Fintech, the audacious upstart of the financial world, is shaking things up like a caffeinated badger in a china shop. Forget stuffy banks and endless paperwork; Fintech offers speed, convenience, and sometimes, a healthy dose of bewilderment. This exploration delves into the disruptive power of Fintech, from its innovative lending platforms to its ever-evolving payment systems, and even its surprisingly sophisticated approach to wealth management. Prepare for a rollercoaster ride through the fascinating, and occasionally chaotic, landscape of modern finance.
We’ll examine how Fintech is reshaping traditional banking, exploring the advantages and disadvantages for consumers and institutions alike. We’ll also dissect the regulatory hurdles Fintech faces, the role of AI and big data in lending, and the future of finance in a world increasingly dominated by digital currencies and blockchain technology. Buckle up, because it’s going to be a wild ride!
Fintech’s Impact on Traditional Banking
The rise of Fintech has sent ripples, nay, tidal waves, through the traditionally staid waters of the banking industry. No longer are banks the sole custodians of our financial lives; a vibrant ecosystem of innovative companies is challenging the status quo, forcing established players to adapt or risk being left behind in the digital dust. This disruption, while sometimes chaotic, is ultimately benefiting consumers with increased choice and efficiency.
Fintech Disruption of Traditional Banking Models
Fintech companies are shaking up traditional banking in several key ways. They leverage technology to offer services faster, cheaper, and often more conveniently than traditional banks. This includes areas like mobile payments (think Venmo’s breezy transactions versus the sometimes-glacial pace of wire transfers), peer-to-peer lending (cutting out the middleman and offering potentially better rates), and robo-advisors (providing automated, algorithm-driven investment advice at a fraction of the cost of a human financial advisor). The sheer speed and accessibility of these services are fundamentally altering the landscape.
Customer Experience Comparison: Traditional Banks vs. Fintech Firms
Traditional banks often prioritize a physical presence and personalized service, but this can translate to longer wait times, complex processes, and higher fees. Fintech firms, on the other hand, typically emphasize digital-first experiences, prioritizing speed, convenience, and user-friendly interfaces. Imagine the difference between navigating a labyrinthine bank branch versus effortlessly managing your finances through a sleek mobile app. While some customers value the personal touch of a traditional bank, many are drawn to the efficiency and accessibility of Fintech alternatives. This shift in preference is forcing traditional banks to invest heavily in digital transformation to remain competitive.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fintech Services
The advantages of using Fintech services are numerous: increased speed and efficiency, lower fees, greater accessibility, and often more innovative features. However, there are also potential drawbacks. Security concerns are paramount; while many Fintech firms employ robust security measures, the risk of fraud or data breaches remains a concern. Furthermore, the lack of personal interaction can be a disadvantage for some customers who prefer face-to-face service. Regulatory oversight, while evolving, is still playing catch-up with the rapid pace of Fintech innovation, leading to potential uncertainties. Finally, the reliance on technology means that system failures or outages can disrupt access to funds and services.
The Evolving Regulatory Landscape for Fintech
The regulatory landscape for Fintech is a dynamic and complex arena, constantly evolving to keep pace with technological advancements. This evolution presents both opportunities and challenges for both Fintech companies and traditional banks.
Key Regulatory Changes and Their Impact
The increasing regulatory scrutiny is a double-edged sword. While it can increase consumer protection and trust, it can also stifle innovation and increase compliance costs for Fintech companies. Here are three examples of key regulatory changes and their impact:
- Increased Data Privacy Regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA): These regulations require Fintech firms to be more transparent about how they collect, use, and protect customer data. This has led to increased investment in data security infrastructure and a greater focus on user consent. For traditional banks, this means needing to adapt their data handling practices to meet the same high standards, impacting operational costs and processes.
- Open Banking Initiatives (e.g., PSD2 in Europe): These initiatives mandate that banks share customer data with third-party providers, fostering competition and innovation. This creates new opportunities for Fintech companies to build innovative services on top of existing banking infrastructure. Traditional banks, however, face the challenge of adapting their systems to comply with data-sharing mandates while ensuring the security and privacy of customer information.
- Cryptocurrency Regulation: The rise of cryptocurrencies has forced regulators worldwide to grapple with how to classify and regulate these digital assets. This uncertainty presents both challenges and opportunities. Fintech companies specializing in crypto services need to navigate a complex and evolving regulatory environment. Traditional banks are exploring ways to incorporate cryptocurrencies into their offerings while adhering to regulatory requirements, potentially leading to innovative financial products and services.
Fintech Innovation in Lending and Borrowing

The world of lending and borrowing, once the exclusive domain of stuffy suits in dimly lit bank offices, has undergone a seismic shift thanks to the disruptive force of Fintech. Gone are the days of endless paperwork and agonizing wait times; in their place, we find a vibrant ecosystem of innovative platforms offering speed, convenience, and (dare we say it?) a touch of fun. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of Fintech lending, where algorithms rule and approval is almost instantaneous.
Types of Fintech Lending Platforms and Their Target Markets
Fintech lending platforms cater to a diverse range of borrowers, each platform employing a unique approach. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms, for example, connect individual lenders with borrowers, often bypassing traditional financial institutions. These platforms typically target individuals seeking personal loans or small business financing who may not qualify for traditional loans. Marketplaces, on the other hand, aggregate loan offers from multiple lenders, providing borrowers with a broader selection and potentially more competitive rates. These platforms often target a wider audience, including individuals and small businesses. Finally, robo-advisors leverage algorithms to automate the lending process, offering quick and efficient loan approvals. Their target market often consists of borrowers with strong credit scores seeking streamlined processes.
Interest Rates and Fees Charged by Traditional Lenders and Fintech Lenders
The interest rates and fees charged by Fintech lenders can vary significantly depending on the platform, the borrower’s creditworthiness, and the loan type. While some Fintech lenders offer competitive rates, others may charge higher rates than traditional banks, especially for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit. The fees associated with Fintech loans can also vary, with some platforms charging origination fees, late payment fees, or prepayment penalties. Traditional lenders generally have more established pricing structures, although their rates may be less flexible and often higher for higher-risk borrowers. A crucial factor to consider is the transparency of fees; some Fintech platforms may bury fees in the fine print, so careful comparison is essential.
The Role of Big Data and AI in Fintech Lending Processes
Big data and AI are revolutionizing the lending process. Fintech lenders use these technologies to analyze vast amounts of data, including credit scores, income, spending habits, and social media activity, to assess a borrower’s creditworthiness more accurately and efficiently. This allows for faster loan approvals and potentially lower interest rates for creditworthy borrowers. AI-powered algorithms can also automate many aspects of the lending process, from loan application processing to fraud detection, resulting in reduced costs and improved efficiency. However, ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and potential bias in algorithms are important aspects to consider.
Hypothetical Fintech Lending Platform: “LoanAmigo”
LoanAmigo is a hypothetical Fintech lending platform designed for young professionals and entrepreneurs. It leverages AI-powered credit scoring that considers non-traditional data points, such as social media engagement and professional network size, alongside traditional credit scores. The platform boasts a user-friendly interface, instant loan approvals, and flexible repayment options. LoanAmigo also incorporates features such as financial literacy tools and personalized budgeting assistance to promote responsible borrowing habits.
| Feature | LoanAmigo | Traditional Lender |
|---|---|---|
| Application Process | Fully automated, instant approval | Manual review, lengthy process |
| Credit Scoring | AI-powered, considers non-traditional data | Relies primarily on traditional credit scores |
| Interest Rates | Competitive, personalized based on risk profile | Generally higher for higher-risk borrowers |
| Customer Service | 24/7 online support, chatbots | Limited hours, phone-based support |
| Transparency | Clearly displayed fees and terms | Potentially less transparent fee structures |
Fintech and Payments Technology

The world of payments has undergone a revolution, thanks in no small part to the disruptive – and often hilarious – innovations of Fintech. Gone are the days of solely relying on checks (remember those?), and even credit cards are feeling the pressure from a dazzling array of new payment methods. This section delves into the vibrant and ever-evolving landscape of Fintech payment solutions, exploring their functionalities, comparing their strengths and weaknesses, and, of course, addressing the elephant in the room: security.
Fintech payment solutions offer a diverse range of options catering to various needs and preferences globally. From the lightning-fast speed of mobile transfers to the intriguing (and sometimes baffling) world of cryptocurrencies, the choices are numerous and constantly expanding. This variety, however, also brings its own set of challenges, especially regarding security and regulatory compliance.
Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets, essentially digital versions of your physical wallet, have become incredibly popular. These applications, available on smartphones, allow users to store credit and debit card information, loyalty cards, and even transit passes. Examples include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, each with its own unique features and integrations. The convenience of contactless payments and the ability to consolidate various payment methods into a single platform have contributed significantly to their widespread adoption. However, the security of mobile wallets relies heavily on the security features of the underlying operating system and the implementation of robust authentication protocols.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Payments
P2P payment systems allow individuals to transfer money directly to each other, often using only a phone number or email address. Venmo, PayPal, and Zelle are prominent examples of this technology. These platforms have revolutionized personal finance, making it easier than ever to split bills, send gifts, or settle debts. The speed and convenience of P2P payments are undeniable, but they also present security risks, particularly concerning fraud and unauthorized access. Strong password management and multi-factor authentication are crucial for mitigating these risks.
Cryptocurrency Payments
Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, represent a more radical departure from traditional payment methods. These decentralized digital currencies operate independently of central banks and rely on blockchain technology to record transactions. While still a relatively nascent technology, cryptocurrency payments offer the potential for faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions, particularly for international payments. However, the volatility of cryptocurrency values and the regulatory uncertainty surrounding their use present significant challenges to widespread adoption. Furthermore, the technical complexity of cryptocurrency transactions can be a barrier to entry for many users.
Security Challenges and Mitigation Measures
The rise of Fintech payment systems has unfortunately also led to an increase in sophisticated cyberattacks. Data breaches, phishing scams, and malware are just some of the threats that users face. To combat these risks, Fintech companies are investing heavily in security technologies, such as encryption, biometric authentication, and fraud detection systems. Regulatory bodies are also playing a crucial role in setting standards and enforcing compliance. Despite these efforts, maintaining the security of Fintech payment systems remains an ongoing challenge requiring constant vigilance and adaptation.
Evolution of Payment Technologies: A Timeline
The evolution of payment technology is a fascinating journey, marked by significant milestones and innovations.
- Early 1900s: The introduction of credit cards, paving the way for electronic payments.
- 1970s: The emergence of Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), allowing for 24/7 access to cash.
- 1990s: The rise of online banking and electronic funds transfers (EFTs).
- 2000s: The proliferation of mobile phones and the development of mobile payment solutions.
- 2010s: The explosion of P2P payment apps and the emergence of cryptocurrencies.
- 2020s: The continued growth of contactless payments and the exploration of new technologies, such as biometrics and blockchain.
Fintech’s Role in Wealth Management

The world of wealth management, once the exclusive domain of pinstripe-suited advisors in mahogany-paneled offices, is undergoing a hilarious yet significant transformation thanks to Fintech. Gone are the days of hefty fees and opaque investment strategies; in their place are sleek apps, algorithmic wizardry, and a democratization of wealth management that would make Robin Hood blush (though probably not as much as the high-net-worth individuals who now have more accessible investment options).
Fintech is disrupting the traditional wealth management landscape by offering innovative solutions that cater to a wider range of investors. This includes not only high-net-worth individuals but also the burgeoning middle class, who previously lacked access to sophisticated investment strategies. This increased accessibility is driving competition, pushing down fees, and leading to more transparent and efficient services. It’s a win-win, unless you’re a traditional advisor clinging to outdated methods and charging exorbitant fees – then it might feel a bit like a financial apocalypse.
Robo-Advisors and Their Impact on Traditional Financial Advisory
The rise of robo-advisors, automated investment platforms that use algorithms to manage portfolios, has undeniably shaken the foundations of the traditional financial advisory industry. These digital advisors offer personalized investment strategies based on risk tolerance and financial goals, often at a fraction of the cost of human advisors. This has led to a significant shift in the market, forcing traditional firms to adapt or risk being left behind in the digital dust. Some firms are now integrating robo-advisory technology into their services, offering a hybrid approach that combines the personalized touch of human advisors with the efficiency of algorithms. It’s a bit like a butler-robot partnership: the best of both worlds, hopefully without the robot uprising.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Robo-Advisors
Using robo-advisors for investment management presents both compelling advantages and some potential drawbacks. On the plus side, they offer low fees, 24/7 accessibility, and a user-friendly interface that simplifies investing for even the most technologically challenged (we’re looking at you, Uncle Barry). They also provide diversification and rebalancing capabilities, ensuring portfolios remain aligned with investment goals. However, robo-advisors may lack the personalized attention and human interaction that some investors crave. Furthermore, the algorithms driving their investment decisions are not infallible, and unforeseen market fluctuations can still impact portfolio performance. It’s a bit like a self-driving car: great for most situations, but you might still want a human behind the wheel for those tricky mountain passes.
Comparative Analysis of Robo-Advisor Platforms
The following table provides a comparative analysis of three prominent robo-advisor platforms. Note that these details are subject to change, so always check the provider’s website for the most up-to-date information. It’s a bit like comparing apples and oranges (and maybe a grapefruit for good measure) – each platform has its own strengths and weaknesses.
| Platform Name | Investment Strategy | Fees | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Betterment | Diversified portfolios based on risk tolerance and goals; ESG options available | Variable, depending on account size and features | Individuals seeking automated, low-cost investing |
| Wealthfront | Tax-loss harvesting, portfolio diversification, and personalized financial planning | Variable, depending on account size and features | Individuals with a range of investment goals and risk tolerances |
| Schwab Intelligent Portfolios | Diversified portfolios, rebalancing, and access to Schwab’s broader financial services | No advisory fees for accounts under a certain threshold; fees apply for larger accounts | Individuals with various investment goals and experience levels; integrated with existing Schwab accounts |
The Future of Fintech
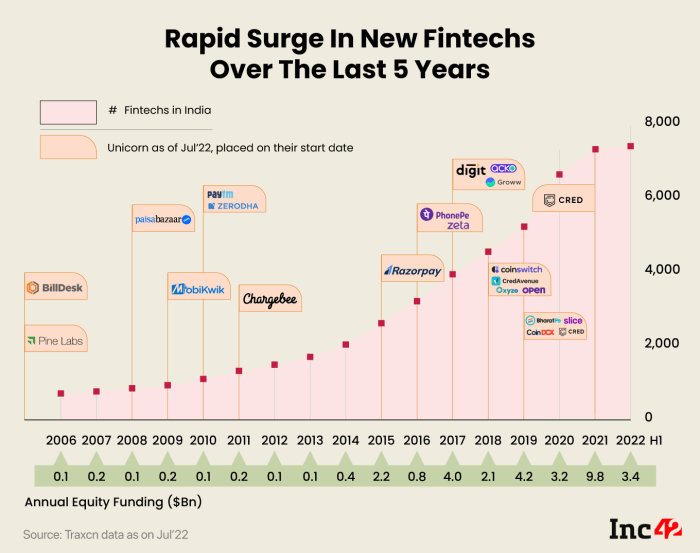
The Fintech landscape, currently a vibrant tapestry woven with threads of innovation, is poised for a dramatic transformation in the next five years. Prepare yourselves, dear readers, for a whirlwind of technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and, dare we say it, even a little bit of controlled chaos. Buckle up, because the future of finance is about to get a whole lot more interesting.
Predicting the next five years in Fintech is like predicting the weather in Scotland – you can make an educated guess, but be prepared for a sudden downpour of unexpected developments. However, based on current trends and emerging technologies, several key developments seem almost inevitable.
Major Trends and Developments in Fintech
Several significant trends will shape the Fintech industry over the next five years. Open banking, fueled by regulatory changes, will continue to gain momentum, allowing consumers greater control over their financial data and fostering the development of innovative third-party applications. Embedded finance, the seamless integration of financial services into non-financial platforms, will become increasingly prevalent, blurring the lines between traditional industries and the financial sector. Think of booking a flight and simultaneously securing travel insurance – all within the same app. Finally, the rise of super apps, offering a comprehensive suite of financial and non-financial services, will continue its rapid expansion, challenging the dominance of traditional banking institutions. Examples include Alipay and WeChat Pay in China, demonstrating the power of integrated platforms.
Challenges and Opportunities Facing Fintech Companies
The path to Fintech dominance is paved with both golden opportunities and treacherous potholes. Competition will intensify, requiring companies to continuously innovate and differentiate themselves. Regulatory hurdles, particularly concerning data privacy and security, will remain a significant challenge. However, the growing demand for personalized financial services and the increasing adoption of digital technologies present lucrative opportunities for Fintech companies that can navigate these complexities. Successfully addressing cybersecurity concerns and building trust with consumers will be crucial for long-term success. Consider the recent surge in fraud attempts; companies that can effectively mitigate these risks will be rewarded.
The Role of Blockchain Technology and Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology, while still in its relative infancy, holds immense potential to revolutionize the financial industry. Its inherent security and transparency features can streamline cross-border payments, reduce transaction costs, and enhance data security. Cryptocurrencies, while volatile, are slowly gaining acceptance as a legitimate form of payment and investment, further driving the adoption of blockchain technology within the Fintech ecosystem. The potential for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications built on blockchain is particularly exciting, offering alternative financial services outside the traditional banking system. For example, the increasing use of stablecoins as a means of facilitating transactions and reducing volatility showcases the potential for blockchain’s impact.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to transform Fintech applications in profound ways. These technologies are no longer futuristic fantasies; they’re already actively shaping the financial landscape.
AI and ML Applications in Fintech
The integration of AI and ML offers significant benefits across various Fintech applications. Here are three examples:
- Personalized Financial Advice: AI-powered robo-advisors can provide customized investment strategies based on individual risk profiles and financial goals, making sophisticated financial planning accessible to a broader audience. These algorithms can analyze market trends and adjust investment portfolios accordingly, offering a level of personalization previously unavailable. Consider Betterment or Wealthfront as examples of robo-advisors already utilizing AI.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of transaction data in real-time to identify and prevent fraudulent activities, significantly reducing financial losses for both businesses and consumers. These systems can detect unusual patterns and flag suspicious transactions with far greater speed and accuracy than human analysts, thereby protecting consumers from financial scams.
- Credit Scoring and Lending: AI and ML can analyze alternative data sources, such as social media activity and online behavior, to assess creditworthiness more accurately and provide access to credit for individuals who may be underserved by traditional lending institutions. This allows for a more inclusive financial system, extending credit to individuals who might otherwise be denied based on traditional credit scoring methods. Examples include companies using AI to assess creditworthiness based on mobile phone usage data.
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, Fintech’s impact on the financial landscape is undeniable, a whirlwind of innovation and disruption. While challenges remain, particularly in regulation and security, the potential for Fintech to democratize access to financial services and create more efficient, customer-centric solutions is immense. The future of finance is undeniably digital, and Fintech is leading the charge – albeit sometimes with a slightly mischievous grin.
FAQ Explained
What are the biggest security risks associated with Fintech?
Security is a paramount concern. Risks include data breaches, phishing scams, and vulnerabilities in payment systems. Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and reputable providers are crucial for mitigation.
Is Fintech regulated?
Yes, but the regulatory landscape is constantly evolving. Regulations vary by country and often lag behind the rapid pace of technological innovation. This creates both opportunities and challenges for Fintech companies.
How does Fintech compare to traditional banking in terms of customer service?
Fintech often boasts superior customer service through readily available apps, 24/7 support, and personalized experiences. However, traditional banks may offer more personalized advice for complex financial situations.
What is the future of cryptocurrency in Fintech?
The future is uncertain but potentially transformative. Cryptocurrencies could revolutionize cross-border payments and decentralized finance, though widespread adoption depends on regulatory clarity and technological advancements.