Financial Dashboard Template: Prepare yourself for a rollercoaster ride through the exhilarating world of financial data visualization! We’ll unravel the mysteries of crafting the perfect dashboard, from choosing the right charts (pie charts, are you really necessary?) to wrestling with data sources that seem determined to remain elusive. Buckle up, it’s going to be a wild, yet informative, journey.
This exploration will cover everything from the basic components of a financial dashboard—think of it as the cockpit of your financial empire—to advanced techniques involving AI and machine learning (because who doesn’t want a robot to manage their money?). We’ll examine different dashboard types for personal finance, businesses of all sizes, and even investment portfolios. We’ll also tackle the crucial design considerations, ensuring your dashboard isn’t just functional but also aesthetically pleasing (because let’s face it, pretty charts make data more digestible).
Defining “Financial Dashboard Template”
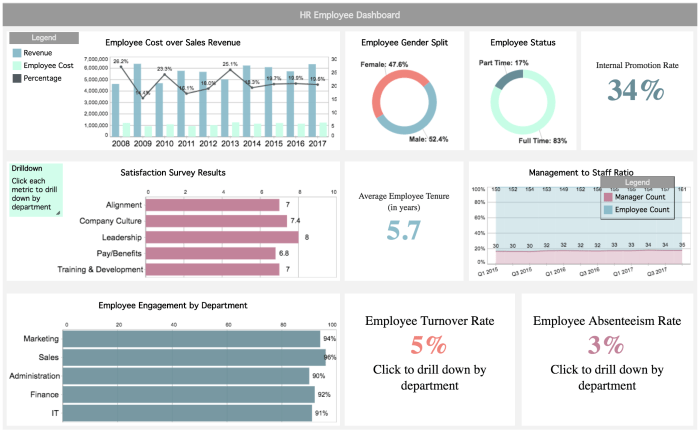
A financial dashboard template, in its purest form, is a pre-designed framework for visualizing key financial data. Think of it as a meticulously crafted spreadsheet, but far more visually appealing and insightful – less “Excel spreadsheet” and more “Mission Control for your money.” It’s essentially a customizable blueprint that allows you to track your financial health, whether you’re managing a lemonade stand or a multi-national corporation. The beauty lies in its ability to transform raw numbers into easily digestible, actionable information.
Core Components of a Typical Financial Dashboard Template
A typical financial dashboard template usually includes several key components working in harmony. These components might vary slightly depending on the specific needs of the user, but generally speaking, you’ll find elements such as charts and graphs (bar charts, pie charts, line graphs – the usual suspects), key performance indicators (KPIs) prominently displayed, and data tables presenting detailed information. Interactive elements, such as filtering and drill-down capabilities, often enhance the user experience, allowing for a deeper dive into the data. A well-designed dashboard is more than just pretty pictures; it’s a powerful tool for decision-making.
Examples of Different Types of Financial Dashboards
The applications of financial dashboards are as diverse as the financial situations they represent. For example, a personal financial dashboard might track income, expenses, savings goals, and debt levels. A visual representation of spending habits, perhaps categorized by spending categories (groceries, entertainment, etc.), would be a common feature. On the other hand, a business financial dashboard would focus on metrics like revenue, profit margins, cash flow, and key sales figures. Imagine seeing a real-time update on sales performance across different product lines. Finally, an investment dashboard could monitor portfolio performance, asset allocation, and risk levels, allowing for quick adjustments to investment strategies. Think of it as a constantly updated snapshot of your investment journey.
Key Metrics Commonly Displayed on Financial Dashboards
The specific metrics displayed depend heavily on the context. However, some common themes emerge. For instance, revenue and profit are almost always present in business dashboards. Net worth is a cornerstone metric in personal finance dashboards, representing the difference between assets and liabilities. For investment dashboards, return on investment (ROI) and portfolio diversification are key indicators of performance and risk. These are just a few examples; the choice of metrics should always be driven by the specific goals and objectives of the user.
Software Used to Create Financial Dashboards
Numerous software options exist for creating financial dashboards, catering to different levels of technical expertise and budget. Below is a table outlining some popular choices:
| Software | Description | Ease of Use | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Excel | Widely accessible spreadsheet software; capable of creating basic dashboards. | Beginner-friendly | Subscription or one-time purchase |
| Google Sheets | Cloud-based spreadsheet software; offers collaboration features. | Beginner-friendly | Free (with limitations), paid options available |
| Tableau | Powerful data visualization tool; ideal for complex dashboards. | Intermediate to Advanced | Subscription-based |
| Power BI | Microsoft’s business analytics service; provides interactive dashboards. | Intermediate to Advanced | Subscription-based |
Design Considerations for Financial Dashboard Templates

Crafting a truly magnificent financial dashboard is less about spreadsheets and more about a captivating narrative whispered to the user. It’s about transforming cold, hard numbers into a compelling story that speaks volumes without uttering a single word (except maybe a celebratory “cha-ching!”). The key? A thoughtful blend of user interface and user experience.
The Importance of UI and UX in Dashboard Design
A well-designed financial dashboard isn’t just pretty; it’s practical. The user interface (UI) is the visual presentation – the colors, fonts, and layout – while user experience (UX) encompasses the overall interaction and ease of use. A clunky, confusing dashboard, no matter how aesthetically pleasing, is akin to a Ferrari with square wheels – beautiful, but utterly useless. Think of UI as the makeup and UX as the personality; both are crucial for a successful and engaging experience. A poor UX can lead to misinterpretations, missed opportunities, and possibly, a very grumpy CFO. Therefore, intuitive navigation, clear labeling, and a consistent design language are paramount.
Best Practices for Data Visualization in Financial Dashboards
Data visualization isn’t just about presenting numbers; it’s about revealing insights. The goal is to transform complex financial data into easily digestible visuals that tell a story, highlighting key trends and patterns. This requires careful consideration of chart types, color palettes, and overall layout. For example, a cluttered dashboard with too many charts can overwhelm the user, rendering it practically useless. A well-designed dashboard, on the other hand, will guide the user’s eye to the most important information, presenting it in a clear and concise manner. Think of it as a carefully curated art exhibition, not a chaotic garage sale.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Different Chart Types
Choosing the right chart is crucial. Bar charts excel at comparing discrete categories, while line graphs are ideal for showing trends over time. Pie charts, while visually appealing, can become cumbersome with too many slices, making them less effective for complex datasets. For example, a bar chart might perfectly illustrate year-over-year revenue growth, while a line graph could track daily stock prices. A pie chart could be used to illustrate the breakdown of expenses by category, but only if the categories are limited to avoid a confusing visual mess. Consider the data and the message you want to convey when selecting your chart type; the wrong chart can obscure, rather than illuminate, the data.
Sample Layout for a Financial Dashboard Template
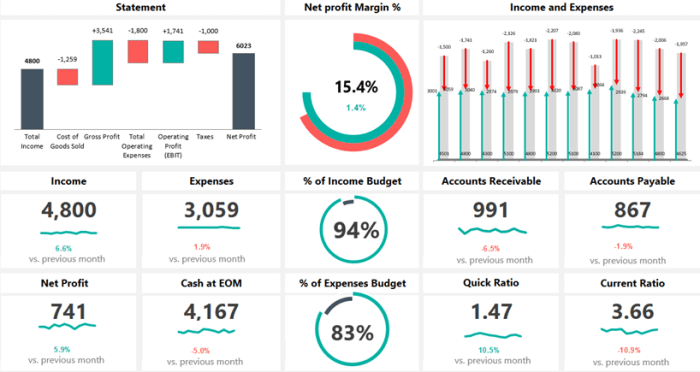
Imagine a dashboard divided into three sections. The top section displays key performance indicators (KPIs) such as revenue, profit margin, and cash flow, using large, easily readable numbers and clear icons. The middle section features interactive charts showing trends in key metrics over time (e.g., a line graph for revenue growth and a bar chart for expense categories). The bottom section provides detailed information, such as a breakdown of expenses by department or a comparison of actual vs. budgeted performance, perhaps displayed in a well-organized table. This hierarchical layout ensures that the most critical information is immediately visible, while allowing users to drill down for more detailed analysis as needed. This layout prioritizes clarity and accessibility, enabling users to quickly grasp the overall financial picture and investigate specific areas of interest.
Data Integration and Sources for Financial Dashboards
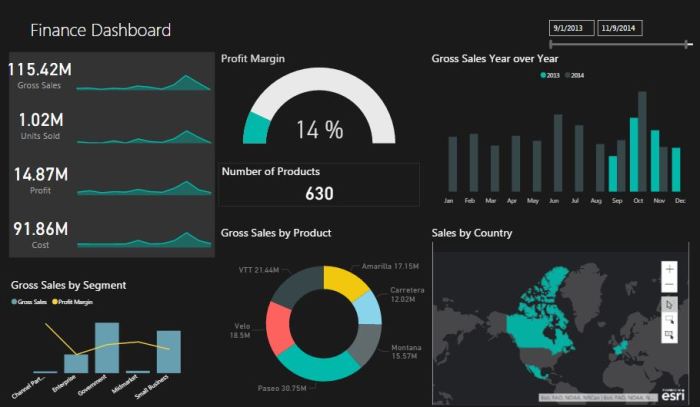
Building a financial dashboard is like constructing a magnificent castle: you need the right blueprints (your template) and, crucially, the bricks (your data). Without a reliable flow of accurate financial information, your dashboard becomes a glorified picture frame, empty and utterly pointless. This section explores the thrilling world of data integration, tackling the methods, security concerns, and reliable sources that will make your financial dashboard a true marvel of modern accounting.
Data integration is the process of bringing together information from disparate sources into a unified view. Think of it as a financial orchestra, where each instrument (data source) plays its part to create a harmonious whole (your dashboard). Failing to integrate your data effectively is like having a drummer who only plays on Tuesdays – it throws the entire performance off-kilter.
Methods for Connecting a Dashboard to Data Sources
Connecting your dashboard to your data sources involves choosing the right tools for the job. This isn’t about choosing between a hammer and a feather duster; it’s about selecting the appropriate instrument to handle the specific task. Spreadsheet integration is perfect for small-scale operations, while database connections provide scalability for larger enterprises. APIs offer flexibility and real-time updates, but require a bit more technical expertise. The key is to find the method that best fits your specific needs and technical capabilities.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Financial data is, quite obviously, sensitive. Protecting this information requires careful consideration. Unauthorized access could lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Strong passwords, encryption, and access controls are your knights in shining armor, protecting your valuable data from the dragons of cybercrime. Regular security audits are like a castle’s moat, creating a barrier to keep out the unwanted guests.
Examples of Reliable Data Sources for Financial Information
Choosing your data sources wisely is paramount. You wouldn’t build a castle on a foundation of sand, would you? Reliable sources include accounting software (Xero, QuickBooks), banking APIs, and reputable financial data providers (Bloomberg, Refinitiv). Each source offers a unique set of capabilities and data points, allowing you to tailor your dashboard to your specific needs. Remember, the quality of your data directly impacts the accuracy and usefulness of your dashboard.
Connecting a Spreadsheet to a Simple Dashboard Template
Let’s assume you’re using a simple dashboard template and a spreadsheet containing your financial data. Here’s a straightforward, step-by-step guide:
- Prepare your spreadsheet: Ensure your data is clean, organized, and consistent. Use clear column headers and avoid unnecessary blank rows or columns. This is the foundation upon which your dashboard will be built.
- Choose your dashboard template: Select a template that aligns with your needs and technical skills. Many free and paid options are available.
- Import your data: Most dashboard templates offer direct import functionality from spreadsheets. Follow the template’s instructions to import your data. This is usually as simple as selecting your spreadsheet file.
- Map your data: Link the columns in your spreadsheet to the corresponding fields in your dashboard template. This is like assigning roles in a play – each data point needs its place on the stage.
- Test and refine: Once the data is linked, thoroughly test your dashboard. Ensure all the charts and graphs display correctly. Make any necessary adjustments to improve clarity and accuracy. This is the final polish, ensuring your dashboard shines.
Customization and Functionality of Financial Dashboard Templates
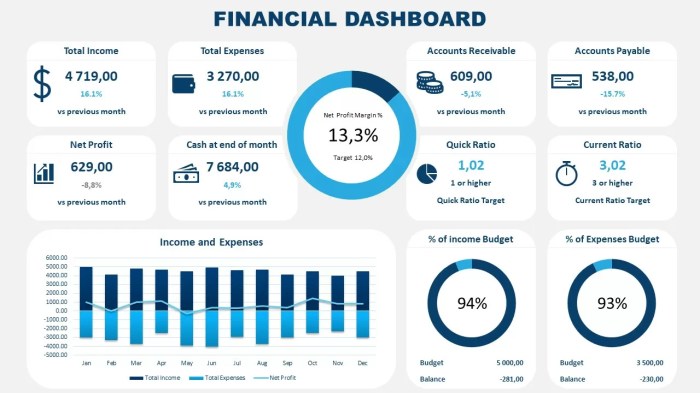
Choosing the right financial dashboard template is like picking the perfect pair of shoes – you need something comfortable, stylish, and that fits your needs perfectly. Pre-built templates offer a convenient starting point, while custom-built dashboards provide unparalleled flexibility. Let’s delve into the delightful world of dashboard customization and the features that make them truly shine.
The functionality of a financial dashboard is directly tied to its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights. A well-designed dashboard should not only display key performance indicators (KPIs) but also offer interactive elements, forecasting capabilities, and automated alerts to keep you ahead of the game. Think of it as your financial crystal ball, but without the mystical fog and questionable accuracy.
Pre-built versus Custom-built Dashboards
Pre-built templates are like off-the-rack suits – readily available and relatively inexpensive. They offer a quick solution for those with basic needs and limited technical expertise. However, they might not perfectly fit your specific requirements, potentially leading to compromises in functionality or aesthetics. Custom-built dashboards, on the other hand, are akin to bespoke tailoring. They require more upfront investment in time and resources but offer unparalleled flexibility and customization, allowing you to create a dashboard perfectly aligned with your unique business needs and preferences. Imagine a dashboard designed to precisely reflect the quirks and intricacies of your specific financial landscape; that’s the power of custom-built.
Features Enhancing Dashboard Functionality
Several features can dramatically enhance the utility of your financial dashboard, transforming it from a simple display of numbers into a powerful decision-making tool. These features are not mere embellishments; they’re the secret sauce that elevates your financial insights.
- Alerts: Imagine your dashboard sending you a gentle (or not-so-gentle) nudge when a critical KPI deviates from the expected range. This proactive notification system ensures you’re always aware of potential problems, allowing for timely intervention.
- Forecasting: Predictive analytics is the next level of financial understanding. By integrating forecasting capabilities, your dashboard can project future trends based on historical data, allowing for proactive planning and strategic decision-making. Think of it as having a financial weatherman, predicting potential storms before they hit.
- Reporting: The ability to generate customized reports directly from your dashboard is invaluable. This eliminates the need for manual data extraction and report generation, saving you time and reducing the risk of errors. It’s like having a dedicated financial scribe, always ready to produce beautifully formatted reports at your command.
Incorporating Interactive Elements, Financial Dashboard Template
Interactive elements transform a static dashboard into a dynamic and engaging tool. These features allow for deeper exploration of the data, fostering a more intuitive and insightful experience. They’re the secret weapons to unlock the full potential of your financial data.
- Drill-down capabilities: Allow users to delve deeper into specific data points, uncovering granular details and uncovering hidden trends. This is like having a magnifying glass for your financial data, revealing insights that might otherwise be missed.
- Interactive charts and graphs: Visualizations are key to effective data communication. Interactive charts and graphs allow users to manipulate data displays, exploring different perspectives and gaining a more comprehensive understanding. It’s like having a visual storyteller, presenting your financial narrative in a compelling and easily digestible format.
- Data filtering and sorting: The ability to filter and sort data based on specific criteria allows users to focus on relevant information and quickly identify key trends. This is like having a highly skilled librarian, quickly retrieving the precise information you need.
Features in Popular Financial Dashboard Templates
Many popular templates boast a range of features designed to streamline financial management. The following are commonly found features, often tailored to specific industries or needs. Think of this as a “best-of” list for your financial dashboard shopping spree.
- Real-time data updates
- Customizable KPIs and metrics
- Integration with accounting software
- Automated report generation
- Data visualization tools (charts, graphs, maps)
- Security features (user access control)
- Mobile accessibility
- Data export capabilities
Illustrative Examples of Financial Dashboard Templates

Financial dashboards are like the Swiss Army knives of finance – incredibly versatile and useful, but only if you know how to use them. Let’s explore some examples, showcasing the diverse applications of these powerful tools. We’ll avoid any overly complicated jargon, promising a delightfully straightforward (and hopefully, amusing) journey through the world of financial dashboards.
Financial Dashboard Template for a Small Business Owner
A small business owner needs a dashboard that’s clear, concise, and tells a story at a glance. Imagine a dashboard divided into four quadrants. The top left quadrant displays key revenue metrics: total revenue for the month, year-to-date revenue, and revenue compared to the previous year (with a charming little up or down arrow indicating growth or, *ahem*, shrinkage). The top right quadrant focuses on expenses, showing total expenses, major expense categories (like rent, salaries, and marketing), and a comparison to the budgeted expenses. The bottom left quadrant presents profitability indicators: net profit margin, gross profit, and cash flow. Finally, the bottom right quadrant provides a simple inventory overview, displaying low-stock items that need immediate attention – because nothing says “fun” like a sudden shortage of essential supplies. This layout prioritizes quick understanding of the business’s overall health.
Personal Finance Dashboard
Picture a personal finance dashboard resembling a well-organized spreadsheet, but far more visually appealing. The left side shows a summary of assets and liabilities, including bank accounts, investments, and outstanding debts. A pie chart elegantly displays the allocation of assets, highlighting the proportion in savings, investments, and emergency funds. The right side features monthly income and expense tracking, with a bar graph comparing actual spending against a pre-set budget. A section dedicated to upcoming bills provides a visual calendar view, avoiding any nasty surprises of forgotten payments. A small section at the bottom provides a net worth calculation, updated dynamically as the user inputs data. This user-friendly design allows for quick financial overviews and promotes mindful spending habits. Think of it as your personal financial therapist, always available and completely judgment-free (mostly).
Financial Dashboard Template for Investment Tracking
For investment tracking, imagine a dashboard dominated by interactive charts and graphs. A prominent area displays the overall portfolio performance, showing the total value, percentage change over time, and key performance indicators (KPIs) like Sharpe ratio and Alpha. Individual asset allocations are shown in a dynamic pie chart, allowing the user to easily see the weighting of different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.). A table below provides detailed information on each asset, including current price, purchase price, dividends received, and unrealized gains/losses. Think of it as a constantly updated snapshot of your investment journey, providing insights into performance and risk levels. No more frantic spreadsheet scrolling – just pure, unadulterated investment clarity.
Financial Dashboard Template for a Large Corporation
A large corporation’s dashboard is a beast of a different color – a multi-layered, highly secure behemoth. The top-level dashboard, accessible to executives, displays high-level summaries of key performance indicators (KPIs) across different business units. This overview uses aggregated data, focusing on profitability, revenue growth, and market share. Mid-level managers have access to more detailed dashboards, providing insights into their specific departments, including operational metrics, team performance, and project progress. Finally, individual employees might have access to personalized dashboards tailored to their roles, showing metrics relevant to their day-to-day tasks. Access control is crucial, ensuring data security and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information. It’s a carefully orchestrated symphony of data, ensuring everyone gets the information they need, without the chaos of a rogue data orchestra.
Future Trends in Financial Dashboard Templates
The world of financial dashboards is hurtling towards a future as exciting as a spreadsheet filled with unexpectedly high returns. Gone are the days of static charts and tables; the future is dynamic, intelligent, and frankly, a bit dazzling. Prepare yourself for a whirlwind tour of what’s coming next in the thrilling realm of financial data visualization.
Predicting the future is, of course, a risky business (much like investing itself!), but based on current trends and technological advancements, we can make some educated guesses about the evolution of financial dashboards.
The Rise of AI and Machine Learning in Financial Dashboards
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are poised to revolutionize financial dashboards, moving them beyond simple data presentation to proactive insights and predictive analytics. Imagine a dashboard that not only shows you your current profit margins but also predicts future trends based on market analysis and historical data, complete with a charmingly understated warning if things look a bit dicey. This isn’t science fiction; companies are already using AI to identify patterns and anomalies in financial data, providing users with early warnings of potential risks and opportunities. For example, a dashboard could use machine learning algorithms to analyze sales data and predict future demand, allowing businesses to optimize inventory and resource allocation. This predictive capability could transform decision-making, moving from reactive to proactive, saving both time and money.
Evolution of Data Visualization Techniques
Data visualization is undergoing a dramatic transformation. We’re moving beyond traditional bar charts and pie graphs towards more sophisticated and interactive visualizations. Think 3D models that dynamically display financial performance, augmented reality overlays that show real-time data on physical assets, and even virtual reality environments that allow users to “walk through” their financial data. Imagine exploring your portfolio performance as if you were navigating a vibrant, interactive cityscape, where each building represents an investment, its size reflecting its value. This isn’t just about making dashboards look pretty; it’s about making complex data more accessible and understandable to a wider audience. The goal is intuitive comprehension, even for those less familiar with the intricacies of financial analysis.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Financial Dashboard Design
Emerging technologies like blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing are set to significantly impact financial dashboard design. Blockchain technology, for example, could be used to enhance the security and transparency of financial data, ensuring that dashboards display accurate and verifiable information. The IoT, meanwhile, could integrate real-time data from various sources, providing a more holistic view of financial performance. Cloud computing offers scalability and accessibility, allowing dashboards to be accessed from anywhere, at any time, on any device. The integration of these technologies promises a future where financial dashboards are not only more informative but also more secure, reliable, and accessible.
Conceptual Futuristic Financial Dashboard Template
Imagine a dashboard with a sleek, minimalist design. The background is a calming gradient of blues and greens, evoking a sense of stability and growth. Instead of static charts, the dashboard uses interactive 3D models to display key financial metrics. For instance, a rotating globe could showcase global investment performance, with each country represented by a light that pulsates in intensity according to its economic activity. An augmented reality overlay could show real-time stock prices superimposed on a physical trading floor, providing an immersive experience. The dashboard also incorporates AI-powered predictive analytics, providing users with forecasts and risk assessments. Users could interact with the dashboard using voice commands or gestures, navigating the data with ease. The entire system would be secured using blockchain technology, ensuring data integrity and security. This conceptual dashboard represents a future where technology enhances human understanding of complex financial data, leading to better decisions and greater financial success.
Final Summary

So, there you have it: a whirlwind tour of the captivating world of financial dashboard templates. From the simple elegance of a personal finance tracker to the complex intricacies of a corporate behemoth’s dashboard, we’ve covered the spectrum. Remember, the key is to find the right balance between functionality and aesthetics, creating a tool that empowers you to make informed financial decisions—without inducing a migraine. Now go forth and conquer your spreadsheets!
Q&A
What’s the difference between a dashboard and a report?
Dashboards provide a real-time, at-a-glance overview of key metrics. Reports offer more detailed, historical analysis.
Can I create a financial dashboard without coding skills?
Absolutely! Many user-friendly tools and pre-built templates require minimal or no coding experience.
How often should my financial dashboard be updated?
The frequency depends on your needs; some dashboards update in real-time, while others may update daily, weekly, or monthly.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when designing a financial dashboard?
Overcrowding with too much data, using inappropriate chart types, and neglecting user experience are common pitfalls.