Understanding market trends is paramount for businesses seeking sustainable growth and competitive advantage. This Market Trend Analysis Review delves into the multifaceted world of identifying, interpreting, and leveraging market shifts. We explore various data sources, analytical techniques, and visualization methods, providing a comprehensive framework for navigating the complexities of market dynamics.
From identifying cyclical patterns to predicting future trends using forecasting models, this review equips readers with the knowledge and tools necessary to make informed business decisions. We’ll examine both successful and unsuccessful case studies, highlighting critical learning points and the potential pitfalls to avoid. The impact of technological advancements on market trends and how businesses can leverage these changes for competitive gain will also be explored.
Defining Market Trends

Understanding market trends is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and ultimately, achieve success. Market trends represent the general direction of a market over time, reflecting changes in consumer behavior, technological advancements, and economic conditions. By analyzing these trends, businesses can anticipate future demand, adapt their strategies, and gain a competitive edge.
Market trends are not simply random fluctuations; they represent patterns and shifts in market dynamics. Recognizing these patterns allows businesses to proactively adjust their offerings and marketing strategies to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate potential risks. Ignoring market trends, on the other hand, can lead to missed opportunities and ultimately, business failure.
Types of Market Trends
Several distinct types of market trends exist, each with its own characteristics and implications for businesses. Understanding these different types is vital for accurate forecasting and strategic planning.
- Cyclical Trends: These trends repeat over extended periods, often influenced by economic cycles. For example, the housing market often experiences boom and bust cycles, with periods of high growth followed by periods of decline. These cycles are typically longer than seasonal trends, spanning several years or even decades.
- Seasonal Trends: These trends are predictable and recurring within a specific time frame, usually a year. For instance, the demand for ice cream increases significantly during summer months, while the demand for winter coats peaks during the colder seasons. Businesses can leverage seasonal trends by adjusting inventory and marketing campaigns to match the anticipated demand.
- Technological Trends: These trends are driven by technological innovation and adoption. The rapid rise of smartphones and the subsequent growth of mobile applications represent a significant technological trend that has profoundly impacted numerous industries, from retail to finance. Staying abreast of these trends is crucial for businesses to remain competitive and avoid obsolescence.
Factors Influencing Market Trends
Numerous factors interact to shape market trends, making it a complex and dynamic process. Understanding these influencing factors is essential for effective trend analysis and forecasting.
- Economic Conditions: Macroeconomic factors like inflation, interest rates, and unemployment significantly influence consumer spending and business investment, directly impacting market trends. For example, a recession typically leads to reduced consumer spending, impacting various industries.
- Consumer Preferences: Shifting consumer tastes and preferences play a pivotal role in shaping market trends. The growing preference for sustainable and ethically sourced products, for instance, has led to increased demand for eco-friendly goods and services. Understanding these changing preferences is key to product development and marketing.
- Technological Advancements: Technological breakthroughs often disrupt existing markets and create new ones. The emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, for example, is transforming various sectors, impacting everything from customer service to manufacturing processes. Businesses must adapt to these advancements to stay relevant.
- Government Regulations: Government policies and regulations can significantly impact market trends. New environmental regulations, for example, might encourage the development of green technologies and sustainable practices, while trade restrictions can affect international markets.
- Social and Cultural Factors: Social and cultural shifts also play a role. The rise of social media, for instance, has dramatically altered marketing and advertising strategies, influencing consumer behavior and brand perception. Changes in demographics also significantly impact market demand.
Data Collection and Sources
Accurately assessing market trends requires a robust data collection strategy. This involves identifying reliable sources, employing appropriate methodologies, and understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various data types. The quality of your analysis is directly dependent on the quality of your data.
Reliable data sources are crucial for generating accurate and insightful market trend analyses. Various methods exist for collecting both qualitative and quantitative data, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages depending on the research objective and available resources. A well-rounded approach often combines multiple sources to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the market.
Reliable Data Sources for Market Trend Analysis
Several reliable sources provide valuable data for market trend analysis. These include industry-specific reports, government statistics, consumer surveys, and company financial reports. Industry reports, often published by market research firms, offer in-depth analysis of specific sectors, providing valuable insights into market size, growth rates, and competitive landscapes. Government statistics, accessible through agencies like the U.S. Census Bureau or Eurostat, offer macroeconomic data such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment figures, providing a broader context for market trends. Consumer surveys, conducted by market research companies or academic institutions, directly capture consumer preferences, behaviors, and attitudes, offering invaluable qualitative data. Finally, company financial reports, accessible through public filings, provide valuable data on sales, profits, and market share.
Methods for Collecting Qualitative and Quantitative Data
Quantitative data, expressed numerically, provides objective measurements of market trends. This can include sales figures, market share percentages, and consumer demographics. Methods for collecting quantitative data include analyzing sales data from company records, conducting large-scale surveys using structured questionnaires, and employing statistical modeling techniques. Qualitative data, on the other hand, provides rich descriptive information about consumer attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors. Methods for gathering qualitative data include conducting focus groups, in-depth interviews, and analyzing social media sentiment. Combining both quantitative and qualitative data allows for a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of market trends.
Comparison of Data Sources
| Data Source | Strengths | Weaknesses | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industry Reports (e.g., Gartner, Forrester) | Detailed sector analysis, expert insights, comprehensive market overviews | Can be expensive, may contain bias, not always publicly accessible | Quantitative & Qualitative |
| Government Statistics (e.g., Census Bureau, Eurostat) | Reliable, objective, covers broad macroeconomic trends | May lag in timeliness, data may not be specific to niche markets | Quantitative |
| Consumer Surveys (e.g., Nielsen, Ipsos) | Direct insights into consumer behavior and preferences | Can be expensive, sample bias is possible, responses may not always be truthful | Quantitative & Qualitative |
| Company Financial Reports | Objective financial performance data, reveals market share and competitive positioning | Limited to publicly traded companies, data may not fully reflect market trends | Quantitative |
Trend Identification and Interpretation
Identifying and interpreting market trends effectively requires a systematic approach that combines data analysis with a keen understanding of market dynamics. This involves moving beyond simply observing data points to uncovering the underlying narratives that shape market behavior. The process necessitates a blend of quantitative analysis and qualitative interpretation, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the observed trends.
The raw data collected (as discussed in the previous section) rarely reveals trends directly. Instead, it presents a complex picture that needs careful examination and interpretation. Several techniques can be employed to uncover meaningful patterns, which we will explore below.
Trend Identification Techniques
Effective trend identification involves a multi-faceted approach. It’s not simply about looking for increases or decreases, but also understanding the *rate* of change, the *duration* of the trend, and the *magnitude* of its impact. Combining various analytical tools enhances the accuracy and reliability of trend identification.
For instance, moving averages (simple, exponential, weighted) smooth out short-term fluctuations to reveal underlying trends. Regression analysis can help establish relationships between variables and predict future values. Statistical process control charts can highlight significant shifts from established norms, signaling potential emerging trends. Qualitative methods, such as expert interviews and sentiment analysis of news articles and social media, provide crucial context and can complement quantitative data.
Data Pattern Interpretation and Insight Generation
Once trends are identified, the next step involves interpreting the patterns and drawing meaningful insights. This requires careful consideration of various factors. Correlation does not equal causation – just because two variables move together doesn’t mean one causes the other. External factors, such as economic shifts, regulatory changes, and technological advancements, must be considered when interpreting trends. Furthermore, understanding the context within which the data is collected is crucial. A seemingly significant trend might be confined to a specific demographic or geographic region, limiting its overall market relevance.
For example, a sharp increase in sales of electric vehicles might be interpreted as a growing market trend. However, a deeper analysis might reveal that this increase is primarily driven by government subsidies in a particular country, not a widespread global shift in consumer preferences. This contextual understanding is vital for accurate interpretation.
Trend Validation and Reliability Assessment
Validating identified trends is crucial for ensuring the reliability of the analysis. Several techniques can be employed. First, the identified trend should be tested against multiple data sources to ensure consistency. Discrepancies between data sets require further investigation and may indicate limitations in the initial analysis. Second, the robustness of the trend should be evaluated. Does the trend persist over time, or is it a temporary anomaly? Third, the significance of the trend should be assessed. Is the magnitude of the change large enough to be considered meaningful, or is it simply statistical noise?
For example, if a trend is identified using only data from a single online retailer, its validity might be questionable. Confirming the trend with data from multiple retailers, industry reports, and consumer surveys would significantly strengthen its reliability. Furthermore, comparing the observed trend with historical data and industry benchmarks provides additional context and helps assess its significance.
Visualizing Market Trends
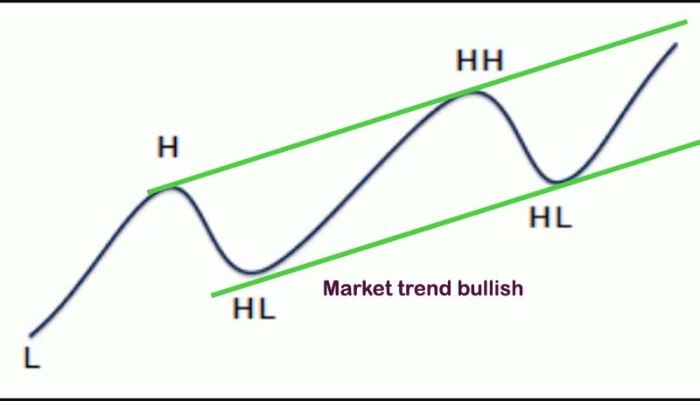
Effective visualization is crucial for understanding and communicating market trends. Charts and graphs transform complex datasets into easily digestible formats, allowing for quick identification of patterns, anomalies, and potential future movements. Choosing the right visualization method depends heavily on the type of data and the message you wish to convey.
Different chart types highlight different aspects of the data. Line graphs are ideal for showing trends over time, bar charts excel at comparing discrete categories, and scatter plots reveal correlations between two variables. The selection of the appropriate visualization is key to effective communication and insightful analysis.
Market Trend Visualization Methods
The following are three common visualization methods, each suited to different data characteristics and analytical goals.
- Line Graphs: Line graphs are exceptionally useful for displaying data that changes continuously over time. For example, visualizing the daily closing price of a stock over a year would be perfectly suited to a line graph. The continuous line clearly illustrates the price fluctuations, highlighting upward or downward trends, periods of stability, and significant price jumps or drops. A clear title, labeled axes (date and price), and a legend (if multiple stocks are compared) are essential for readability and accurate interpretation. For instance, a line graph could effectively demonstrate the growth of e-commerce sales over the past decade, clearly showing periods of rapid expansion and slower growth.
- Bar Charts: Bar charts are best suited for comparing discrete data points across different categories. Imagine comparing the market share of different brands of smartphones. A bar chart would clearly illustrate which brand holds the largest market share and how the others compare. The length of each bar directly represents the value of the data point, making comparisons straightforward. Clear labeling of the axes (brand and market share percentage) is crucial. Using a bar chart to show the sales figures for different product categories in a retail store would provide a clear visual comparison of the relative performance of each category.
- Scatter Plots: Scatter plots are valuable for exploring the relationship between two continuous variables. For instance, a scatter plot could show the correlation between advertising expenditure and sales revenue. Each point on the graph represents a data point, with its horizontal position reflecting one variable (advertising expenditure) and its vertical position representing the other (sales revenue). A positive correlation would show points clustered along an upward-sloping line, indicating that increased advertising expenditure tends to lead to increased sales. A negative correlation would display points along a downward-sloping line. A scatter plot could effectively illustrate the relationship between consumer confidence index and housing market activity.
Market Trend Forecasting
Predicting future market trends is a crucial aspect of strategic decision-making for businesses. Accurate forecasting allows companies to optimize resource allocation, anticipate market shifts, and proactively adjust their strategies to maintain a competitive edge. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that forecasting is inherently probabilistic; no method guarantees perfect accuracy.
Forecasting methods vary widely in their complexity and underlying assumptions. The choice of method depends heavily on the nature of the data available, the desired level of accuracy, and the resources available for analysis.
Comparison of Forecasting Methods
Time series analysis and regression analysis are two commonly used methods for market trend forecasting. Time series analysis focuses on the historical patterns of the data itself, identifying trends, seasonality, and cyclical components to extrapolate future values. Regression analysis, on the other hand, examines the relationship between the variable of interest (e.g., sales) and other relevant factors (e.g., advertising spend, economic indicators), using this relationship to predict future values. Time series analysis is best suited for situations where historical data is abundant and the primary focus is on identifying patterns within the data itself. Regression analysis is more useful when there are clearly identifiable independent variables that influence the dependent variable. A key difference lies in their treatment of external factors; time series analysis often implicitly accounts for external factors through the patterns in the data, while regression analysis explicitly models their influence.
Limitations of Market Trend Forecasting and Uncertainty
Market trend forecasting, despite its importance, is subject to several limitations. Unforeseen events, such as natural disasters, geopolitical instability, or sudden technological breakthroughs, can significantly disrupt predicted trends. Furthermore, the accuracy of forecasts is highly dependent on the quality and completeness of the data used. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed predictions. Finally, the inherent complexity of markets means that even the most sophisticated models may fail to capture all relevant factors. Therefore, it is crucial to acknowledge the inherent uncertainty in any forecast and to develop contingency plans to adapt to unexpected changes. Sensitivity analysis, which examines how the forecast changes with variations in input parameters, is a valuable tool for understanding and managing this uncertainty.
Hypothetical Scenario: Forecasting Smartphone Sales
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario: a smartphone manufacturer wants to forecast sales for the next quarter. They possess historical sales data for the past five years, broken down by month. They also have data on competitor sales, marketing expenditure, and key economic indicators (e.g., GDP growth, consumer confidence index). A suitable forecasting method in this scenario would be a multiple linear regression model. This model would incorporate historical sales as the dependent variable and competitor sales, marketing expenditure, and economic indicators as independent variables. The model would be trained on the historical data to determine the coefficients that best explain the relationship between these variables. Once trained, the model could then be used to predict sales for the next quarter by inputting the anticipated values for the independent variables. For example, if the manufacturer anticipates increased marketing expenditure and stable economic conditions, the model would predict higher sales compared to a scenario with reduced marketing and weakening economic indicators. The results of this analysis should be interpreted cautiously, recognizing the limitations and potential for unforeseen events to impact the actual sales figures. The forecast should be accompanied by a range of possible outcomes reflecting the uncertainty inherent in the prediction.
Case Studies of Market Trend Analysis

Analyzing real-world examples of market trend analysis provides valuable insights into effective methodologies and potential pitfalls. Examining both successful and unsuccessful case studies allows for a deeper understanding of the factors contributing to accurate forecasting and the challenges that can lead to inaccurate predictions. This section will present two contrasting case studies to illustrate these points.
Netflix’s Successful Expansion into International Markets
Netflix’s global expansion serves as a compelling case study in successful market trend analysis. Their strategy involved meticulous data collection and analysis to identify and target international markets poised for growth in streaming services. This involved analyzing factors such as internet penetration rates, disposable income levels, existing competition, and cultural preferences for online video content. Netflix utilized sophisticated algorithms to personalize content recommendations, adapting their offerings to local tastes. Their data-driven approach allowed them to successfully penetrate new markets, resulting in significant subscriber growth and revenue expansion. The methodology involved a combination of quantitative data analysis (market size, demographics, subscription rates) and qualitative research (cultural insights, content preferences). The results speak for themselves: Netflix became a global streaming giant, demonstrating the power of insightful market trend analysis in achieving international success. Their success wasn’t simply about identifying growth; it was about understanding the nuances of each market and adapting their service accordingly.
The Failure of Juicero’s Cold-Pressed Juice Machine
In contrast to Netflix’s success, Juicero’s high-tech juice machine provides a stark example of a failed market trend analysis. The company targeted health-conscious consumers interested in convenience and premium-quality juice. Their market analysis, however, failed to accurately assess the true demand for such an expensive and ultimately unnecessary product. While they identified a trend towards healthier lifestyles, they overestimated the willingness of consumers to pay a premium for a machine that essentially automated a process easily achievable manually. The failure to accurately gauge consumer price sensitivity and the lack of a compelling value proposition led to the company’s downfall. The methodology lacked sufficient qualitative research into consumer behavior and purchasing habits. Their focus was primarily on technological innovation, overlooking crucial aspects of market demand and practicality. The result was a product that was both expensive and unnecessary, ultimately leading to the company’s bankruptcy. This highlights the importance of considering all factors – not just technological advancements – when analyzing market trends. The overreliance on a perceived trend without thorough validation proved disastrous.
Comparison of Successes and Failures
The contrasting outcomes of Netflix and Juicero underscore the crucial differences between successful and unsuccessful market trend analyses. Netflix’s success stemmed from a comprehensive and nuanced approach, incorporating both quantitative and qualitative data, and adapting their strategy to local markets. Juicero’s failure, on the other hand, highlighted the dangers of overestimating market demand based on incomplete data and failing to fully understand consumer behavior and price sensitivity. The key learning point is the importance of a holistic approach, combining robust data collection with a deep understanding of the target market’s needs, preferences, and purchasing power. A successful market trend analysis goes beyond simply identifying trends; it involves a thorough assessment of market dynamics, consumer behavior, and the overall competitive landscape. Ignoring any of these crucial elements can lead to costly mistakes, as exemplified by Juicero’s failure.
Impact of Market Trends on Business Strategy
Understanding market trends is crucial for effective business decision-making. A comprehensive analysis allows businesses to proactively adapt to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and competitive landscapes, ultimately maximizing opportunities and minimizing risks. Ignoring these trends, conversely, can lead to significant setbacks and even failure.
Understanding market trends informs business decision-making by providing a roadmap for future actions. By identifying emerging trends, businesses can anticipate shifts in demand, adjust their product offerings, refine their marketing strategies, and allocate resources effectively. This proactive approach allows for a more competitive position and enhanced profitability. For example, a company noticing a growing trend towards sustainable products can adjust its manufacturing processes and marketing messaging to align with this preference, capturing a significant market share.
Implications of Ignoring Market Trends
Ignoring market trends can have severe consequences for businesses. Failure to adapt to changing consumer preferences can lead to declining sales and market share. Technological disruptions, if not anticipated and addressed, can render existing business models obsolete. Furthermore, neglecting emerging competitors can result in a loss of market dominance. For instance, the rise of e-commerce significantly impacted brick-and-mortar retailers who failed to adapt their strategies, leading to closures and bankruptcies for many. This highlights the importance of continuous market monitoring and strategic adaptation.
Using Market Trend Analysis to Develop Effective Business Strategies
Market trend analysis is a powerful tool for developing robust business strategies. By systematically identifying and interpreting market trends, businesses can develop proactive strategies to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks. This involves several key steps: firstly, defining clear objectives aligned with the identified trends; secondly, developing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals to achieve these objectives; and finally, creating a detailed action plan outlining the steps required to reach those goals, including resource allocation and timeline management.
For example, a company observing a growing demand for personalized experiences might develop a strategy that includes investing in data analytics to better understand customer preferences, customizing product offerings, and implementing personalized marketing campaigns. This proactive approach allows the company to not only maintain but also increase its market share by catering to the evolving needs of its target audience. This strategic approach, informed by market trend analysis, ensures the business remains competitive and profitable in a dynamic market environment.
Technological Advancements and Market Trends
Technological advancements are profoundly reshaping market trends, acting as both a catalyst for change and a response to evolving consumer demands. The pace of innovation is accelerating, creating both opportunities and challenges for businesses across all sectors. Understanding this interplay is crucial for strategic planning and competitive success.
Technological advancements directly influence market trends by introducing new products and services, altering consumer behavior, and disrupting existing business models. This impact is multifaceted, ranging from incremental improvements to completely novel market segments. For example, the rise of smartphones fundamentally altered the landscape of communication, entertainment, and commerce, creating entirely new markets for app developers, mobile payment systems, and location-based services.
Emerging Technologies Shaping Future Market Trends
Several emerging technologies are poised to significantly shape future market trends. These technologies are not isolated but often interact and reinforce each other’s impact. The convergence of these technologies will lead to unprecedented opportunities and challenges.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming various industries, from personalized marketing and customer service to predictive maintenance and fraud detection. AI-powered systems are capable of analyzing vast datasets to identify patterns and insights that would be impossible for humans to discern, leading to more efficient operations and better decision-making. For instance, Netflix uses AI algorithms to recommend shows and movies to its subscribers, significantly increasing user engagement and retention.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is connecting billions of devices, generating massive amounts of data that can be used to improve efficiency, optimize processes, and create new products and services. Smart homes, wearable technology, and connected cars are just a few examples of the IoT’s impact. The data generated by these devices allows businesses to gain valuable insights into consumer behavior and preferences, enabling them to tailor their offerings accordingly. For example, smart refrigerators can track food consumption and automatically reorder groceries, streamlining the shopping experience.
Blockchain technology, initially known for its use in cryptocurrencies, is finding applications in various sectors, including supply chain management, digital identity verification, and secure data storage. Its decentralized and transparent nature offers increased security and trust, which can be leveraged to build more efficient and reliable systems. For example, blockchain can be used to track the origin and authenticity of products, combating counterfeiting and improving transparency in supply chains.
Leveraging Technology for Competitive Advantage
Businesses can leverage technology to gain a competitive advantage by adopting a proactive and strategic approach. This involves not just implementing new technologies, but also fostering a culture of innovation and data-driven decision-making.
Investing in research and development (R&D) is crucial for staying ahead of the curve. This includes exploring emerging technologies and adapting them to specific business needs. Companies that fail to innovate risk being overtaken by more agile competitors. For example, companies like Tesla have aggressively invested in battery technology and electric vehicle design, disrupting the traditional automotive industry.
Data analytics plays a critical role in understanding market trends and customer behavior. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, businesses can gain valuable insights that inform their strategic decisions. This includes using data to personalize marketing campaigns, optimize pricing strategies, and improve customer service. Companies like Amazon utilize vast amounts of data to personalize recommendations and target advertisements effectively.
Building a strong digital infrastructure is essential for supporting technological advancements. This includes investing in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data management systems. A robust digital infrastructure enables businesses to scale their operations, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experience. For instance, companies using cloud-based solutions can quickly adapt to changing market demands by scaling their resources up or down as needed.
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, mastering market trend analysis is crucial for any organization aiming to thrive in today’s dynamic business landscape. By combining rigorous data analysis with insightful interpretation and strategic foresight, businesses can effectively anticipate market shifts, adapt their strategies, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. This review has provided a structured approach to understanding and utilizing market trend analysis, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions and achieve sustainable success.
Top FAQs
What are some common pitfalls to avoid in market trend analysis?
Common pitfalls include relying on outdated data, failing to consider external factors, misinterpreting correlations as causations, and neglecting qualitative data.
How often should market trend analysis be conducted?
The frequency depends on the industry and market volatility. Some industries require continuous monitoring, while others may benefit from periodic reviews (e.g., quarterly or annually).
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data in market trend analysis?
Qualitative data provides descriptive insights (e.g., customer feedback, interviews), while quantitative data focuses on numerical measurements (e.g., sales figures, market share).
Can market trend analysis predict the future with certainty?
No, market trend analysis provides informed predictions, but uncertainty is inherent. Forecasts should be treated as probabilities, not certainties.



