Financial Technology Trends Indonesia are exploding! Forget your dusty old piggy banks; the archipelago is embracing digital payments, lending platforms that would make a pirate captain blush, and insurtech so innovative it’s practically magic. This isn’t your grandma’s banking system; prepare for a whirlwind tour of Indonesia’s vibrant and rapidly evolving fintech landscape, where tradition meets technological disruption in a way that’s both exciting and occasionally bewildering. We’ll explore the booming digital payments scene, the rise of peer-to-peer lending, the innovative world of Insurtech, and the intriguing potential (and regulatory hurdles!) of blockchain and cryptocurrency. Buckle up, it’s going to be a wild ride.
This exploration will delve into the specifics of each area, examining the major players, the regulatory environment, and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. We’ll compare and contrast different fintech solutions, analyze their impact on various segments of the Indonesian population, and offer a glimpse into the future of finance in this dynamic nation. Expect insightful analysis, surprising statistics, and perhaps a few witty observations along the way.
Digital Payments in Indonesia

Indonesia’s digital payment landscape is a vibrant, chaotic, and frankly, hilarious whirlwind of activity. Think of it as a bustling Jakarta street market, but instead of spices and textiles, it’s overflowing with e-wallets, mobile banking apps, and enough QR codes to make your head spin. This rapid growth is fueled by a young, tech-savvy population and a government pushing for financial inclusion. Let’s dive into the delicious details.
The Current Landscape of Digital Payment Methods
Indonesia’s digital payment ecosystem is a fascinating blend of established players and disruptive newcomers. E-wallets, like GoPay and OVO, dominate the scene, offering seamless integration with ride-hailing apps and online marketplaces. Mobile banking, provided by established banks like BCA and BRI, provides a more traditional approach, albeit with increasingly sophisticated mobile apps. Beyond these, we see the emergence of Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services and other innovative payment solutions vying for a piece of the pie. This dynamic environment constantly evolves, reflecting Indonesia’s unique economic and technological landscape.
Comparison of Major Digital Payment Players
The Indonesian digital payments market is fiercely competitive. Below is a comparison of four major players, keeping in mind that market share fluctuates frequently:
| Player | Approximate Market Share (Illustrative, varies by source) | Key Features | Target Demographics |
|---|---|---|---|
| GoPay | Significant (exact figures vary widely) | Integrated with Gojek’s ecosystem (ride-hailing, food delivery, etc.), wide merchant acceptance, various financial services. | Broad, particularly strong among younger generations and urban populations. |
| OVO | Significant (exact figures vary widely) | Wide merchant acceptance, partnerships with various businesses, points reward programs. | Broad appeal, particularly popular among younger generations. |
| Dana | Moderate (exact figures vary widely) | Focus on ease of use, competitive fees, partnerships with various merchants. | Broad appeal, potentially targeting price-sensitive consumers. |
| LinkAja | Moderate (exact figures vary widely) | Government-backed, strong presence in government services, wide acceptance among state-owned enterprises. | Broad appeal, with a potential focus on less tech-savvy users through its partnership with Telkomsel. |
Note: Market share data is constantly shifting and varies depending on the source and methodology. These figures are illustrative and should not be considered precise.
Government Regulations and Their Impact
The Indonesian government has actively promoted the growth of digital payments through various regulations and initiatives. These policies aim to increase financial inclusion, reduce reliance on cash, and foster a more transparent financial system. However, navigating the regulatory landscape can be a rollercoaster for digital payment providers, requiring significant compliance efforts. These regulations, while intended to be beneficial, sometimes create complexities for businesses. Think of it as a well-meaning but slightly overzealous traffic officer trying to manage a chaotic intersection.
Challenges and Opportunities for Digital Payment Providers
The Indonesian digital payments market presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. Opportunities include the vast untapped market of unbanked and underbanked individuals, the rising adoption of e-commerce, and the potential for innovative financial products. However, challenges include maintaining security and trust in a rapidly evolving environment, navigating complex regulations, and managing competition from both established players and emerging fintech startups. It’s a jungle out there, but one with a lot of potential for those who can navigate it successfully.
Fintech Lending and Borrowing: Financial Technology Trends Indonesia

Indonesia’s fintech lending scene is a rollercoaster ride of innovation and, let’s be honest, occasional stomach-churning uncertainty. It’s a vibrant market experiencing explosive growth, fueled by a massive underserved population and a burgeoning appetite for digital financial solutions. This growth, however, isn’t without its bumps and bruises, requiring careful navigation through regulatory landscapes and the occasional financial cliffhanger.
The Indonesian P2P lending market is a fascinating case study in rapid expansion. Driven by the increasing accessibility of smartphones and internet penetration, it offers a compelling alternative to traditional banking for both borrowers and lenders. This alternative financial ecosystem has attracted significant investment, leading to a proliferation of platforms, each vying for a piece of the burgeoning pie. This competitive landscape has, in turn, led to some innovative products and services, but also highlighted the need for robust regulatory frameworks to ensure responsible lending practices.
The Indonesian P2P Lending Market Overview
The Indonesian P2P lending market has witnessed phenomenal growth in recent years. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for credit from individuals and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) who are either unbanked or underserved by traditional financial institutions. Many platforms cater to specific niches, such as micro-loans for street vendors or financing for small businesses in the agricultural sector. This targeted approach allows lenders to manage risk effectively while simultaneously expanding financial inclusion. The market is characterized by a wide range of players, from established fintech giants to smaller, more specialized platforms. The competition fosters innovation and drives down costs, ultimately benefiting borrowers. However, it also necessitates careful scrutiny to ensure the sustainability and responsible operation of these platforms. While exact figures fluctuate, reputable sources consistently point to a significant and rapidly expanding market share within Indonesia’s overall financial landscape.
Fintech Lending Product Comparison
Fintech lending platforms in Indonesia offer a diverse range of products tailored to various needs. For consumers, this includes personal loans, buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) options, and even micro-loans for immediate financial needs. Businesses, on the other hand, can access various financing options, such as working capital loans, inventory financing, and equipment financing. These products differ significantly in terms of loan amounts, interest rates, repayment periods, and eligibility criteria. Some platforms specialize in offering unsecured loans based on credit scoring algorithms, while others might require collateral or guarantors. The diversity of products ensures that a wider range of individuals and businesses can access credit, but it also underscores the need for consumers and businesses to carefully compare options before committing to a loan.
Technology’s Role in Expanding Credit Access
Technology plays a pivotal role in expanding credit access to underserved populations in Indonesia. Leveraging big data analytics and alternative credit scoring methods, fintech platforms can assess creditworthiness even for individuals with limited or no formal credit history. This is particularly crucial in Indonesia, where a significant portion of the population lacks access to traditional banking services. Mobile lending apps, for instance, simplify the application process and make it more accessible to people in remote areas. Furthermore, technology enables efficient loan disbursement and repayment tracking, reducing administrative costs and improving overall efficiency.
- Benefits: Increased financial inclusion, lower borrowing costs, faster loan disbursement, convenient application process, improved access to credit for SMEs.
- Risks: High interest rates for some borrowers, potential for over-indebtedness, data privacy concerns, lack of regulatory oversight in certain areas, potential for fraud and scams.
Insurtech in Indonesia

Indonesia’s burgeoning insurtech scene is a fascinating blend of traditional insurance practices and cutting-edge technology. While the country boasts a large population ripe for insurance penetration, a significant portion remains uninsured, largely due to a lack of accessibility and understanding of traditional insurance products. Enter insurtech, riding in on a wave of digital disruption to make insurance more relevant and user-friendly for the Indonesian market. Think of it as insurance, but with a much-needed dose of millennial charm.
Insurtech solutions are leveraging technology to bridge the gap between insurers and the Indonesian public, offering innovative ways to improve both the efficiency and affordability of insurance products. This isn’t just about making apps prettier; it’s about fundamentally changing how insurance is bought, sold, and experienced.
Innovative Insurtech Solutions in Indonesia
Several Indonesian insurtech companies are making waves with creative solutions. For example, some are using big data analytics to assess risk more accurately, leading to more personalized and affordable premiums. Imagine a system that understands your individual risk profile better than your own mother (no offense to mothers!). Others are utilizing mobile platforms to provide micro-insurance, catering to the needs of the underserved segments of the population. This makes insurance accessible to individuals who previously lacked the means or opportunity to secure coverage. Another exciting development is the use of embedded insurance, seamlessly integrating insurance products into other platforms, such as e-commerce sites or ride-hailing apps. This “insurance-as-a-service” approach removes the friction often associated with purchasing insurance, making it a more intuitive part of daily life.
Improving Efficiency and Affordability Through Technology
The impact of technology on insurance efficiency and affordability is nothing short of revolutionary. Automated underwriting processes, driven by AI and machine learning, drastically reduce processing times and administrative costs. This translates to quicker claim settlements and lower premiums for consumers. Furthermore, the use of digital platforms eliminates the need for physical intermediaries, reducing operational expenses and making insurance more accessible to those in remote areas. Think of it as cutting out the middleman, but instead of just saving money, you’re also making insurance more convenient and available to everyone.
Hypothetical Insurtech Product: “Go-Aman” Micro-Insurance for Gojek Drivers
Let’s imagine a hypothetical insurtech product tailored specifically for Gojek drivers, Indonesia’s ubiquitous ride-hailing service. This product, called “Go-Aman,” would offer affordable, on-demand accident and illness insurance directly integrated into the Gojek driver app. The target audience is the vast network of Gojek drivers, many of whom are self-employed and lack access to comprehensive health and accident coverage. Go-Aman would offer various coverage options, from basic accident insurance to more comprehensive plans including hospitalization and income protection. Premium payments would be seamlessly integrated into the driver’s existing Gojek earnings system, making it easy and convenient to pay. The claims process would be streamlined through the app, with digital documentation and quick payouts. The data-driven nature of the platform would allow for personalized risk assessment and premium adjustments, ensuring affordability while maintaining profitability. This is not just insurance; it’s a safety net woven directly into the fabric of their daily livelihood. Go-Aman: peace of mind, on demand.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency in Indonesia

Indonesia, a nation brimming with entrepreneurial spirit and a rapidly growing digital economy, is naturally curious about the potential of blockchain and cryptocurrency. While still navigating the regulatory waters, the archipelago’s embrace of technological innovation suggests a fascinating future for these technologies within its financial landscape. The potential benefits are significant, but so are the hurdles. Let’s delve into the details.
Blockchain technology, at its core, offers a secure and transparent way to record and verify transactions. Imagine a digital ledger that’s shared across a network, making it virtually impossible to tamper with. This inherent security is incredibly attractive to financial institutions grappling with fraud and inefficiencies. In Indonesia, this could revolutionize supply chain management, enhancing traceability and reducing counterfeiting in sectors like agriculture and pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, blockchain’s potential extends to streamlining cross-border payments, a particularly relevant application given Indonesia’s significant international trade.
Potential Applications of Blockchain in the Indonesian Financial Sector
Beyond supply chain management and cross-border payments, blockchain’s decentralized nature offers exciting possibilities for various financial services. Imagine a system where microloans are processed faster and more transparently, benefiting Indonesia’s vast informal economy. Or consider the potential for improved KYC (Know Your Customer) processes, reducing compliance costs for banks while enhancing security. The use of smart contracts could automate processes, further improving efficiency and reducing the need for intermediaries. The possibilities are as limitless as the Indonesian archipelago itself!
Regulatory Challenges Surrounding Cryptocurrencies in Indonesia
While the potential benefits are substantial, the Indonesian government has taken a cautious approach to cryptocurrencies. The regulatory landscape is still evolving, with ongoing debates about the appropriate level of oversight and the potential risks associated with crypto investments. Balancing innovation with investor protection is a delicate act, and Indonesia, like many other nations, is still finding its footing in this rapidly changing space. This cautious approach, while understandable, presents challenges for businesses seeking to operate legitimately within the cryptocurrency sector.
Future Prospects of Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Adoption in Indonesia
Despite the regulatory challenges, the future of blockchain and cryptocurrency adoption in Indonesia appears bright, albeit with a few caveats. The young, tech-savvy population is naturally inclined towards digital innovation, and the government’s commitment to developing a digital economy will likely drive further adoption. However, widespread adoption hinges on clear and consistent regulations that encourage innovation while protecting consumers from scams and market volatility. Successful implementation will require collaboration between the government, financial institutions, and the burgeoning fintech community. Think of it as a collaborative archipelago of innovation, navigating the currents of regulation to reach a prosperous future.
Investment and Wealth Management Technologies

The Indonesian investment landscape is undergoing a thrilling metamorphosis, fueled by the rise of technology. Forget stuffy suits and hushed whispers; the future of wealth management is sleek, automated, and surprisingly accessible, even for those who previously felt intimidated by the world of stocks and bonds. This transformation is largely thanks to the emergence of robo-advisors and other automated investment platforms, which are democratising access to sophisticated investment strategies.
Robo-advisors and automated platforms are changing the game by offering personalized investment portfolios based on an individual’s risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment timeline. These platforms often leverage algorithms and big data to optimize portfolio performance, minimizing human error and emotional decision-making—factors that can significantly impact investment success. This shift towards automation is not just about convenience; it’s about making sound investment strategies available to a much wider segment of the Indonesian population. This democratization has significant implications for economic growth and wealth distribution.
Robo-Advisors and Automated Investment Platforms Transforming Wealth Management
The impact of robo-advisors is multifaceted. Firstly, they significantly reduce the cost of investment management. Traditional wealth management often involves hefty fees charged by financial advisors. Robo-advisors, with their lower operational costs, can offer similar services at a fraction of the price, making investment more affordable for the average Indonesian. Secondly, these platforms enhance accessibility. Geographic location is no longer a barrier; individuals in remote areas can access sophisticated investment tools through their smartphones. Finally, the increased transparency offered by these platforms helps build trust and encourages greater participation in the investment market. For example, a platform might visually represent a portfolio’s allocation across different asset classes with simple, color-coded charts. This visualization makes it easier for even novice investors to understand their investments.
Fintech’s Impact on Financial Literacy and Investor Education, Financial Technology Trends Indonesia
Fintech plays a crucial role in bridging the financial literacy gap in Indonesia. Many platforms incorporate educational resources, such as interactive tutorials, webinars, and articles, explaining investment concepts in simple, accessible language. Gamification techniques, like awarding points or badges for completing educational modules, are also employed to engage users and encourage learning. This proactive approach to investor education empowers individuals to make informed decisions, fostering a more sophisticated and responsible investment culture. Furthermore, the increased use of financial technology leads to greater transparency and accountability within the financial system, further boosting trust and encouraging participation. For instance, a user-friendly interface that clearly displays transaction fees and investment performance data fosters transparency and reduces the potential for misinformation.
Hypothetical Infographic: “InvestAja: Your Smart Investment Journey”
Imagine a vibrant infographic dominated by a stylized, upward-trending graph symbolizing growth. The title, “InvestAja” (meaning “Just Invest” in Indonesian), is prominently displayed in a friendly, modern font. The infographic would then be divided into four key sections, each represented by a distinct color-coded block.
The first block, a calming blue, highlights “Ease of Use,” depicting a simplified flowchart showing the straightforward steps of creating an account, setting investment goals, and managing portfolios. The second block, a vibrant green, represents “Personalized Portfolio Management,” showcasing a diverse selection of assets—stocks, bonds, and mutual funds—with percentage allocations clearly indicated, emphasizing the customization options. The third block, a sunny yellow, illustrates “Educational Resources,” with icons representing tutorials, webinars, and interactive learning modules. Finally, the fourth block, a reassuring purple, details “Security and Transparency,” showing a shield icon alongside clear depictions of security protocols and transparent fee structures. The overall design is clean, modern, and reassuring, aimed at attracting a wide range of Indonesian investors.
Regulatory Landscape and Future Outlook
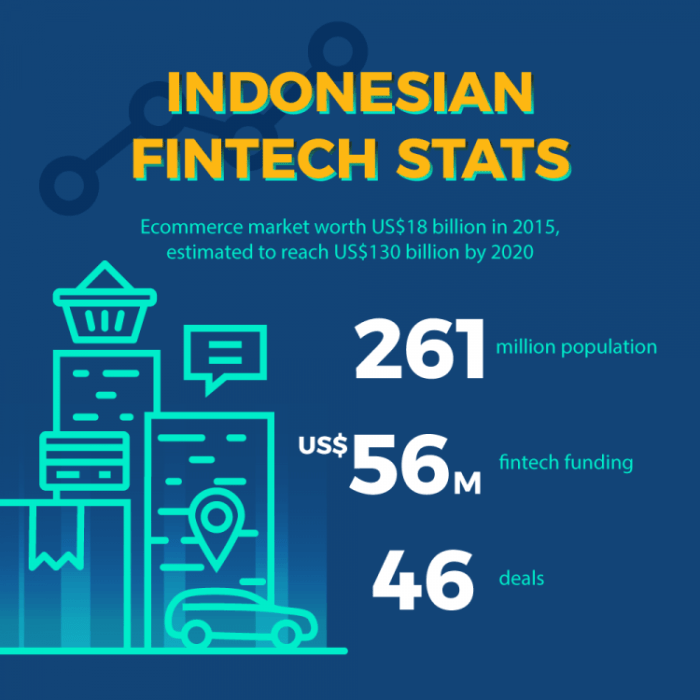
Navigating the Indonesian fintech scene is like riding a motorbike through a bustling Jakarta market – exciting, chaotic, and potentially very rewarding, provided you know the rules of the road. Understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial for anyone hoping to thrive in this dynamic environment. Indonesia’s fintech growth isn’t a free-for-all; it’s carefully guided (sometimes a little *too* carefully) by a complex web of regulations and oversight.
The Indonesian government, eager to harness the power of fintech while mitigating risks, has implemented a multi-pronged approach to regulation. This involves a delicate balancing act: fostering innovation while protecting consumers and maintaining financial stability. It’s a bit like herding cats, but with more spreadsheets.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Policies
Indonesia’s fintech regulatory framework is primarily shaped by several key players. The Financial Services Authority (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan or OJK) acts as the primary regulator, overseeing banks, insurance companies, and, increasingly, fintech firms. Bank Indonesia (BI), the central bank, plays a significant role in regulating payments and digital currencies. Other relevant ministries, such as the Ministry of Communication and Informatics, also contribute to the overall regulatory environment. Key policies include regulations on digital payment systems, peer-to-peer lending, and crowdfunding platforms, each designed to encourage responsible growth and minimize potential risks. These policies often involve licensing requirements, data protection standards, and consumer protection measures. The approach is often iterative, with regulations evolving as the fintech landscape itself changes. Think of it as a constant game of regulatory catch-up – exciting for the spectators, slightly less so for the players.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) is poised to revolutionize the Indonesian financial sector, much like the introduction of the ATM revolutionized banking decades ago. AI and ML can enhance credit scoring accuracy, personalize financial products, and improve fraud detection. For instance, AI-powered chatbots can provide 24/7 customer support, reducing the need for extensive human intervention. This also translates to significant cost savings for fintech companies, allowing them to compete more effectively and potentially offer lower fees to consumers. However, the implementation of these technologies raises concerns about data privacy and algorithmic bias, necessitating careful regulation and ethical considerations. It’s a double-edged sword – the potential benefits are immense, but responsible implementation is key.
Future Trends and Challenges
Over the next five years, the Indonesian fintech industry faces both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. Increased competition is inevitable, as both domestic and international players vie for market share. Maintaining cybersecurity and protecting consumer data will remain paramount. Furthermore, bridging the digital divide and ensuring financial inclusion for all segments of the population will be a critical ongoing challenge. The government’s commitment to digitalization, coupled with the burgeoning young and tech-savvy population, presents a significant growth opportunity. However, navigating the regulatory landscape effectively and adapting to rapid technological advancements will be crucial for success. Think of it as a high-stakes game of Jenga, where one wrong move could topple the whole tower – but the rewards for careful planning are substantial. One example of a potential future trend is the rise of embedded finance, where financial services are integrated into non-financial platforms. Imagine ordering a ride-hailing service and seamlessly paying through an integrated digital wallet – this is just the tip of the iceberg.
Last Recap
From the ubiquitous e-wallets to the burgeoning P2P lending market and the innovative applications of blockchain, Indonesia’s fintech journey is a testament to the power of technological disruption. While challenges remain, particularly in terms of regulation and financial literacy, the future of finance in Indonesia looks bright, dynamic, and undeniably exciting. The nation’s embrace of fintech holds immense potential for economic growth, financial inclusion, and a more accessible and efficient financial system for all. So, grab your Rupiah (digital or otherwise), and let’s dive into the fascinating world of Indonesian fintech!
FAQ Guide
What are the biggest risks associated with Indonesian P2P lending?
Risks include potential defaults by borrowers, lack of regulatory oversight in some areas, and the possibility of scams targeting unsuspecting lenders.
How is the Indonesian government promoting fintech adoption?
Through initiatives like simplifying regulations, promoting digital literacy, and investing in digital infrastructure.
What role does sharia compliance play in Indonesian fintech?
A significant portion of the population adheres to Islamic principles, thus many fintech solutions incorporate sharia-compliant features.
What are the long-term implications of increased fintech usage in Indonesia?
Long-term implications include increased financial inclusion, economic growth driven by innovation, and a more efficient and competitive financial services sector.



