keep stakeholders informed. This transparency, while initially slightly stressful, ultimately helped maintain trust and prevent unnecessary panic. Remember, clear and consistent communication can be the difference between a smooth recovery and a complete digital meltdown.
Testing and Maintenance of the Plan
Let’s face it, a disaster recovery plan gathering dust on a shelf is about as useful as a chocolate teapot in a hurricane. A well-crafted plan needs regular testing and maintenance to ensure it’s ready to spring into action when the metaphorical (or literal!) excrement hits the oscillating rotary blade. Think of it as a fire drill for your entire IT infrastructure – slightly less exciting, but infinitely more important.
Regular testing and updates are crucial to validating the effectiveness of your disaster recovery plan and ensuring its continued relevance in a constantly evolving technological landscape. Ignoring this vital aspect could lead to a painful and costly discovery during an actual disaster, a scenario best avoided. Think of it as insurance – you hope you never need it, but you’re awfully glad you have it when you do.
Comprehensive Testing Strategy
A robust testing strategy involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing various scenarios and levels of intensity. This might include tabletop exercises, where the team walks through the plan in a simulated disaster scenario, identifying potential bottlenecks and communication breakdowns. More intensive tests could involve partial system failures or even full-scale simulations of a disaster, migrating systems to the recovery site and verifying functionality. The frequency and scope of testing should be tailored to the criticality of the systems and the potential impact of a disruption. For example, a critical financial system might require more frequent and thorough testing than a less critical internal communication system. Regular testing allows for the identification and remediation of flaws, ensuring the plan’s effectiveness when needed. Imagine the chaos of discovering a crucial step is missing only *after* the disaster has struck.
Importance of Regular Plan Reviews and Updates
The business environment, technology, and even your own organization are constantly changing. What worked perfectly last year might be hopelessly outdated today. Regular reviews ensure the plan remains relevant and adaptable. Consider factors like changes in infrastructure, personnel, regulatory compliance, and the emergence of new threats. Think of your disaster recovery plan as a living document, constantly evolving to reflect the changing needs of your organization. Failing to update the plan could result in outdated procedures, insufficient resources, or an inability to address emerging threats, potentially exacerbating the impact of a disaster. A regularly updated plan is the difference between a smooth recovery and a complete meltdown.
Procedures for Documenting Changes and Updates
Maintaining a meticulous record of all changes and updates is crucial for transparency and accountability. A version control system, like Git, can be incredibly useful here. Each change should be documented with a clear description of the modification, the date of implementation, and the person responsible. This allows for easy tracking of the plan’s evolution and aids in identifying the source of any potential issues. A well-maintained version history provides a clear audit trail, enabling quick identification of changes and ensuring the most up-to-date version is always readily available. This also helps with regulatory compliance and demonstrates preparedness to auditors. Without proper documentation, chaos reigns supreme.
Schedule for Conducting Regular Tests and Reviews
Establishing a clear schedule is paramount for maintaining a proactive approach to disaster recovery. This schedule should Artikel the frequency and type of tests to be conducted, along with the responsible parties. A sample schedule might include quarterly tabletop exercises, annual partial system failure simulations, and a full-scale disaster recovery simulation every three years. The specific schedule should be tailored to the organization’s risk profile and the criticality of its systems. This is not a set-it-and-forget-it proposition. A proactive, scheduled approach ensures that the plan is regularly tested and updated, mitigating the risks associated with unforeseen events. Think of it as regular checkups for your organization’s health – preventative maintenance is always cheaper than emergency surgery.
Business Continuity and Resumption

Ah, business continuity – the art of keeping the metaphorical ship afloat even when a kraken of catastrophic proportions attacks. It’s less about surviving the initial deluge and more about emerging, slightly damp but otherwise unscathed, ready to serve your loyal customers (and maybe even attract a few new ones who were impressed by your resilience). This isn’t about simply restoring your systems; it’s about ensuring your business keeps ticking, even if it’s doing so with a slightly wonky rhythm for a while.
Maintaining business operations during a disaster requires a multifaceted approach, a strategic dance between technology, communication, and a healthy dose of “winging it” (only when absolutely necessary, of course). The key is to have pre-planned alternative operational models in place, ready to spring into action when the primary systems go down. Think of it as having a backup band ready to take the stage if the headliners get food poisoning.
Strategies for Maintaining Business Operations During a Disaster
Effective strategies hinge on preemptive planning. This involves identifying critical business functions and developing alternative methods for performing them. For instance, if your office is flooded, can your employees work remotely? Do you have a robust cloud infrastructure? Do you have a secret, hidden bunker stocked with enough supplies to keep your team productive for a week? (Just kidding… mostly). The strategy should Artikel procedures for shifting operations to alternative locations, utilizing backup systems, and ensuring communication channels remain open. A well-defined communication plan is vital, preventing chaos and enabling coordinated action. Think clear, concise instructions, not a rambling, panicked email chain.
Steps for Resuming Normal Business Operations After a Disaster
The resumption process isn’t a simple flick of a switch. It’s a carefully orchestrated re-entry. First, assess the damage – both to your physical infrastructure and your data. Then, prioritize the restoration of critical systems and functions, focusing on what brings the most value to your business. This phased approach ensures a smooth transition, avoiding the overwhelming chaos of trying to fix everything at once. Regular communication updates keep employees and stakeholders informed, minimizing anxiety and maintaining confidence. Imagine it like rebuilding a Lego castle after a toddler’s rampage – you tackle the towers first, then the walls, then the tiny, easily-lost flags.
Checklist for Verifying Successful Restoration of Business Operations
Before declaring victory and popping the champagne, a thorough verification process is essential.
- All critical systems restored and functioning correctly.
- Data integrity confirmed – no data loss or corruption.
- Employee access to necessary resources and systems restored.
- Communication channels fully operational.
- Business processes operating at pre-disaster levels (or close to it).
- Customer service restored and operating effectively.
This checklist ensures that not only are systems back online, but the business is functioning effectively and efficiently. Skipping this step is like baking a cake and forgetting the eggs – technically, it’s a cake, but not a very good one.
Procedures for Documenting Lessons Learned After a Disaster Recovery Event, Disaster Recovery Planning Checklist
After the dust settles (and the champagne is gone), it’s time for a post-mortem. Documenting lessons learned is crucial for continuous improvement. This involves recording what worked well, what didn’t, and what could be improved for future events. This isn’t about assigning blame; it’s about identifying weaknesses and strengthening your disaster recovery plan. A detailed report, including timelines, challenges faced, and solutions implemented, provides invaluable insights for future preparedness. Consider using a standardized format to ensure consistency and easy analysis across different recovery events. Think of it as a debriefing session – not for punishment, but for collective learning and growth. The goal is to make your next disaster recovery a little smoother, a little faster, and a lot less stressful.
Illustrative Scenario: Data Center Inferno

Our intrepid data center, affectionately nicknamed “The Fortress of Information” (mostly because of its surprisingly robust security system, not its architectural elegance), found itself facing an unexpected challenge: a rather significant fire. Picture this: a rogue server, overheating like a particularly stressed-out teenager, decided to stage a fiery protest. This minor electrical malfunction escalated into a full-blown inferno, filling the data center with smoke and the distinct aroma of burning silicon. The resulting chaos was, let’s just say, less than ideal.
The initial alarm bells (both literal and metaphorical) triggered our pre-planned disaster recovery procedures. Our meticulously crafted Disaster Recovery Plan, previously viewed with a mixture of cautious optimism and mild boredom during our regular training exercises, suddenly became the organization’s lifeline.
Incident Response and Activation of the Disaster Recovery Plan
The initial response was swift, thanks to our well-defined escalation protocols. Within minutes, the fire department was on-site, battling the blaze while our IT team, already remotely connected, began executing the disaster recovery plan. The plan’s first phase focused on securing personnel, containing the fire, and assessing the extent of the damage. Simultaneously, the secondary data center, located a safe distance away (and thankfully, without any disgruntled servers), was prepped for activation. The whole process, from initial alarm to beginning the data restoration process at the secondary site, took approximately 45 minutes. This was significantly faster than our projected 2-hour window, a small victory in the face of utter chaos.
Data Recovery and System Restoration
Our backup and recovery strategy, previously deemed “slightly over-engineered” by the budget committee, proved its worth. The automated backup system had already kicked in before the fire reached critical mass, creating a near-real-time replication of our critical data. The recovery process was meticulously documented and followed a predefined sequence. We prioritized the restoration of essential business applications first, followed by less critical systems. This phased approach minimized disruption and ensured a smooth transition back to normal operations. The entire process, from initiating data recovery to full system functionality, took approximately 12 hours.
Challenges Faced and Solutions Implemented
The situation presented several unforeseen challenges, but our team’s adaptability and the robust plan helped navigate them effectively.
The importance of having well-defined procedures and a practiced team cannot be overstated. The following points highlight some key challenges and their solutions:
- Challenge: Loss of network connectivity to the primary data center due to smoke and fire damage.
Solution: Our failover mechanisms, including redundant internet connections and a dedicated satellite link, were immediately engaged, ensuring continued communication and data access. - Challenge: Initial difficulties in accessing certain physical backups due to the intense heat and smoke damage to the storage area.
Solution: Our offsite backups, stored in a climate-controlled facility, were promptly accessed, ensuring data integrity and a smooth restoration process. A review of backup location strategies is currently underway. - Challenge: Employee stress and emotional impact from witnessing the fire and subsequent disruption.
Solution: Our Employee Assistance Program was immediately activated, offering counseling and support to affected employees. Regular communication updates helped maintain morale and transparency.
Final Thoughts
Creating a comprehensive disaster recovery plan might seem daunting, but remember, it’s an investment in your business’s future. By meticulously following this checklist, you’ll not only safeguard your valuable data and systems but also build a resilient organization capable of bouncing back from any adversity. So, go forth and conquer—or at least, prepare for the unexpected with a smile. After all, a little preparedness can go a long way in avoiding a catastrophic meltdown (of the digital, or possibly even the actual, kind).
FAQ Section
What if my disaster recovery plan is too complicated for my team to understand and use?
Simplicity is key! A complex plan is useless if no one can implement it. Use clear, concise language, diagrams, and even flowcharts to make it accessible and easy to follow. Regular training and drills are also crucial.
How often should I test my disaster recovery plan?
Regular testing is vital. Aim for at least annual full-scale tests and more frequent smaller tests of individual components. The frequency depends on your risk tolerance and the criticality of your systems.
What’s the difference between RTO and RPO?
RTO (Recovery Time Objective) is the maximum acceptable downtime after a disaster. RPO (Recovery Point Objective) is the maximum acceptable data loss. Balancing these two is crucial for effective planning.
How do I choose the right data backup solution?
Consider factors like cost, storage capacity, recovery speed, security, and compliance requirements. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and offsite protection, while on-premise solutions provide more control.