Pajak Penghasilan (PPh) Guide: Navigating the wonderfully bewildering world of Indonesian income tax doesn’t have to be a tax-ing experience! This guide unravels the mysteries of PPh, from its surprisingly interesting history to the surprisingly straightforward (mostly) calculations. Prepare to be amazed – and maybe even slightly amused – as we demystify PPh Pasal 21, 25, and 29, those enigmatic numbers that hold the key to your financial freedom (or at least, your compliance).
We’ll cover everything from understanding your tax obligations and deadlines (yes, those are important) to exploring the delightful world of tax deductions and allowances. Think of it as a treasure hunt, but instead of gold, you get to keep more of your hard-earned rupiah. We’ll even tackle those tricky scenarios involving freelancers, foreign income, and investments – because even your side hustle deserves proper tax treatment.
Introduction to Pajak Penghasilan (PPh): Pajak Penghasilan (PPh) Guide
Pajak Penghasilan (PPh), or Income Tax in Indonesian, is the tax you pay on your income earned within Indonesia. Think of it as the government’s share of your hard-earned rupiah – a necessary evil, perhaps, but one that contributes to essential services like infrastructure and healthcare. Navigating the intricacies of PPh can feel like trekking through a dense jungle, but fear not, this guide will help you machete your way through the undergrowth.
PPh regulations in Indonesia have evolved significantly since their inception. Early forms of income tax were introduced during the colonial era, but the modern system, with its various articles and complexities, solidified post-independence. The system has undergone numerous revisions and updates to keep pace with economic changes and global tax standards. It’s a constantly evolving beast, so staying informed is key. Think of it as a game of tax-whack-a-mole, where the moles (tax regulations) keep popping up in new and exciting locations.
Types of PPh
Indonesia employs a system of various PPh articles, each targeting different income sources and taxpayers. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate tax compliance. Failure to do so could result in penalties that will make your wallet weep.
PPh Pasal 21: Withholding Tax on Employment Income
PPh Pasal 21 applies to income from employment, such as salaries and wages. Your employer is responsible for withholding and remitting this tax to the government. The amount withheld depends on your gross income and various allowances. Think of it as a pre-emptive strike against your paycheck – a small price to pay for the privilege of living in Indonesia. Imagine a friendly vampire gently sucking a small portion of your earnings each month. It’s not pleasant, but it’s necessary.
PPh Pasal 25: Income Tax on Self-Employment Income
PPh Pasal 25 is for those with income from self-employment, business, or investments. Instead of having your tax withheld, you are responsible for making advance payments on a regular basis (usually monthly). This requires careful estimation of your annual income to avoid underpayment penalties or excessive overpayments. This is like being your own tax accountant, a task that requires both mathematical prowess and a degree of psychic ability to predict your future earnings.
PPh Pasal 29: Income Tax on Final Withholding
PPh Pasal 29 is a final tax on certain types of income, meaning no further tax adjustments are needed. Examples include certain types of royalties and interest income. It’s a simpler tax regime compared to Pasal 21 and 25, though the types of income it applies to are specific. Think of it as a streamlined, no-frills approach to taxation—efficient, if somewhat limited in scope.
Key Differences Between PPh Types
The primary difference lies in who is responsible for withholding or remitting the tax. PPh Pasal 21 is handled by the employer, while Pasal 25 requires self-assessment and payment by the taxpayer. Pasal 29 is a final withholding tax, eliminating the need for further adjustments. The types of income each article applies to also vary significantly. It’s like choosing between three different flavors of tax: employer-withheld, self-assessed, and final-withheld. Each has its own unique taste and level of complexity.
PPh Calculation Methods
Navigating the world of Indonesian PPh can feel like trying to assemble IKEA furniture without the instructions – challenging, but ultimately rewarding (especially when you avoid a hefty tax bill!). Let’s demystify the calculation methods, turning potential tax headaches into manageable tasks. We’ll focus on two key PPh types: Pasal 21 (for employees) and Pasal 25 (for businesses).
Understanding the different calculation methods is crucial for accurate tax reporting and avoiding unpleasant surprises from the taxman. Remember, accuracy is key – a small mistake can snowball into a larger problem down the line. So buckle up, and let’s dive in!
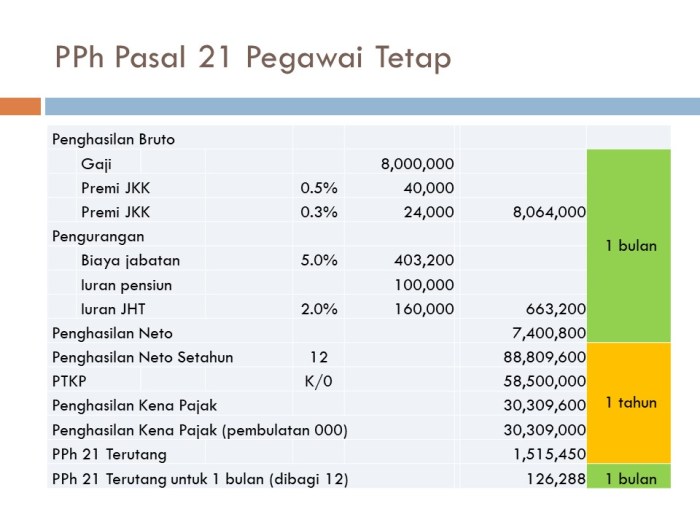
PPh Pasal 21 Calculation for Employees
PPh Pasal 21, the tax withheld from your salary, is calculated based on your monthly taxable income. Think of it as a pre-payment of your annual income tax. The beauty of it? Your employer handles most of the heavy lifting!
- Determine Gross Monthly Income: This is your total salary before any deductions.
- Calculate Nettaxable Income: Subtract allowable deductions (such as social security contributions, health insurance premiums, and other officially recognized deductions) from your gross monthly income.
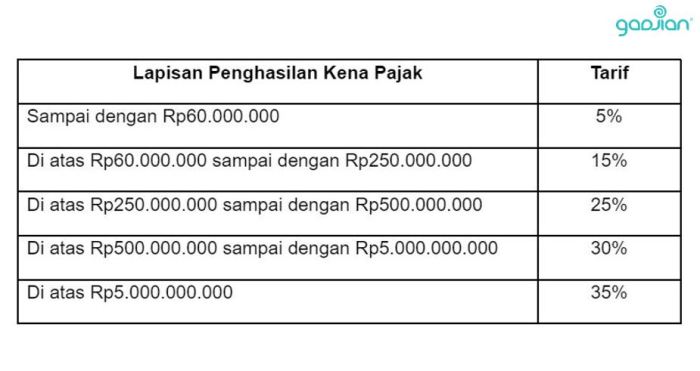
- Determine the Applicable Tax Bracket: Using the tax brackets (see table below), find the bracket corresponding to your net taxable income.
- Calculate the Tax: Apply the tax rate from the applicable bracket to your net taxable income. This is your monthly PPh Pasal 21.
- Withholding by Employer: Your employer will deduct this amount from your monthly salary and remit it to the tax authorities.
| Income Range (IDR) | Tax Rate (%) | Example Income (IDR) | Tax Amount (IDR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 – 50,000,000 | 5 | 20,000,000 | 1,000,000 |
| 50,000,001 – 250,000,000 | 15 | 100,000,000 | 15,000,000 |
| 250,000,001 – 500,000,000 | 25 | 300,000,000 | 75,000,000 |
| > 500,000,000 | 30 | 600,000,000 | 180,000,000 |
Note: These tax brackets and rates are simplified examples and may not reflect the current Indonesian tax regulations. Always refer to the official Directorate General of Taxes (DGT) website for the most up-to-date information.
PPh Pasal 25 Calculation for Businesses
PPh Pasal 25 is a bit more involved, as it’s a monthly tax payment estimated on a company’s projected annual income. It’s a proactive approach to tax payment, preventing a large lump sum at the end of the year. Think of it as paying your taxes in installments.
- Estimate Annual Net Taxable Income: This requires careful forecasting of your business’s income and deductible expenses for the entire year.
- Determine the Applicable Tax Rate: The tax rate depends on your company’s type and structure. Consult the official DGT guidelines.
- Calculate Annual PPh Payable: Multiply your estimated annual net taxable income by the applicable tax rate.
- Divide by 12: Divide the annual PPh payable by 12 to determine your monthly PPh Pasal 25 payment.
- Monthly Payment: Remit this amount to the tax authorities each month.
Accurate estimation is crucial for PPh Pasal 25. Underestimating can lead to penalties, while overestimating ties up your working capital. Consider consulting a tax professional for assistance with accurate forecasting.
Tax Obligations and Deadlines
Navigating the world of Pajak Penghasilan (PPh) deadlines can feel like trying to catch a greased piglet – slippery and potentially painful if you miss the mark. But fear not, intrepid taxpayer! This section will illuminate the path to PPh compliance, shedding light on obligations and deadlines to keep you on the right side of the taxman (and out of trouble). We’ll unravel the mysteries of who pays what, when, and the unfortunate consequences of procrastination.
Understanding your tax obligations depends heavily on your status: are you a humble individual filing your own return, or a bustling business with a complex web of transactions? This dictates the specific PPh type you’ll be dealing with and, consequently, your payment schedule. Let’s dive in!
Tax Obligations for Different Taxpayers
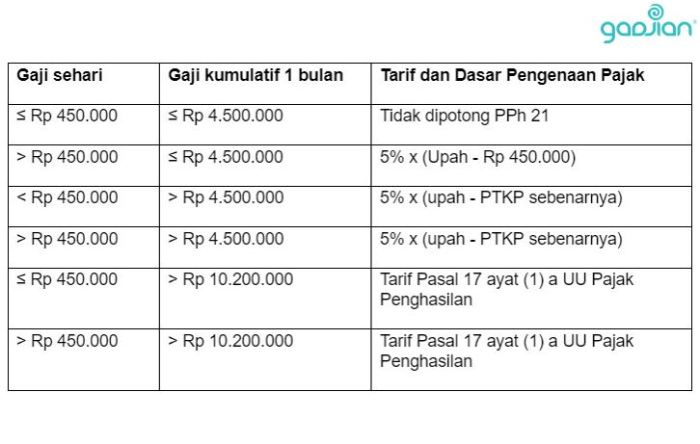
Individuals generally pay PPh 21 (income tax for individuals), while businesses face a more diverse landscape depending on their structure and revenue. Sole proprietorships might fall under PPh 21, while larger companies could be dealing with PPh 25 (corporate income tax) or other types of taxes, depending on their specific business activities and turnover. The complexity increases with the size and structure of the business, requiring specialized accounting knowledge or professional assistance. Imagine trying to navigate a maze blindfolded – it’s best to have a guide!
PPh Payment Deadlines
The deadlines for PPh payments vary depending on the type of PPh and the taxpayer’s reporting frequency. For example, PPh 21 for employees is typically withheld monthly by their employers. Businesses, however, often have quarterly or annual deadlines, depending on their chosen reporting method and the regulations applicable to their specific business type. Think of it like a meticulously choreographed dance – each step (payment) must be taken at the precisely right time. Missing a beat can be costly.
| PPh Type | Payment Frequency | Typical Deadline (Illustrative – Always Check Official Regulations) |
|---|---|---|
| PPh 21 (Individuals) | Monthly (withheld by employer) | Last day of the following month |
| PPh 25 (Corporations) | Quarterly or Annually | Varies, check official DJP guidelines |
Note: The deadlines provided above are illustrative and may vary. Always consult the official Directorate General of Taxes (DJP) website or a tax professional for the most up-to-date and accurate information. Ignoring this advice is like ignoring a ticking time bomb.
Penalties for Late or Non-Payment of PPh
Let’s face it, nobody likes penalties. They’re like uninvited guests at a party – unwelcome and potentially expensive. Late or non-payment of PPh can result in significant financial penalties, including interest charges and even potential legal action. These penalties can range from a percentage of the unpaid tax to substantial fines. The severity depends on the amount owed and the length of the delay. It’s a costly game of financial catch-up that’s best avoided.
Filing PPh Returns
Filing your PPh return correctly is crucial, even if you’re not a tax aficionado. It’s the formal declaration of your income and the taxes you owe, much like sending a postcard to the tax authorities. This process typically involves completing the relevant tax forms accurately and submitting them electronically through the DJP’s online system (e-Filing). Failure to file correctly or on time can lead to penalties similar to those for late payments. Think of it as a crucial step in a well-orchestrated tax symphony. A missed note can throw the whole piece off.
Remember to keep meticulous records of all your financial transactions, including receipts and invoices. This will simplify the process significantly.
Tax Deductions and Allowances
Navigating the world of Pajak Penghasilan (PPh) can feel like traversing a jungle – dense, potentially confusing, but ultimately rewarding if you know the right path. One of the most crucial paths to financial freedom (or at least, financial sanity) lies in understanding tax deductions and allowances. These are essentially ways to legally reduce your taxable income, making your tax burden lighter and leaving more Rupiah in your pocket. Think of it as a treasure hunt, where the treasure is more disposable income!
Tax deductions and allowances are available to both individuals and businesses, offering a variety of ways to lessen your tax liability. The process of claiming these deductions involves careful record-keeping and accurate reporting on your tax return. Failing to claim legitimate deductions is like leaving money on the table – a missed opportunity for financial gain. Different methods exist for claiming these deductions, each with its own set of rules and requirements. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Allowable Tax Deductions for Individuals and Businesses
Individuals can deduct expenses directly related to generating their income. This might include things like work-related travel, professional development courses (imagine mastering the art of tax preparation!), or even home office expenses if you work from home. For businesses, the possibilities expand considerably. They can deduct expenses like salaries, rent, utilities, marketing costs, and depreciation of assets. Imagine a small restaurant deducting the cost of their fancy espresso machine – that’s a deduction! Remember, proper documentation is key; keep those receipts!
Claiming Tax Deductions
The process of claiming tax deductions typically involves meticulously documenting all eligible expenses. This includes gathering receipts, invoices, and any other supporting evidence. Then, this information is carefully reported on the relevant tax forms. Accuracy is paramount; incorrect reporting can lead to penalties. Think of it like baking a cake – precise measurements are essential for a perfect result. Similarly, precise reporting is essential for a successful tax filing. Consult a tax professional if you need assistance; they can guide you through the complexities and ensure you don’t miss out on any valuable deductions.
Comparison of Tax Deduction Methods
While the fundamental principle remains the same – reducing taxable income – the *methods* of claiming deductions can vary. Some deductions are claimed directly by reducing your gross income, while others might be claimed as credits against your tax liability. The specific method depends on the type of deduction and the applicable tax regulations. For instance, some deductions are straightforward subtractions from your income, while others might require more complex calculations. It’s vital to understand these nuances to maximize your tax benefits. Consider consulting the official tax guidelines for a comprehensive understanding.
Common Tax Deductions for Employees
It’s crucial for employees to understand the deductions they are entitled to claim. Properly utilizing these deductions can significantly impact your net income. Here’s a list of common deductions:
- Health insurance premiums
- Pension contributions
- Certain job-related expenses (e.g., professional subscriptions)
- Work-related transportation costs (within reasonable limits)
- Union dues
Remember, always refer to the latest official guidelines to ensure you’re claiming all eligible deductions. Don’t let your hard-earned money slip away unnecessarily!
Understanding Tax Forms and Documents

Navigating the world of Indonesian PPh forms can feel like deciphering an ancient hieroglyphic script – but fear not! With a little guidance, you’ll be filling out those forms like a tax-filing ninja. This section will demystify the process, providing you with a clear understanding of the essential forms and supporting documents needed for a successful PPh filing. We’ll even throw in some tips to make the experience slightly less painful (we promise!).
The structure and purpose of PPh tax forms vary depending on your specific tax situation. However, understanding the common elements and required information is crucial for accurate and timely filing. Generally, these forms request personal information, income details, deductions, and tax calculations. The forms are designed to be somewhat self-, but we’ll clarify any potential ambiguities here. Think of it as your personal tax cheat sheet (but, you know, a legal one).
PPh Tax Form Structures and Purposes
Most PPh forms follow a logical structure, starting with your personal identification details (think name, address, tax identification number – NPWP). Then, you’ll move on to sections detailing your income sources, whether it’s salary, business income, or capital gains. Each section will have specific fields to fill in the relevant amounts. Finally, you’ll calculate your tax liability based on the applicable tax rates and deductions. Remember, accuracy is key here – a small mistake can lead to unexpected consequences. Think of it as a carefully orchestrated financial ballet; one wrong step, and the whole thing falls apart.
Required Supporting Documents for PPh Filings
The supporting documents required depend heavily on the type of income you’re reporting. For salaried employees, a copy of your payslip for the entire tax year is typically sufficient. For business owners, however, the requirements are more extensive and can include financial statements, invoices, receipts, and bank statements. These documents serve as proof of your income and expenses, allowing the tax authorities to verify the accuracy of your tax return. Without these documents, your filing might be delayed or even rejected – and nobody wants that.
Procedures for Obtaining Necessary Tax Forms
Obtaining the necessary PPh forms is generally straightforward. You can download them directly from the official website of the Directorate General of Taxes (DGT) in Indonesia. The website provides various forms in PDF format, ready for you to download and fill out. Alternatively, you can visit a local tax office (Kantor Pelayanan Pajak – KPP) to obtain physical copies. While the online option is generally preferred for its convenience, visiting a KPP can be helpful if you need assistance understanding the forms or have specific questions.
Common Tax Documents and Their Significance
Let’s delve into some common tax documents and their importance:
- Form 1770: This form is for annual income tax reporting for salaried employees. It’s like the cornerstone of your tax filing – get this right, and the rest falls into place.
- Form 1770S: A simplified version of Form 1770, designed for those with simpler income streams. Think of it as the ‘easy mode’ for tax filing.
- Form 1771: Used for reporting income from various sources, including business income and capital gains. This one is for those with more complex income situations – a bit more challenging, but manageable with the right guidance.
- NPWP (Nomor Pokok Wajib Pajak): Your Indonesian tax identification number. This is your unique identifier in the Indonesian tax system, so keep it safe! It’s like your passport to the world of Indonesian taxation.
- Payslips: Essential for salaried employees to prove income earned during the tax year. These are your proof of income – keep them organized!
- Financial Statements: Crucial for businesses to report income and expenses. These are like a financial diary for your business, meticulously documenting every transaction.
Remember, accurate record-keeping is your best friend throughout the entire tax process. Staying organized and keeping copies of all your documents will make the process significantly smoother. And who doesn’t love a smooth tax filing experience?
PPh for Specific Scenarios
Navigating the world of Pajak Penghasilan (PPh) can feel like traversing a jungle filled with tax-eating vines and confusing paperwork. But fear not, intrepid tax adventurer! This section illuminates the PPh landscape for specific scenarios, ensuring you don’t get lost in the leafy undergrowth of Indonesian tax regulations. We’ll tackle the tricky terrain of freelancers, businesses with international connections, and investment income, providing you with a clearer path to tax compliance (and maybe even a little bit of fun along the way).
PPh for Freelancers and Self-Employed Individuals, Pajak Penghasilan (PPh) Guide
The self-employed often face a unique PPh challenge: they are both the employer and the employee. This means they are responsible for calculating and paying their own taxes, a task that can seem daunting but is ultimately manageable with the right understanding. The key lies in accurately tracking income and expenses, a task best accomplished with meticulous record-keeping. Failing to do so is like trying to navigate a jungle without a map – you’re bound to get lost!
PPh Obligations for Businesses with Foreign Income
Ah, the international arena of PPh – a world of exciting possibilities and complex regulations. Businesses receiving income from foreign sources must navigate a labyrinth of international tax treaties and Indonesian tax laws. This often involves determining the tax residency of both the business and the foreign entity, and understanding the applicable tax rates in both jurisdictions. Proper documentation is paramount; think of it as your passport through this intricate tax landscape. Without it, you’re likely to face delays and potential penalties. A qualified tax advisor can be invaluable in this process, acting as your expert guide through this international jungle.
Special Considerations for PPh Related to Investment Income
Investing your hard-earned Rupiah can be a rewarding experience, but understanding the PPh implications is crucial. Different investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, have varying PPh implications. For instance, dividends often attract a different tax rate than capital gains from selling stocks. Accurate reporting of investment income is essential to avoid any unpleasant surprises during tax season. Think of it as tending your financial garden; proper care and attention will yield the best results.
Examples of PPh Calculations for Different Income Sources
Let’s illustrate with some examples. Imagine a freelancer earning Rp 100,000,000 annually from various projects. After deducting allowable expenses (such as office supplies and professional development), their net taxable income might be Rp 70,000,000. Applying the relevant tax brackets, their PPh payable could be calculated. Alternatively, a business with foreign income might receive Rp 50,000,000 from a client in Singapore. Depending on the tax treaty between Indonesia and Singapore, and the nature of the income, the applicable PPh rate and calculation method would vary. Finally, consider an individual earning Rp 20,000,000 in dividend income. The PPh on this income would be calculated according to the specific regulations for dividend income. Remember, these are simplified examples, and the actual calculations can be more complex depending on individual circumstances. Consulting a tax professional is always a good idea to ensure accuracy and compliance. Consider it an investment in peace of mind.
Resources and Further Information
Navigating the world of Pajak Penghasilan (PPh) can feel like navigating a particularly aggressive game of tax-themed whack-a-mole. Fear not, intrepid taxpayer! We’ve compiled some resources to help you avoid a hefty tax bill and the accompanying existential dread. Consider this your survival guide to the often-bewildering jungle of Indonesian tax law.
We understand that wrestling with tax forms can feel like wrestling a greased piglet – slippery, unpredictable, and potentially very messy. To help you tame this beast, we’ve gathered essential information to make the process smoother, less stressful, and dare we say, even mildly enjoyable (okay, maybe not enjoyable, but definitely less nightmarish).
Helpful Government Websites and Resources
Finding the right information online can be a bit like searching for a needle in a haystack made of tax codes. But don’t despair! Here are some official websites that can provide clarity and maybe even a touch of bureaucratic charm (we’re aiming for optimistic here).
- Direktorat Jenderal Pajak (DJP) Website: This is the main hub for all things PPh in Indonesia. Expect official regulations, forms, and a wealth of information (some might say an overwhelming wealth). Think of it as the tax equivalent of a well-stocked library – you’ll find what you need, eventually.
- Other relevant government portals: Depending on your specific tax situation, you might also find useful information on websites related to the Ministry of Finance or other relevant government agencies. These sites often contain supplementary information and might offer different perspectives on the same regulations. Think of them as the helpful librarians who can point you towards the right section of the tax library.
Filing PPh Returns: A Flowchart
Visual learners rejoice! Below is a simplified flowchart illustrating the PPh return filing process. Imagine it as a treasure map leading you to the sweet, sweet relief of a correctly filed tax return.
[Diagram Description: The flowchart would begin with a box labeled “Determine your tax obligation.” This would branch into two boxes: “Taxable income” and “Non-taxable income.” The “Taxable income” box would lead to a box labeled “Calculate your tax liability,” which would then lead to “Prepare your tax return.” The “Non-taxable income” box would lead to a box labeled “No tax liability.” Both the “Prepare your tax return” box and the “No tax liability” box would lead to a final box labeled “File your return.” Arrows would connect all the boxes, indicating the flow of the process.]
Contact Information for Tax Authorities
Knowing who to contact when you’re stuck in the tax quagmire is crucial. This information will be your lifeline when the going gets tough.
- Direktorat Jenderal Pajak (DJP) Contact Center: The DJP likely offers a contact center with phone numbers and email addresses for inquiries. Think of them as your friendly tax advisors – although their friendliness might be inversely proportional to the complexity of your tax situation.
- Local Tax Offices (Kantor Pelayanan Pajak – KPP): For more personalized assistance, you can contact your local KPP. They’re the tax professionals who are geographically closest to you, ready to tackle your tax issues. Think of them as your neighborhood tax superheroes.
Seeking Professional Tax Advice
Sometimes, even the most diligent taxpayer needs a helping hand. Seeking professional advice is not a sign of weakness; it’s a sign of smart tax planning.
Engaging a tax consultant or accountant can significantly reduce the stress and complexity of tax compliance. They possess the expertise to navigate the intricacies of tax laws, ensuring that you comply with regulations and optimize your tax position. Consider them your tax Sherpas, guiding you safely through the mountainous terrain of Indonesian tax law. They can provide tailored advice based on your specific circumstances, which is invaluable when dealing with the unique aspects of Indonesian tax regulations. The cost of professional advice can be easily offset by the savings achieved through accurate and efficient tax planning.
Conclusive Thoughts

So, there you have it: a journey through the sometimes-confusing, often-surprising, but ultimately conquerable landscape of Indonesian income tax. While we’ve aimed for clarity and a touch of humor, remember, this guide is for informational purposes only. For personalized advice, always consult a qualified tax professional. After all, even the most amusing tax guide can’t replace expert guidance. Now go forth and file with confidence (and maybe a small celebratory snack).
Q&A
What happens if I miss a PPh payment deadline?
Prepare for penalties! Late payment usually incurs interest charges and potentially additional fines. The exact amount depends on the amount owed and the duration of the delay. It’s best to avoid this entirely.
Can I deduct my pet’s grooming expenses from my taxes?
Sadly, no. While we appreciate the pampered pooch, only specific business-related or officially recognized deductions are allowed. Check the official regulations for a comprehensive list.
Where can I find the official PPh tax forms?
The official website of the Indonesian tax authority (DJP) is your best resource. They usually have downloadable forms and clear instructions on how to complete them. Be warned, it might be in Bahasa Indonesia.
What if my income fluctuates throughout the year?
For fluctuating income, you might need to adjust your monthly PPh 25 payments accordingly. Consult a tax professional or refer to DJP guidelines for proper estimation and adjustment procedures.



