Risk Management Software: Ah, yes, the software that transforms the terrifying prospect of unforeseen calamities into a mildly amusing spreadsheet exercise. This isn’t your grandma’s risk assessment; we’re talking sophisticated algorithms, elegant dashboards, and the satisfying *thwack* of a mitigated threat. Prepare to be amazed (and slightly less stressed) as we delve into the world of proactive risk management, where the only thing more exciting than identifying potential problems is elegantly solving them.
This guide will explore the core functionalities of risk management software, from identifying various risk types (financial, operational, compliance—oh my!) to selecting the right software for your organization’s unique needs. We’ll navigate the implementation process, data management strategies, and even peek into the crystal ball of future trends in risk mitigation. Buckle up, it’s going to be a wild (but organized) ride!
Defining Risk Management Software
Risk management software: the unsung hero of the corporate world, preventing catastrophes before they become headlines (and lawsuits!). It’s the digital guardian angel, constantly watching for potential problems and helping businesses navigate the treacherous waters of uncertainty. Think of it as a highly caffeinated, detail-oriented detective, always on the case.
Risk management software is a category of applications designed to identify, analyze, and mitigate potential risks across various aspects of an organization. It leverages data analysis, reporting, and collaborative tools to provide a holistic view of the risk landscape, empowering businesses to make informed decisions and proactively address potential threats. This isn’t just about avoiding financial ruin; it’s about ensuring operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and ultimately, business success.
Core Functionalities of Risk Management Software
Typical risk management software boasts a suite of functionalities designed to streamline the entire risk management process. These functionalities often include risk identification through various methods such as questionnaires, data analysis, and even predictive modeling. Subsequently, the software facilitates risk assessment, prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. The software then aids in the development and implementation of mitigation strategies, often tracking progress and reporting on effectiveness. Finally, the reporting and visualization features allow stakeholders to understand the overall risk profile and track key metrics over time. Imagine a dashboard displaying the health of your business, not just financially, but across all areas of risk.
Types of Risks Addressed
Risk management software isn’t a one-trick pony. It addresses a wide array of risks, each requiring a unique approach. Financial risks, such as market volatility or credit defaults, are often addressed through sophisticated financial modeling and scenario planning. Operational risks, encompassing things like supply chain disruptions or IT failures, require a different tact, often involving process mapping and contingency planning. Compliance risks, ensuring adherence to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, necessitate a focus on policy management and audit trails. The software’s flexibility allows it to adapt to the specific needs of each organization and the types of risks they face. Think of it as a Swiss Army knife for risk management, with a tool for every potential threat.
Key Features Differentiating Risk Management Software
The market is brimming with risk management software, each with its own unique selling points. Some prioritize advanced analytics and predictive modeling, offering insights into future risks. Others excel at collaboration and communication, facilitating seamless information sharing across teams. Integration capabilities with existing systems, such as ERP or CRM, are also crucial for seamless data flow. Finally, user-friendliness and reporting capabilities are often key differentiators, determining how effectively stakeholders can understand and act on the information provided. Choosing the right software depends on the specific needs and priorities of the organization – much like choosing the right superhero for the job!
Benefits of Implementing Risk Management Software
Implementing risk management software isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about transforming your organization from a potential disaster zone into a well-oiled, risk-mitigating machine. Think of it as upgrading from a rusty abacus to a supercharged financial calculator – far more efficient and less prone to human error (and the resulting existential dread). The benefits span every department, offering a significant return on investment in both tangible cost savings and intangible peace of mind.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity Across Departments
The beauty of risk management software lies in its ability to automate tedious tasks and streamline workflows. This translates to significant gains in efficiency and productivity across all departments. Imagine a world where identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks is less of a Herculean effort and more of a smoothly functioning, well-oiled machine. This frees up valuable time and resources, allowing employees to focus on strategic initiatives rather than getting bogged down in administrative minutiae.
Financial Department Benefits
The finance department often bears the brunt of risk-related issues. Risk management software provides enhanced financial controls, improving accuracy in forecasting, budgeting, and reporting. This reduces the likelihood of financial losses due to unforeseen circumstances and enhances regulatory compliance, potentially avoiding hefty fines and legal battles.
Operations Department Benefits
For operations, risk management software offers real-time monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) and operational risks. This allows for proactive identification and mitigation of potential disruptions, minimizing downtime and improving overall operational efficiency. Imagine the ability to predict and prevent a production line failure before it even happens – a significant boon to productivity and profitability.
Legal Department Benefits
The legal department benefits from improved compliance management and reduced legal risk. The software helps ensure adherence to relevant regulations and standards, minimizing the risk of lawsuits and penalties. This translates to significant cost savings and enhanced corporate reputation.
Enhanced Decision-Making Through Data-Driven Insights
Risk management software empowers data-driven decision-making by providing a centralized repository of risk information. This allows for a holistic view of the organization’s risk profile, facilitating more informed and strategic decisions. By leveraging the data provided, organizations can make proactive adjustments to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, effectively navigating uncertainty with a clear, informed perspective.
| Benefit | Description | Cost Savings | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced Financial Losses | Improved forecasting and risk mitigation prevent costly errors. | Variable, depending on the prevented loss. Could range from thousands to millions. | Avoiding a major supply chain disruption by predicting potential delays and securing alternative suppliers. |
| Improved Operational Efficiency | Automated processes and real-time monitoring reduce downtime and improve productivity. | Increased output, reduced operational costs. Quantifiable through improved production metrics. | Predictive maintenance reducing equipment failures and resulting production halts. |
| Enhanced Compliance | Automated compliance checks reduce the risk of fines and legal battles. | Avoidance of penalties, legal fees, and reputational damage. Amounts vary drastically based on violations. | Avoiding a significant fine for non-compliance with data privacy regulations. |
| Better Decision-Making | Data-driven insights lead to more informed and strategic decisions. | Improved resource allocation, reduced wasted effort. Difficult to quantify directly but contributes to overall efficiency. | Identifying and prioritizing high-impact risks, allowing for focused mitigation efforts. |
Selecting the Right Risk Management Software
Choosing the perfect risk management software is like selecting the ideal superhero sidekick – it needs to complement your organization’s unique strengths and weaknesses, possess the right superpowers (features), and seamlessly integrate into your existing operations. A wrong choice can leave you battling villains (risks) with a spork instead of a laser beam.
Selecting the appropriate risk management software demands careful consideration of several critical factors. Ignoring these can lead to a system that’s more hindrance than help, leaving your organization vulnerable and your budget depleted. The process should be methodical and informed, much like planning a meticulously executed heist (but with less potential jail time).
Critical Factors in Software Selection
The decision hinges on a variety of factors, each contributing to the overall efficacy of the chosen software. A thorough evaluation ensures a solution that aligns precisely with the organization’s needs and capabilities. Consider these key aspects as you embark on your software selection journey.
- Scalability: The software must be able to adapt to your organization’s growth. Imagine starting with a small team and then suddenly needing to manage risks across multiple departments and international locations. Scalability prevents costly system overhauls down the line.
- User-Friendliness: Complexity can hinder adoption. The software should be intuitive and easy to navigate, ensuring that all users, regardless of their technical expertise, can effectively utilize its features. A user-friendly interface reduces training time and encourages consistent use.
- Reporting and Analytics Capabilities: Comprehensive reporting is essential for monitoring risk levels and identifying trends. The software should provide customizable reports, dashboards, and analytics to give you a clear and concise view of your risk landscape. This data-driven insight enables proactive risk mitigation.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamless integration with your existing CRM, ERP, or other business systems is crucial for efficient workflow. Data silos are the enemy of effective risk management. Choose software that plays nicely with your current technology stack.
- Budget and Cost: Consider not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing maintenance, support, and training costs. A cost-benefit analysis will help determine the most financially viable solution for your organization. Don’t forget to factor in the potential cost of *not* having adequate risk management.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Deployment
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise deployment significantly impacts cost, security, and accessibility. Each option presents unique advantages and disadvantages, necessitating careful consideration of the organization’s specific circumstances.
- Cloud-Based: Offers scalability, accessibility, and reduced infrastructure costs. Think of it as renting a powerful risk-management fortress in the cloud – no need to build and maintain it yourself. However, security and data privacy concerns should be thoroughly investigated.
- On-Premise: Provides greater control over data and security but demands significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure. It’s like building your own impenetrable fortress – you control everything, but it comes with a higher price tag and ongoing maintenance responsibilities.
Essential Integration Capabilities
Effective risk management requires seamless data flow between various systems. The chosen software must integrate effortlessly with other critical business applications to provide a holistic view of risk.
- CRM Integration: Linking risk management data with customer information provides valuable context for assessing customer-related risks. Imagine instantly seeing the risk profile of a client based on their past interactions.
- ERP Integration: Integrating with ERP systems allows for the analysis of financial data and operational processes to identify potential risks within the organization’s core functions. This provides a financial perspective on risk assessment.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Integration: This integration enables the correlation of security events with identified risks, enhancing the organization’s ability to proactively address security threats. This is crucial for identifying and mitigating cyber risks.
Implementation and Integration of Risk Management Software
Implementing risk management software isn’t just about installing a program; it’s about orchestrating a symphony of data, people, and processes. Think of it as a meticulously planned heist, but instead of robbing a bank, you’re robbing risk from your organization. A successful implementation requires careful planning, strategic execution, and a healthy dose of caffeine.
A phased approach ensures a smoother transition and minimizes disruption. Jumping in headfirst, like a caffeinated squirrel into a pile of nuts, can lead to chaos. A well-structured implementation plan, however, will allow you to smoothly integrate the software into your existing operational rhythm.
Step-by-Step Implementation Plan
The implementation process should be divided into manageable stages. Rushing this critical phase is like trying to bake a cake in a microwave – the results might be edible, but probably not very appealing. A well-defined plan ensures a successful outcome.
- Project Initiation and Planning: Define project goals, scope, timelines, and resources. This phase involves establishing clear objectives and assembling your team of risk management superheroes.
- Data Migration and Cleansing: Prepare existing risk data for import into the new system. This crucial step involves cleaning up messy data, ensuring accuracy, and preventing the software from choking on corrupted information. Think of it as spring cleaning for your data.
- System Configuration and Customization: Configure the software to match your organization’s specific needs and workflows. This might involve customizing reports, dashboards, and workflows to align with your unique risk profile.
- User Training and Adoption: Provide comprehensive training to users, ensuring they understand the software’s functionalities and how to effectively use it. This involves creating engaging training materials, providing hands-on workshops, and establishing ongoing support channels.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the system before full deployment. This involves performing various tests to ensure data integrity, functionality, and user experience. This stage helps identify and resolve any bugs or glitches before they cause problems in the live environment.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support: Deploy the system and provide ongoing support to users. This involves monitoring system performance, addressing user queries, and making necessary adjustments based on feedback. Think of it as the post-launch party for your new risk management system.
User Training and Adoption Strategies
Successful implementation hinges on user buy-in. Forcing employees to use a new system without proper training is like asking a chef to cook with a set of rusty sporks. Effective training strategies are essential for user adoption.
- Interactive Training Sessions: Hands-on workshops and interactive tutorials ensure users understand the software’s features and functionalities.
- Gamification: Incorporate game mechanics into training to increase engagement and motivation.
- Ongoing Support and Mentorship: Provide ongoing support and mentorship to users after training.
- Incentivize Adoption: Reward users for adopting the new system and providing feedback.
Integrating Risk Management Software with Existing Systems
Integrating risk management software with existing systems, such as ERP and CRM, is like connecting the dots on a complex puzzle. This seamless integration ensures data consistency and efficient workflow. A poorly integrated system is like trying to build a house with mismatched bricks.
The integration process should be carefully planned and executed to minimize disruptions. This may involve using APIs, ETL tools, or other integration technologies. Consider the potential challenges and develop mitigation strategies. For example, ensure data compatibility between systems, establish clear data governance policies, and define integration points.
Pre-Implementation Checklist and Post-Implementation Monitoring
Before launching the software, a comprehensive checklist is crucial. Ignoring this step is like leaving home without your keys—you’ll be locked out. Post-implementation monitoring is equally important to ensure smooth operation and ongoing effectiveness.
Pre-Implementation Checklist
- Data backup and recovery plan.
- User accounts and access permissions.
- System testing and validation.
- Training materials and schedule.
- Communication plan for stakeholders.
Post-Implementation Monitoring Procedures
- Regular system performance monitoring.
- User feedback collection and analysis.
- System updates and patches.
- Security audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Ongoing training and support.
Data Management and Reporting in Risk Management Software

Risk management software isn’t just about identifying potential problems; it’s about taming the data beast and turning it into insightful, actionable intelligence. Think of it as a highly caffeinated librarian, meticulously organizing chaos and presenting it in a way that even the most spreadsheet-averse executive can understand. This section delves into the fascinating world of data wrangling within risk management software, exploring how data is collected, stored, analyzed, and ultimately transformed into compelling reports and dashboards.
Data within risk management software is typically collected through a variety of methods, ranging from manual data entry (yes, sometimes even the old-fashioned way is necessary!) to automated integrations with other systems. Imagine a digital spiderweb, subtly capturing data from various sources – spreadsheets, databases, surveys, even sensors – all feeding into the central risk management system. This data might include risk descriptions, likelihood scores, impact assessments, mitigation strategies, and associated costs. Storage methods leverage robust databases, ensuring data integrity and accessibility. Advanced software often incorporates encryption and access controls, adding a layer of security worthy of Fort Knox (albeit with a friendlier interface). Analysis techniques, from simple statistical summaries to complex predictive modeling, empower organizations to understand risk patterns, prioritize mitigation efforts, and ultimately, make better decisions. Think of it as data alchemy, transforming raw information into gold – or at least, very valuable insights.
Data Collection Methods
Risk management software utilizes various methods to collect risk data, ensuring comprehensive coverage. These include manual input via forms, automated data imports from other systems (like CRM or project management software), and integration with external data sources for broader context. For instance, a financial institution might integrate market data feeds to assess economic risks, while a manufacturing company might connect with production line sensors to identify operational risks. The software often employs validation rules to ensure data accuracy and consistency, reducing errors and improving the reliability of subsequent analyses. Imagine it as a diligent quality control team, ensuring every piece of data is properly vetted before entering the system.
Risk Visualization through Reports and Dashboards
The software’s ability to transform raw data into visually appealing and insightful reports and dashboards is crucial. These tools present complex risk information in a readily understandable format, facilitating effective communication and decision-making across different levels of the organization. Dashboards typically provide a high-level overview of key risk indicators (KRIs), such as the number of open risks, the total risk exposure, and the status of mitigation efforts. Reports, on the other hand, offer more detailed analysis, exploring specific risks, trends, and scenarios. These can be customized to meet specific reporting requirements, enabling users to tailor their view of the risk landscape. It’s like having a personal risk cartographer, providing customized maps to navigate the complex terrain of potential problems.
Report Customization
Customizing reports allows organizations to tailor their risk reporting to meet specific needs and preferences. Users can select specific risk categories, timeframes, and data fields to include in their reports. They can also modify the format, layout, and visual elements to enhance readability and impact. For example, a financial institution might generate a report focusing solely on credit risk, while a healthcare provider might create a report highlighting patient safety incidents. The ability to filter, sort, and group data allows for in-depth analysis and identification of key trends and patterns. This level of customization ensures that the information presented is relevant, actionable, and readily understood by the intended audience. It’s like having a personal chef preparing a risk report tailored to your exact specifications, with all the right ingredients and no unwanted extras.
Sample Report Design
The following table provides a simple example of a customizable risk report. Imagine this table populated with real data, dynamically updated by the software, providing a clear, concise picture of the organization’s risk profile.
| Risk Type | Probability | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Breach | Medium | High | Implement multi-factor authentication and regular security audits. |
| Supply Chain Disruption | Low | Medium | Diversify suppliers and establish contingency plans. |
| Regulatory Non-Compliance | High | High | Conduct regular compliance reviews and invest in compliance training. |
| Reputational Damage | Medium | High | Proactive communication and crisis management plan. |
Addressing Common Challenges in Risk Management Software
Implementing risk management software, while offering a plethora of benefits, isn’t always a smooth sail through a calm sea. Think of it like trying to herd cats – each cat (department, user) has its own agenda, and getting them all to cooperate seamlessly can be… challenging. This section explores some common hurdles and provides practical strategies for navigating them successfully. We’ll steer clear of overly technical jargon, promising a journey as smooth as possible.
The adoption of any new software system presents unique obstacles, and risk management software is no exception. Successful implementation requires careful planning, proactive communication, and a willingness to adapt to unforeseen circumstances. Think of it as building a sturdy bridge – one wrong step, and the whole thing could crumble. Let’s reinforce that bridge with the right strategies.
Data Migration and Integration Challenges
Migrating existing risk data into a new system can be a significant undertaking. Inconsistent data formats, outdated information, and the sheer volume of data can lead to delays and inaccuracies. For example, imagine trying to merge data from spreadsheets that have been updated inconsistently over 10 years, each using different naming conventions. A well-defined data migration plan, including data cleansing and validation steps, is crucial to ensure a smooth transition. This includes assigning clear roles and responsibilities for data cleansing and verification to ensure quality. Investing in data mapping tools and potentially employing external data migration specialists can significantly streamline this process.
User Adoption and Training
Resistance to change is a common human trait, and this can manifest in reluctance to adopt new risk management software. Users may be comfortable with their existing methods, even if they’re less efficient or effective. For example, a company might rely on outdated spreadsheets, making it difficult to integrate new risk management software. To combat this, comprehensive user training is vital. Interactive training modules, tailored to different user roles and skill levels, can significantly improve user adoption. Providing ongoing support and addressing user concerns promptly is equally important. Think of it like teaching a dog a new trick – patience, positive reinforcement, and clear instructions are key.
Maintaining Data Accuracy and Integrity
Ensuring the accuracy and integrity of risk data is paramount. Inaccurate data can lead to flawed risk assessments and ineffective mitigation strategies. Imagine basing a critical business decision on inaccurate risk data – the consequences could be severe. Implementing robust data validation rules, regular data audits, and access control mechanisms can help maintain data quality. Consider implementing automated data validation checks to flag inconsistencies and potential errors. Regular training on data entry procedures and data governance policies can also enhance data accuracy.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating risk management software with other enterprise systems (like CRM, ERP, etc.) is crucial for a holistic view of risk. A poorly integrated system can lead to data silos and inefficiencies. Imagine having risk data scattered across multiple systems, making it nearly impossible to get a comprehensive overview. A thorough assessment of existing systems and their compatibility with the new software is necessary before implementation. Choosing a software solution with robust API capabilities and employing experienced integration specialists can help ensure a seamless integration.
Lack of Management Support
Lack of buy-in from senior management can significantly hinder the successful implementation of risk management software. Without management support, resources may be insufficient, and the project may lack the necessary priority. For example, insufficient training budget could lead to poor user adoption and hinder the system’s effectiveness. Securing management sponsorship early in the process is crucial. Clearly articulating the benefits of the software and demonstrating a strong return on investment (ROI) can help gain support. Regular updates on progress and highlighting successes along the way are also essential to maintain momentum.
Future Trends in Risk Management Software
The world of risk management is hurtling towards a future where spreadsheets are relics of a bygone era, replaced by sophisticated software that anticipates risks before they even sprout metaphorical legs. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the exciting reality shaped by rapidly evolving technologies. The next generation of risk management software promises to be faster, smarter, and more proactive than ever before, offering businesses a powerful shield against the unpredictable storms of the modern marketplace.
The integration of cutting-edge technologies is revolutionizing how we identify, assess, and mitigate risks. This isn’t just about adding bells and whistles; it’s about fundamentally changing the way we approach risk management, moving from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention. This shift is driven by the increasing sophistication of both risks themselves and the tools available to manage them.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Risk Management
AI and machine learning are poised to dramatically reshape risk management software. Imagine a system that not only identifies potential risks but also predicts their likelihood and potential impact with impressive accuracy, all without needing a team of analysts poring over spreadsheets for weeks. This predictive capability is made possible by machine learning algorithms that analyze vast datasets – financial reports, market trends, news articles, social media sentiment – to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of emerging risks. For instance, an AI-powered system might detect a subtle shift in consumer behavior that signals a potential decline in sales, allowing businesses to proactively adjust their strategies. Further, these systems can learn and adapt over time, becoming increasingly accurate in their predictions as they are fed more data. This continuous learning process ensures the software remains relevant and effective in the face of ever-changing market dynamics.
Predictive Risk Modeling and Scenario Planning
Future risk management software will incorporate advanced predictive risk modeling capabilities. Instead of relying solely on historical data, these systems will leverage AI and machine learning to simulate various scenarios and predict their potential outcomes. This allows businesses to test different mitigation strategies and choose the most effective approach. For example, a financial institution could use such software to model the impact of various economic downturns, enabling them to develop robust contingency plans. The software might simulate different interest rate scenarios, currency fluctuations, or even geopolitical events to assess their potential impact on the institution’s portfolio. This proactive approach allows for better resource allocation and minimizes the impact of unexpected events. The visualization of these scenarios, often through interactive dashboards, will allow stakeholders to understand the potential consequences more effectively, leading to more informed decision-making.
Enhanced Data Visualization and Reporting
The ability to effectively communicate risk is paramount. Future risk management software will go beyond simple tables and charts, offering sophisticated data visualization tools that present complex information in a clear, concise, and engaging manner. Interactive dashboards will allow users to drill down into specific areas of concern, explore different data points, and quickly identify trends and patterns. This improved visualization will empower decision-makers to understand the risk landscape better and make more informed decisions. Imagine a dashboard that displays a real-time risk score, color-coded by severity, along with interactive maps showing geographical risk concentrations. This visual representation of risk makes complex information easily digestible, fostering collaboration and quicker responses to emerging threats.
Automated Risk Response and Remediation
Automation will play a crucial role in the future of risk management software. The software will not only identify and assess risks but also automatically trigger pre-defined responses and remediation actions. For instance, if a system detects a security breach, it could automatically initiate a protocol to contain the damage, notify relevant personnel, and implement corrective measures. This automation streamlines the response process, reducing the time it takes to address risks and minimizing potential losses. This is especially beneficial in situations where rapid action is crucial, such as cybersecurity incidents or supply chain disruptions. The automation, however, will be carefully designed to allow human oversight and intervention where necessary, ensuring a balance between efficiency and control.
Case Studies
Let’s ditch the theoretical and dive headfirst into the thrilling world of real-world risk management software successes! These case studies showcase how different industries wrestled with risk, emerged victorious, and even had a bit of fun along the way. Prepare to be amazed (and maybe a little envious).
We’ll examine two distinct implementations, highlighting the unique challenges each faced, the triumphant benefits reaped, and the invaluable lessons learned. Consider these stories not just case studies, but rather cautionary tales with happy endings, full of wisdom and a dash of “I can’t believe they actually did that!” moments.
Successful Risk Management Software Implementation in the Financial Services Sector: “The Case of the Prudent Penguin”
A large financial institution, let’s call them “Penguin Financial,” was struggling with a chaotic risk management process. Spreadsheets reigned supreme, creating a tangled web of data inconsistencies and a significant risk of regulatory non-compliance. Their risk assessment process was, to put it mildly, less than efficient. Implementing a sophisticated risk management software solution proved to be a game-changer.
Key Challenges Overcome:
- Data Silos: Information was scattered across various departments, making a holistic view of risk impossible. The software successfully integrated data from different sources, creating a single source of truth.
- Manual Processes: The previous system relied heavily on manual data entry and analysis, leading to errors and inefficiencies. Automation features in the new software significantly reduced manual workload and improved accuracy.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent regulatory requirements was a constant struggle. The software provided automated reporting and audit trails, simplifying compliance efforts and reducing the risk of penalties.
Benefits Achieved:
- Improved Risk Identification and Assessment: The software enabled Penguin Financial to identify and assess risks more effectively, leading to proactive mitigation strategies.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: The automated reporting and audit trails significantly simplified compliance efforts, reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Automation and streamlined workflows freed up valuable time and resources, allowing employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Better Decision-Making: Access to real-time, accurate risk data enabled more informed and effective decision-making across the organization.
Lessons Learned:
- Thorough Planning is Crucial: Penguin Financial invested significant time in planning and defining their requirements before implementing the software, ensuring a smooth transition.
- Employee Training is Essential: Adequate training for employees was critical to ensure successful adoption and utilization of the new system.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Regular monitoring and evaluation of the system are essential to identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing effectiveness.
Successful Risk Management Software Implementation in the Healthcare Sector: “The Case of the Resilient Raccoon”
“Resilient Raccoon Hospital,” a large healthcare provider, faced significant challenges in managing patient safety risks. Their existing system was fragmented, leading to communication breakdowns and potential errors. They needed a system that could not only manage risk but also enhance patient care.
Key Challenges Overcome:
- Data Integration: The hospital had multiple systems for patient information, incident reporting, and risk assessment. The new software successfully integrated these disparate systems, creating a unified view of patient safety risks.
- Communication Barriers: Effective communication between departments was crucial for managing risks, but their existing system hindered this. The new software improved communication and collaboration across different teams.
- Incident Reporting and Analysis: The previous incident reporting process was cumbersome and inefficient. The new software streamlined incident reporting, analysis, and tracking, enabling quicker identification of trends and potential hazards.
Benefits Achieved:
- Improved Patient Safety: By identifying and mitigating risks more effectively, the hospital significantly improved patient safety outcomes.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: The software helped the hospital meet regulatory requirements related to patient safety and risk management.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Streamlined workflows and automated reporting freed up valuable time and resources, allowing staff to focus on patient care.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The hospital gained access to valuable data and analytics, enabling data-driven decision-making to improve patient safety and operational efficiency.
Lessons Learned:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Resilient Raccoon Hospital actively engaged all stakeholders, including clinicians, administrators, and IT staff, throughout the implementation process. This ensured buy-in and successful adoption.
- Change Management: A comprehensive change management plan was crucial to address resistance to change and ensure a smooth transition to the new system.
- Continuous Improvement: The hospital established a process for ongoing monitoring and improvement of the risk management system, ensuring its continued effectiveness.
Closing Notes
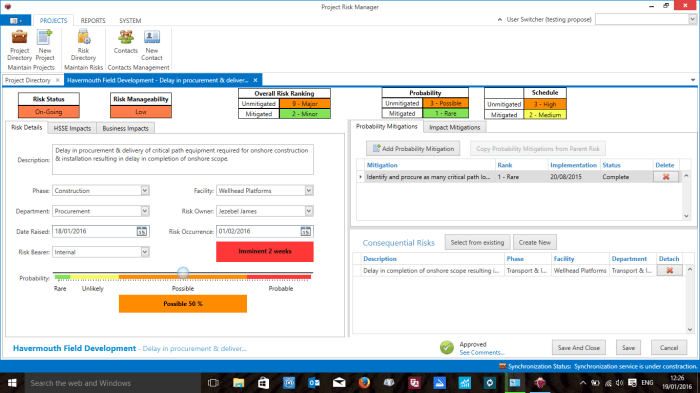
In conclusion, successfully implementing Risk Management Software is not just about ticking boxes; it’s about cultivating a culture of proactive risk assessment and mitigation. By carefully selecting the right software, integrating it seamlessly into existing workflows, and fostering user adoption, organizations can transform risk management from a daunting task into a strategic advantage. So, embrace the power of predictive analytics, celebrate your mitigated risks, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with a well-managed future. After all, who doesn’t love a good spreadsheet?
Key Questions Answered
What if my existing systems aren’t compatible with the new software?
Many risk management software solutions offer robust integration capabilities with various ERP and CRM systems. However, thorough compatibility checks are crucial before implementation to avoid costly integration headaches. Consider engaging a skilled IT professional to ensure a smooth transition.
How much does Risk Management Software typically cost?
Pricing varies wildly depending on features, deployment model (cloud vs. on-premise), and the number of users. Expect to see a range from affordable cloud-based options to enterprise-level solutions with substantial upfront investment. Request detailed pricing quotes from multiple vendors before making a decision.
What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring the success of Risk Management Software implementation?
Key KPIs include a reduction in the number and severity of incidents, improved response times to identified risks, increased stakeholder confidence, and demonstrable cost savings through proactive risk mitigation. Regularly monitor these metrics to assess the software’s effectiveness.